A technique for radioactively labeling proteins is electrophilic radioiodination, in which an aromatic substitution of 131 I
Question:
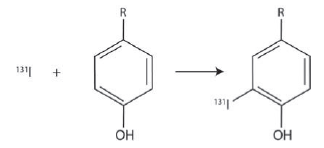
Using the activity of 131I, one can measure protein lifetimes in a variety of biological processes. 131I undergoes beta decay with a half-life of 8.02 days. Initially a protein labeled with 131I has a specific activity of 1.0μCi, which corresponds to 37,000 decay events every second. The protein is suspended in aqueous solution and exposed to oxygen for 5 days. After isolating the protein from solution, the protein sample is found to have a specific activity of 0.32 μCi. Is oxygen reacting with the tyrosine residues of the protein resulting in the loss of 131I?
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





