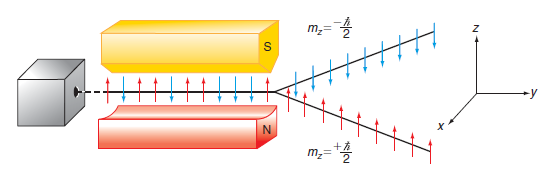
In this problem, you will carry out the calculations that describe the SternGerlach experiment shown in Figure
Question:
a. The geometry of the experiment is shown here. In the region of the magnet indicated by d1, the Ag atom experiences a constant force. It continues its motion in the force-free region indicated by d2.
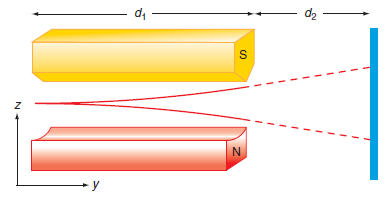
If the force inside the magnet is Fz, show that ˆ£zˆ£ = 1/2(Fz/m Ag)t21 + t2vz (t1). The times t1 and t2 correspond to the regions d1 and d2.
b. Show that, assuming a small deflection,
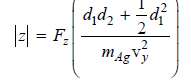
c. The magnetic moment of the electron is given by ˆ£Î¼ˆ£ = gSμB/2. In this equation, μB is the Bohr magneton and has the value 9.274 × 10€“24 J/T. The gyromagnetic ratio of the electron gS has the value 2.00231. If ˆ‚Bz/ˆ‚z = 750. T m€“1, and d1 and d2 are 0.175 and 0.225 m, respectively, and v y = 475 m s€“1, what values of z will be observed?
Figure 17.2
Step by Step Answer:






