Ground reflection model In a two-ray ground reflection model, the transmitter and receiver are placed ht and
Question:
Ground reflection model In a two-ray ground reflection model, the transmitter and receiver are placed ht and hr above the ground, as shown in Figure 7.19. Assume the wave obeys the free-space propagation law, and is given by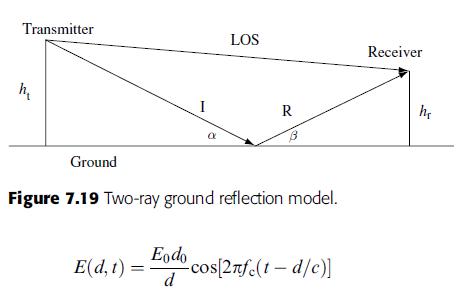
in which E0 is the field at the reference distance d0. Note that the phase is a function of both time and traveling distance. The field at the receiver consists of the direct line of sight component ELOS and the ground reflection component ER.
(a) Assume perfect ground reflection, in other words, at the point of reflection ER ¼ EI and ¼ ;
where EI is the electric field of the incident wave. Determine the distances traveled by the line of sight ray and the reflected ray from the transmitter to the receiver.
Show that the difference of the two distances can be approximated as follows, given dht, hr:
d ¼ dR dLOS
2hthr d :
(b) Show that the field at the receiver can be expressed as ETOTðtÞ ¼
E0d0 dLOS cos 2pfc t
dR c
þ
E0d0 dR cos 2pfc t
dR c
Find the phase shift due to the difference in distance traveled.
(c) Prove that the envelope of the total received field is given approximately by jETOTðtÞj
2E0d0 d sin
2
:
(d) For small, we can use sin(/2) /2. Show that the power propagation in the two-ray ground reflection model obeys the following law:
Pr ¼ jETOTj2
1 d4 :
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Embedded Networked Systems Design
ISBN: 978-0521095235
1st Edition
Authors: Gregory J. Pottie ,William J. Kaiser





