David Rivera Optical has determined that its reorder point for eyeglass frames is 50 (d * L)
Question:
David Rivera Optical has determined that its reorder point for eyeglass frames is 50 (d * L) units. Its carrying cost per frame per year is $5, and stockout (or lost sale) cost is $40 per frame. The store has experienced the following probability distribution for inventory demand during the lead time (reorder period). The optimum number of orders per year is 6.
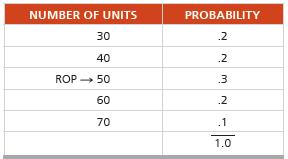
How much safety stock should David Rivera keep on hand?
APPROACH c The objective is to find the amount of safety stock that minimizes the sum of the additional inventory holding costs and stockout costs. The annual holding cost is simply the holding cost per unit multiplied by the units added to the ROP. For example, a safety stock of 20 frames, which implies that the new ROP, with safety stock, is 70 (5 50 1 20), raises the annual carrying cost by $5(20) 5 $100.
However, computing annual stockout cost is more interesting. For any level of safety stock, stockout cost is the expected cost of stocking out. We can compute it, as in Equation (12-12), by multiplying the number of frames short (Demand – ROP) by the probability of demand at that level, by the stockout cost, by the number of times per year the stockout can occur (which in our case is the number of orders per year). Then we add stockout costs for each possible stockout level for a given ROP.
Step by Step Answer:

Operations Management: Sustainability And Supply Chain Management
ISBN: 9780135225899,9780135202722
13th Edition
Authors: Jay Heizer; Barry Render; Chuck Munson






