Katie Long owns and operates KL Company. Transactions for the month of March have been posted to the T accounts. An intern has prepared a
Katie Long owns and operates KL Company. Transactions for the month of March have been posted to the T accounts. An intern has prepared a trial balance from the T accounts, but there seem to be some errors.
Required:
1. In the Transactions panel, descriptions of the transactions for the month of March are provided. Each of the transactions in the Transactions panel has been posted to the T accounts. Referring to the T accounts, select the date on which each transaction occurred, enter the amount of the transaction, and select the account to debit and credit.
2. The trial balance prepared by the intern can be found in the Trial Balance: Unequal Totals panel. The intern is puzzled by the unequal totals. Prepare a corrected trial balance on the Trial Balance: Correct panel.
3. Compare the trial balance prepared by the intern (Trial Balance: Unequal Totals) to the trial balance that you prepared (Trial Balance: Correct). Use the table provided in the Errors in Trial Balance panel to select the accounts for each type of error.
4. The intern is puzzled and asks ?Are you sure the accounting equation is still in balance?? Using the corrected trial balance you prepared, prove that the accounting equation is in balance. Still puzzled, the intern asks ?Why do none of the amounts in the accounting equation equal the totals on the trial balance?? Explain.
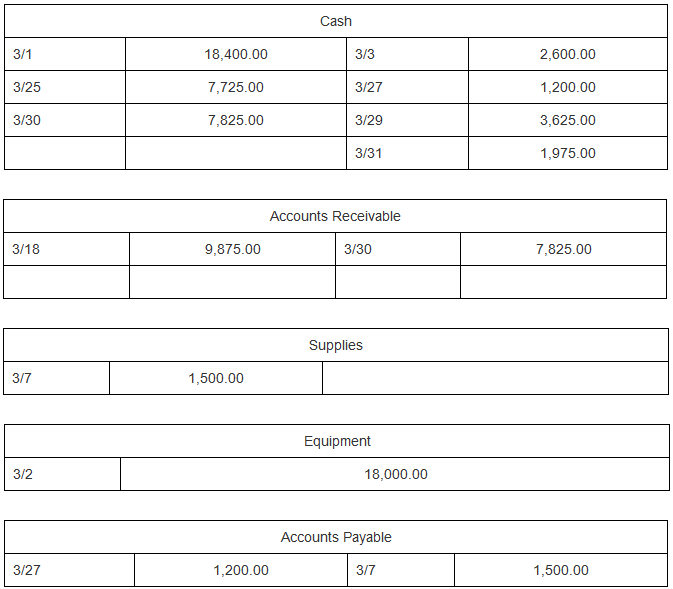
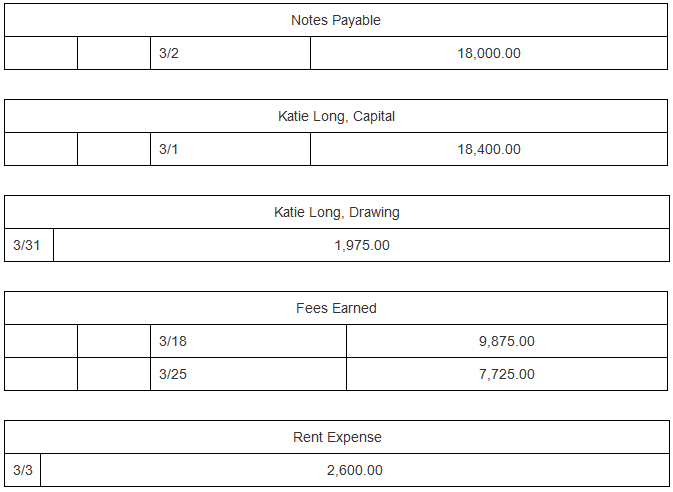
| Wages Expense | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/29 | 3,625.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Descriptions of the transactions for the month of March are provided in the table below. Each of the transactions below has been posted to the T accounts. Referring to the T accounts, select the date on which each transaction occurred, enter the amount of the transaction, and select the account to debit and credit.
Trial Balance: Unequal Totals The intern has prepared the following trial balance for the month of March. KL Company UNADJUSTED TRIAL BALANCE March 31, 20--
Trial Balance: Correct The trial balance prepared by the intern can be found in the Trial Balance: Unequal Totals panel. The intern is puzzled by the unequal totals. Prepare a corrected trial balance. KL Company UNADJUSTED TRIAL BALANCE March 31, 20--
Errors in Trial Balance Compare the trial balance prepared by the intern (Trial Balance: Unequal Totals) to the trial balance that you prepared (Trial Balance: Correct). In the following table, select the accounts for each type of error. Not all accounts contain errors.
Accounting Equation The intern is puzzled and asks ?Are you sure the accounting equation is still in balance?? Using the corrected trial balance you prepared, prove that the accounting equation is in balance.
Still puzzled, the intern asks ?Why do none of the amounts in the accounting equation equal the totals on the trial balance?? Check all that apply. This is because the revenue and expense accounts are part of the owner?s equity element. The accounts with debit balances should be part of the total assets. You point out the total of the assets, liabilities and owner?s equity is equal to the sum of the debit and credit totals in the trial balance. The accounts that make up the total for owner?s equity have a mix of debit and credit balances. The accounts with debit balances are not all classified in the same element of the accounting equation. For example, not all accounts with debit balances are assets. The accounts with credit balances are not all classified in the same element of the accounting equation. For example, not all accounts with credit balances are liabilities. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3/1 3/25 3/30 3/18 3/7 3/2 3/27 18,400.00 7,725.00 7,825.00 9,875.00 1,500.00 Cash 1,200.00 3/3 3/27 3/29 3/31 Accounts Receivable 3/30 Supplies Equipment 18,000.00 Accounts Payable 3/7 2,600.00 1,200.00 3,625.00 1,975.00 7,825.00 1,500.00 3/31 3/3 3/2 3/1 3/18 3/25 Notes Payable Katie Long, Capital Katie Long, Drawing 1,975.00 Fees Earned Rent Expense 2,600.00 18,000.00 18,400.00 9,875.00 7,725.00
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 Complete the requirements in the following manner 2 Prepare the corrected trial balance ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


