The demand for subassembly S is 100 units in week 7. Each unit of S requires 1 unit of T and 2 units of U.
The demand for subassembly S is 100 units in week 7. Each unit of S requires 1 unit of T and 2 units of U. Each unit of T requires 1 unit of V, 2 units of W, and 1 unit of X. Finally, each unit of U requires 2 units of Y and 3 units of Z. One firm manufactures all items. It takes 2 weeks to make S, 1 week to make T, 2 weeks to make U, 2 weeks to make V, 3 weeks to make W, 1 week to make X, 2 weeks to make Y, and 1 week to make Z.
*Construct a product structure. Identify all levels, parents, and components.
1. (Use the following grid to draw the product structure BOM)
1. Same scenario as above. (Use the following grid to draw the time-phased product structure). What is the overall lead time?
*Construct a product structure. Identify all levels, parents, and components.
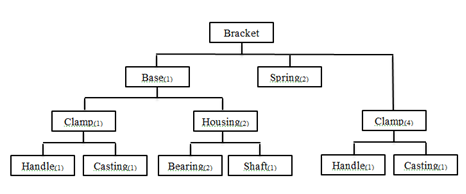
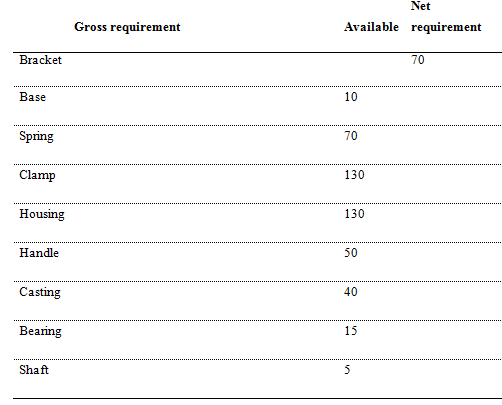
2. Given the following BOM and available on-hand inventory, compute the new requirements for all the dependent items for a batch of 70 units of the Bracket.
3. Develop a complete net material requirements plan for the production of following MPS and prepare the ?exceptions? report.
Master production schedule
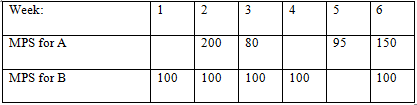
Data:
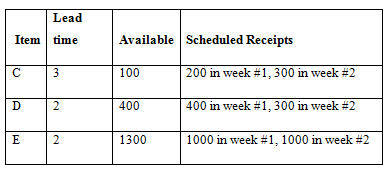
Bill-of-Materials:
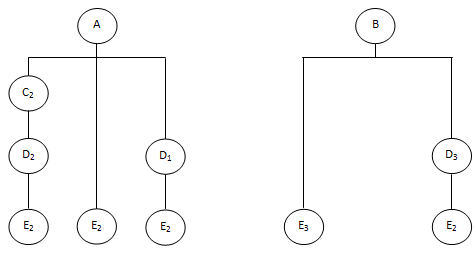
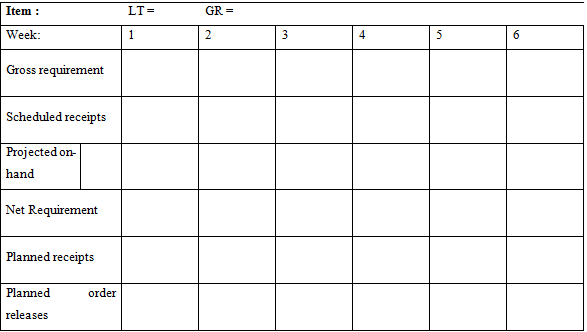
4. Given setup cost of $300 per setup and holding cost of $2.00 per unit per week, develop lot sizes (a) Lot-for-lot, (b) EOQ, and (c) POQ. Determine the total cost for each method. Use lead time of one week.
(a) Lot-for-lot
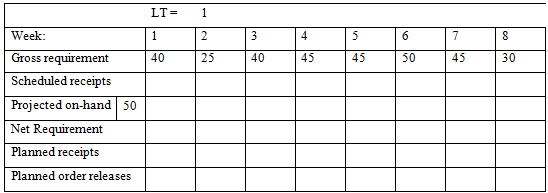
Total ending inventory =
No. of setup =
Carrying cost =
Setup cost =
Total cost =
(b) EOQ
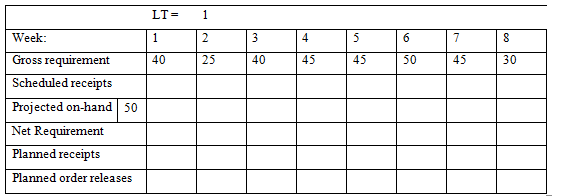
Holding cost/week =
Setup cost/week =
Total cost/week =
Cost for 8 weeks =
POQ
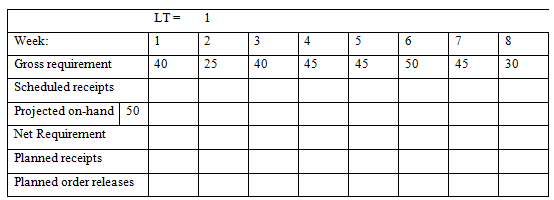
Total ending inventory =
No. of setup =
Carrying cost =
Setup cost =
Total cost =
Handle Clampa) Casting Base() Bracket Housing(2) Bearing(2) Spring(2) Shafta) Clamp (4) Handle) Casting(1) Bracket Base Spring Clamp Housing Handle Casting Bearing Shaft Gross requirement Available requirement 10 70 130 130 50 40 15 Net 5 70 Week: MPS for A MPS for B 1 100 2 200 100 3 80 100 4 100 5. 95 6 150 100 Lead Item time D E 3 2 2 Available Scheduled Receipts 100 400 1300 200 in week #1, 300 in week #2 400 in week #1, 300 in week #2 1000 in week #1, 1000 in week #2 C D E A E D E E3 B D3 E Item: Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on- hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned releases order LT= 1 GR= 2 3 4 5 6 Item: Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on- hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned releases Item: Week: order Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on- hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned releases order LT= 1 LT= 1 GR = 2 GR= 2 3 3 4 5 5 6 6 Item : Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on- hand Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned releases order LT= 1 GR= 2 3 4 5 6 Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand 50 Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases LT= 1 40 1 2 25 3 40 4 45 5 45 6 50 7 45 8 30 Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand 50 Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases LT= 1 2 25 1 40 3 40 4 45 5 45 6 50 7 45 8 30 Week: Gross requirement Scheduled receipts Projected on-hand 50 Net Requirement Planned receipts Planned order releases LT= 1 40 1 2 25 3 40 4 45 5 45 6 50 7 45 8 30
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The demand for subassembly S is 100 units in week 7 Each unit of S requires 1 unit of T and 2 units ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


