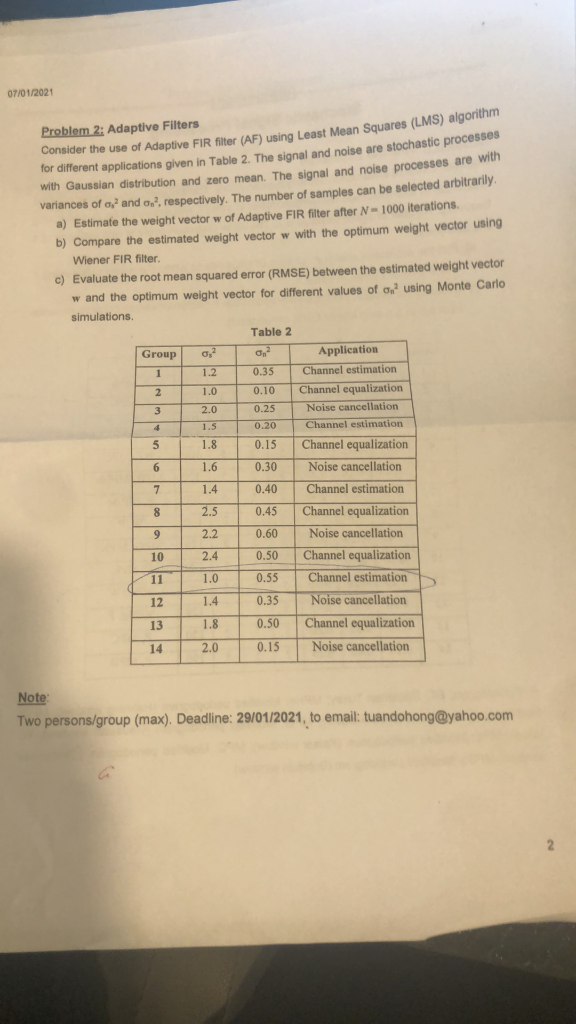
07/01/2021 Problem 2: Adaptive Filters Consider the use of Adaptive FIR filter (AF) using Least Mean Squares (LMS) algorithm for different applications given in Table 2. The signal and noise are stochastic processes with Gaussian distribution and zero mean. The signal and noise processes are with variances of o, and on?, respectively. The number of samples can be selected arbitrarily. a) Estimate the weight vector w of Adaptive FIR filter after N - 1000 iterations b) Compare the estimated weight vector w with the optimum weight vector using Wiener FIR filter c) Evaluate the root mean squared error (RMSE) between the estimated weight vector w and the optimum weight vector for different values of using Monte Carlo simulations Table 2 0,2 Group 1 1.2 0.35 2 1.0 0.10 0.25 3 2.0 1.5 0.20 5 1.8 0.15 6 1.6 0.30 7 1.4 0.40 Application Channel estimation Channel equalization Noise cancellation Channel estimation Channel equalization Noise cancellation Channel estimation Channel equalization Noise cancellation Channel equalization Channel estimation Noise cancellation Channel equalization Noise cancellation 8 2.5 0.45 9 0.60 2.2 2.4 10 0.50 11 1.0 0.55 12 1.4 0.35 13 1.8 0.50 14 2.0 0.15 Note: Two persons/group (max). Deadline: 29/01/2021, to email: tuandohong@yahoo.com 2 07/01/2021 Problem 2: Adaptive Filters Consider the use of Adaptive FIR filter (AF) using Least Mean Squares (LMS) algorithm for different applications given in Table 2. The signal and noise are stochastic processes with Gaussian distribution and zero mean. The signal and noise processes are with variances of o, and on?, respectively. The number of samples can be selected arbitrarily. a) Estimate the weight vector w of Adaptive FIR filter after N - 1000 iterations b) Compare the estimated weight vector w with the optimum weight vector using Wiener FIR filter c) Evaluate the root mean squared error (RMSE) between the estimated weight vector w and the optimum weight vector for different values of using Monte Carlo simulations Table 2 0,2 Group 1 1.2 0.35 2 1.0 0.10 0.25 3 2.0 1.5 0.20 5 1.8 0.15 6 1.6 0.30 7 1.4 0.40 Application Channel estimation Channel equalization Noise cancellation Channel estimation Channel equalization Noise cancellation Channel estimation Channel equalization Noise cancellation Channel equalization Channel estimation Noise cancellation Channel equalization Noise cancellation 8 2.5 0.45 9 0.60 2.2 2.4 10 0.50 11 1.0 0.55 12 1.4 0.35 13 1.8 0.50 14 2.0 0.15 Note: Two persons/group (max). Deadline: 29/01/2021, to email: tuandohong@yahoo.com 2







