Question
1. (3.6 points) A company has been assigned a class B address. A subnet of this company has network address 182.36.161.0 and direct broadcast address
1. (3.6 points) A company has been assigned a class B address. A subnet of this company has network address 182.36.161.0 and direct broadcast address 182.36.167.31. a) Based on the previous information, provide the smallest network address that can be assigned to a subnet of this company. b) Provide the smallest and largest IP address that can be assigned to a host of the subnet of question a). c) Provide the largest network address that can be assigned to a subnet of this company. d) Provide the smallest and largest IP address that can be assigned to a host of the subnet of previous question c). You must provide the values of all derived network addresses and IP addresses in Dotted Decimal Notation. You must show your derivations.
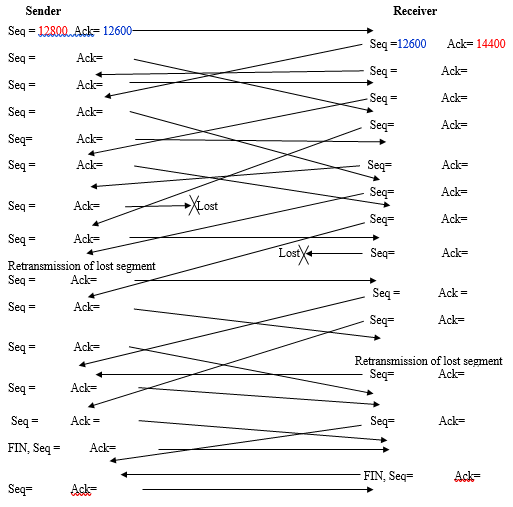
2. (2.6 points) The figure below shows the message exchange between a TCP sender and receiver. Every segment transmitted by the sender carries 1600 data bytes and every segment transmitted by the receiver carries 1800 data bytes; including the segments that have the FIN bits set. Fill in the missing Sequence and ACK numbers. Ensure that your Seq and Ack numbers of your answers fit in the allotted space. If due to large size letters in your answers, or for any other reason, receiver side numbers appear on the left part of the page, or all the answers are not in the same page, you will not receive any points in this question.
3. (3.8 points) Start your Bt5, Kali (or other Linux virtual machine) that has hping3 tool installed. Now use ifconfig to find its IP address; to find the IP address of your host OS you can also use ifconfig (if it is Linux) or ipconfig (if it is Windows). Capture screenshots of your ifconfig (or ipconfig) commands and corresponding outputs; showing the two IP addresses. Now start Wireshark in both Bt5 and host OS and select non-promiscuous mode. In both Bt5 and host OS Wireshark add a SrcPort and a DestPort column in the Packet List Pane. In the Wireshark of the host OS, apply a capture filter that will capture only the TCP packets whose source port is 40 and its source IP address is the one of Bt5. Type this capture filter. Also capture a screenshot of this filter in the Wireshark filter box of the host OS. In the Wireshark of Bt5 apply a packet capture filter that will capture only TCP packets that have ALL of the following properties: a) source port 40, b) destination port 82, c) TCP ECN, URG, PSH, RST bits set to 1, d) 1380 TCP data bytes e) IP Identification field 7746, f) a TCP window size of 48000. Type this capture filter. Also capture a screenshot of this applied filter in the Wireshark filter box of the Bt5. Now start the packet capturing process in both host OS and Bt5 Wiresharks. Next, use (in Bt5) one hping3 command that will transmit 8 TCP packets to the Host OS with source port 40 and destination ports 78,79,80,81,82,83,84 and 85. Moreover, each one of these packets must have the ECN, URG, PSH, and RST bits set to 1, its IP Identification field equal to 7746, 1380 TCP data bytes and a TCP window of 48000. Type the hping3 command you have used. Also capture a screenshot of this hping3 command and its output. Stop the packet capturing process in both Wiresharks. Capture a screenshot of the packet list pane of the Bt5 Wireshark and a screenshot of the packet list pane of the Host OS Wireshark showing the captured packets. Your screenshots in Bt5 and Host OS must show the port numbers of the transmitted packets. How many packets have been captured by Bt5 Wireshark and how many by the Host OS Wireshark? Is that what you expected? Explain why or why not.
Receiver Sender Seq 12800 Ack 12600 SeqAck- Seq = Ack Seq = Ack Seq Ack- Seq Seq =12600 Seq = Seq = Seq= Ack= 14400 Ack Ack Ack Ack Ack= Ack Seq = Ack Seq = Retransmission of lost segment Seq= Ack Ack Seq = Ack Seq Ack= eq Seq= Ack= Ack Seq Seq = Ack- Seq= Ack FIN, Seq= Ack= Retransmission of lost segment Seq Ack- Seq= Ack= FIN, Seq= Ack= Receiver Sender Seq 12800 Ack 12600 SeqAck- Seq = Ack Seq = Ack Seq Ack- Seq Seq =12600 Seq = Seq = Seq= Ack= 14400 Ack Ack Ack Ack Ack= Ack Seq = Ack Seq = Retransmission of lost segment Seq= Ack Ack Seq = Ack Seq Ack= eq Seq= Ack= Ack Seq Seq = Ack- Seq= Ack FIN, Seq= Ack= Retransmission of lost segment Seq Ack- Seq= Ack= FIN, Seq= Ack=Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


