
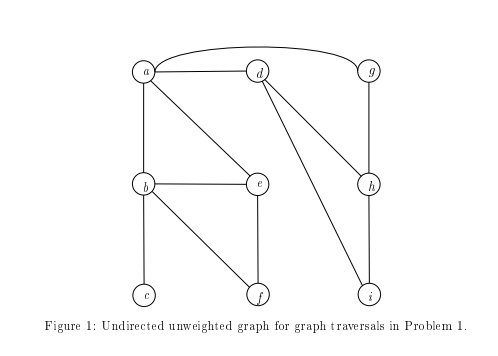
1 (80p) Consider the graph in Figure 1. We assume that this graph is represented in adjacency list format, with the neighbours in each adjacency list sorted in lexicographic order (i.e., in the order a,b,c,d,...), so this is the order in which vertices are encountered when going through neighbour lists. la (30p) Run the code for depth-first search by hand on this graph, starting in the vertex a. Describe in every recursive call which neighbours are being considered and how they are de alt with. Show the spanning tree produced by the search. 1b (30p) Run the code for breadth-first search by hand on this graph, also starting in the vertex a. Describe for every vertex which neighbours are being considered and how they are dealt with, and how the queue changes. Show the spanning tree produced by the search. 1c (20p) Suppose that the graph in Figure 1 is modified to give every edge weight 1, and that we run Dijkstra's algorithm starting in vertex a. How does the tree computed by Dijkstra's algorithm compare to that produced by DFS? What about BFS? Figure 1: Undirected unweighted graph for graph traversals in Problem 1. 1 (80p) Consider the graph in Figure 1. We assume that this graph is represented in adjacency list format, with the neighbours in each adjacency list sorted in lexicographic order (i.e., in the order a,b,c,d,...), so this is the order in which vertices are encountered when going through neighbour lists. la (30p) Run the code for depth-first search by hand on this graph, starting in the vertex a. Describe in every recursive call which neighbours are being considered and how they are de alt with. Show the spanning tree produced by the search. 1b (30p) Run the code for breadth-first search by hand on this graph, also starting in the vertex a. Describe for every vertex which neighbours are being considered and how they are dealt with, and how the queue changes. Show the spanning tree produced by the search. 1c (20p) Suppose that the graph in Figure 1 is modified to give every edge weight 1, and that we run Dijkstra's algorithm starting in vertex a. How does the tree computed by Dijkstra's algorithm compare to that produced by DFS? What about BFS? Figure 1: Undirected unweighted graph for graph traversals in Problem 1








