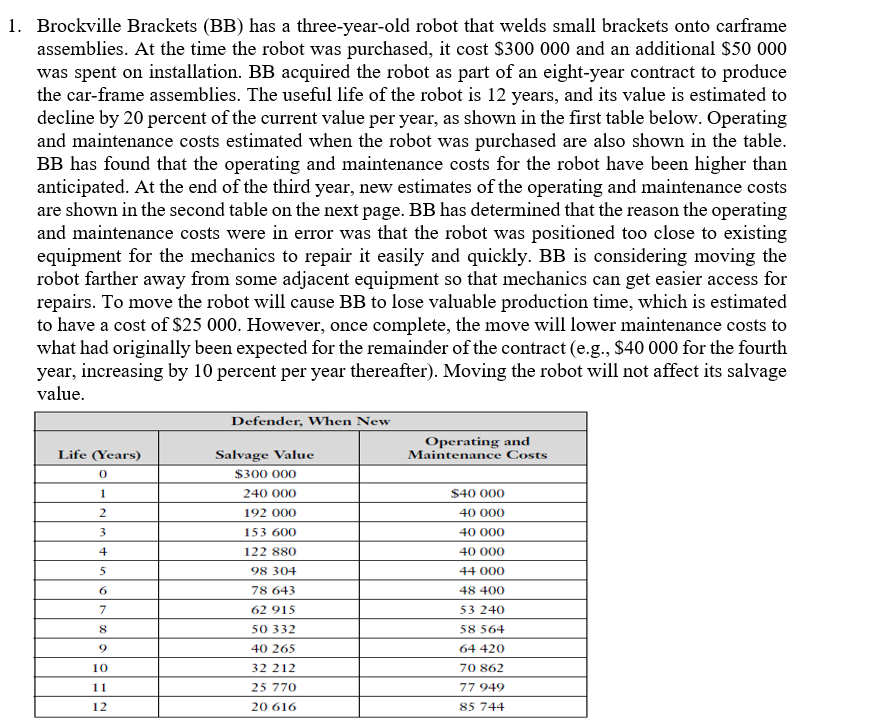
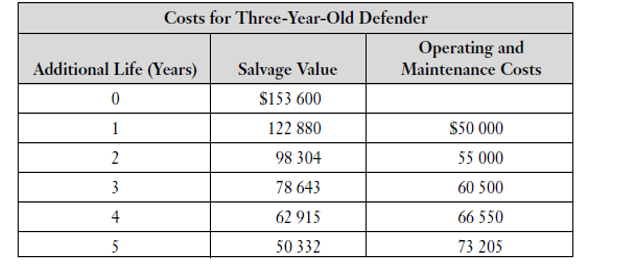
1. Brockville Brackets (BB) has a three-year-old robot that welds small brackets onto carframe assemblies. At the time the robot was purchased, it cost $300 000 and an additional $50 000 was spent on installation. BB acquired the robot as part of an eight-year contract to produce the car-frame assemblies. The useful life of the robot is 12 years, and its value is estimated to decline by 20 percent of the current value per year, as shown in the first table below. Operating and maintenance costs estimated when the robot was purchased are also shown in the table. BB has found that the operating and maintenance costs for the robot have been higher than anticipated. At the end of the third year, new estimates of the operating and maintenance costs are shown in the second table on the next page. BB has determined that the reason the operating and maintenance costs were in error was that the robot was positioned too close to existing equipment for the mechanics to repair it easily and quickly. BB is considering moving the robot farther away from some adjacent equipment so that mechanics can get easier access for repairs. To move the robot will cause BB to lose valuable production time, which is estimated to have a cost of $25 000. However, once complete, the move will lower maintenance costs to what had originally been expected for the remainder of the contract (e.g., $40 000 for the fourth year, increasing by 10 percent per year thereafter). Moving the robot will not affect its salvage value. Defender, When New Operating and Life (Years) Salvage Value $300 000 240 000 192 000 153 600 Maintenance Costs 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 $40 000 40 000 40 000 40 000 44 000 48 400 53 240 58 564 64 420 70 862 77 949 7 122 880 98 304 78 643 62 915 50 332 40 265 32 212 25 770 20 616 8 9 10 11 12 85 744 Costs for Three-Year-Old Defender Operating and Additional Life (Years) Salvage Value Maintenance Costs 0 $153 600 122 880 $50 000 98 304 55 000 78 643 60 500 4 62 915 66 550 5 50 332 73 205 2 3 5 a) If BB uses a MARR of 15 percent, should it move the robot? (5 POINTS) 3-year-old Defender: Additional EAC EAC EAC years Salvage Maintenance Capital Maintenance Total EAC(total costs) of keeping the robot: ....... years is $.............. If so, when? Remember that the contract exists only for a further five years. (10 POINTS) b) Challenger (Move Robot): Additional EAC EAC EAC years Salvage Maintenance Capital Maintenance Total 2. Consider Brockville Brackets (BB) from Question 1 but assume that it has has a contract to produce the car assemblies for an indefinite period. If it does not move the robot, the operating and maintenance costs will be higher than expected. If it moves the robot (at a cost of $25 000), the operating and maintenance costs are expected to be what were originally expected for the robot. Furthermore, BB expects to be able to obtain new versions of the existing robot for an indefinite period in the future; each is expected to have an installation cost of $50 000. Q2 ANSWER: a) Construct a spreadsheet table showing the EAC(total costs) if Brockville Brackets keeps the current robot in its current position for n more years, n_ 1,...,9. (5 POINTS) 3 year old Defender: Additional EAC EAC EAC years Salvage Maintenance Capital Maintenance Total b) Construct a spreadsheet table showing the EAC(total costs) if Brockville Brackets moves the current robot and then keeps it for n more years, n 1, ..., 9.(5 POINTS) Moving the existing robot (challenger): Additional EAC EAC EAC years Salvage Maintenance Capital Maintenance Total 1. Brockville Brackets (BB) has a three-year-old robot that welds small brackets onto carframe assemblies. At the time the robot was purchased, it cost $300 000 and an additional $50 000 was spent on installation. BB acquired the robot as part of an eight-year contract to produce the car-frame assemblies. The useful life of the robot is 12 years, and its value is estimated to decline by 20 percent of the current value per year, as shown in the first table below. Operating and maintenance costs estimated when the robot was purchased are also shown in the table. BB has found that the operating and maintenance costs for the robot have been higher than anticipated. At the end of the third year, new estimates of the operating and maintenance costs are shown in the second table on the next page. BB has determined that the reason the operating and maintenance costs were in error was that the robot was positioned too close to existing equipment for the mechanics to repair it easily and quickly. BB is considering moving the robot farther away from some adjacent equipment so that mechanics can get easier access for repairs. To move the robot will cause BB to lose valuable production time, which is estimated to have a cost of $25 000. However, once complete, the move will lower maintenance costs to what had originally been expected for the remainder of the contract (e.g., $40 000 for the fourth year, increasing by 10 percent per year thereafter). Moving the robot will not affect its salvage value. Defender, When New Operating and Life (Years) Salvage Value $300 000 240 000 192 000 153 600 Maintenance Costs 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 $40 000 40 000 40 000 40 000 44 000 48 400 53 240 58 564 64 420 70 862 77 949 7 122 880 98 304 78 643 62 915 50 332 40 265 32 212 25 770 20 616 8 9 10 11 12 85 744 Costs for Three-Year-Old Defender Operating and Additional Life (Years) Salvage Value Maintenance Costs 0 $153 600 122 880 $50 000 98 304 55 000 78 643 60 500 4 62 915 66 550 5 50 332 73 205 2 3 5 a) If BB uses a MARR of 15 percent, should it move the robot? (5 POINTS) 3-year-old Defender: Additional EAC EAC EAC years Salvage Maintenance Capital Maintenance Total EAC(total costs) of keeping the robot: ....... years is $.............. If so, when? Remember that the contract exists only for a further five years. (10 POINTS) b) Challenger (Move Robot): Additional EAC EAC EAC years Salvage Maintenance Capital Maintenance Total 2. Consider Brockville Brackets (BB) from Question 1 but assume that it has has a contract to produce the car assemblies for an indefinite period. If it does not move the robot, the operating and maintenance costs will be higher than expected. If it moves the robot (at a cost of $25 000), the operating and maintenance costs are expected to be what were originally expected for the robot. Furthermore, BB expects to be able to obtain new versions of the existing robot for an indefinite period in the future; each is expected to have an installation cost of $50 000. Q2 ANSWER: a) Construct a spreadsheet table showing the EAC(total costs) if Brockville Brackets keeps the current robot in its current position for n more years, n_ 1,...,9. (5 POINTS) 3 year old Defender: Additional EAC EAC EAC years Salvage Maintenance Capital Maintenance Total b) Construct a spreadsheet table showing the EAC(total costs) if Brockville Brackets moves the current robot and then keeps it for n more years, n 1, ..., 9.(5 POINTS) Moving the existing robot (challenger): Additional EAC EAC EAC years Salvage Maintenance Capital Maintenance Total











