Question: 1. Compute the percent ionic character of the interatomic bonds for each of the following compounds: TiO2, ZnTe, CsCI, InSb, and MgCl2. 2. Calculate the

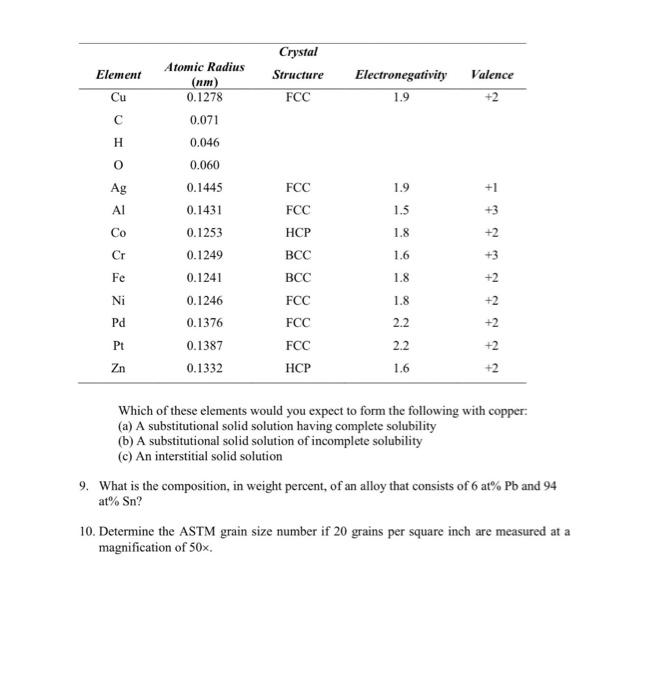
1. Compute the percent ionic character of the interatomic bonds for each of the following compounds: TiO2, ZnTe, CsCI, InSb, and MgCl2. 2. Calculate the number of vacancies per cubic meter in iron at 850C. The energy for vacancy formation is 1.08 eV/atom. The density and atomic weight for Fe are 7.65 g/cm and 55.85 g/mol, respectively. 3. Molybdenum forms a substitutional solid solution with tungsten Compute the weight percent of molybdenum that must be added to tungsten to yield an alloy that contains 1.0 * 10-2 Mo atoms per cubic centimeter. The densities of pure Mo and W are 10.22 and 19.30 g/cm", respectively. 4. A common metal is known to have a cubic unit cell with an edge length of 0.3614 nm and radius 0.128 nm. If this metal has a density of 8.94 gm/cm3 and an atomic weight of 63.55 g/mole, what is the atomic packing factor? 5. Using atomic weight, crystal structure, and atomic radius data tabulated inside the front cover, compute the theoretical densities of lead, chromium, and copper, and then compare these values with the measured densities listed in this same table. 6. The atomic weight, density, and atomic radius for three hypothetical alloys are listed in the following table. For each determine whether its crystal structure is FCC, BCC, or simple cubic and then justify your determination. Alloy Atomic Weight Density Atomic Radius (g/mol) (g/cm3) (nm) A 77.4 8.22 0.125 B 107.6 13.42 0.133 127.3 9.23 0.142 7. Calculate the activation energy for vacancy formation in aluminum, given that the equilibrium number of vacancies at 500C (773 K) is 7.57 10 m?. The atomic weight and density (at 500C) for aluminum are, respectively, 26.98 g/mol and 2.62 g/cm? 8. Below, atomic radius, crystal structure, electronegativity, and the most common valence are tabulated, for several elements; for those that are nonmetals, only atomic radii are indicated. Element Crystal Structure FCC Electronegativity 1.9 Valence +2 Cu H 0 1.9 Ag AI 1.5 +3 Atomic Radius (nm) 0.1278 0.071 0.046 0.060 0.1445 0.1431 0.1253 0.1249 0.1241 0.1246 0.1376 0.1387 0.1332 1.8 +2 Cr 1.6 Fe FCC FCC HCP BCC BCC FCC FCC FCC HCP 1.8 +2 Ni 1.8 Pd 2.2 +2 +2 +2 +2 Pt 22 Zn 1.6 Which of these elements would you expect to form the following with copper: (a) A substitutional solid solution having complete solubility (b) A substitutional solid solution of incomplete solubility (c) An interstitial solid solution 9. What is the composition, in weight percent, of an alloy that consists of 6 at% Pb and 94 at% Sn? 10. Determine the ASTM grain size number if 20 grains per square inch are measured at a magnification of 50x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


