Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Consider the layers in TCP/IP reference model (Figure 1.22) of your text Assume that the user data is I KB, Layers Application Transport
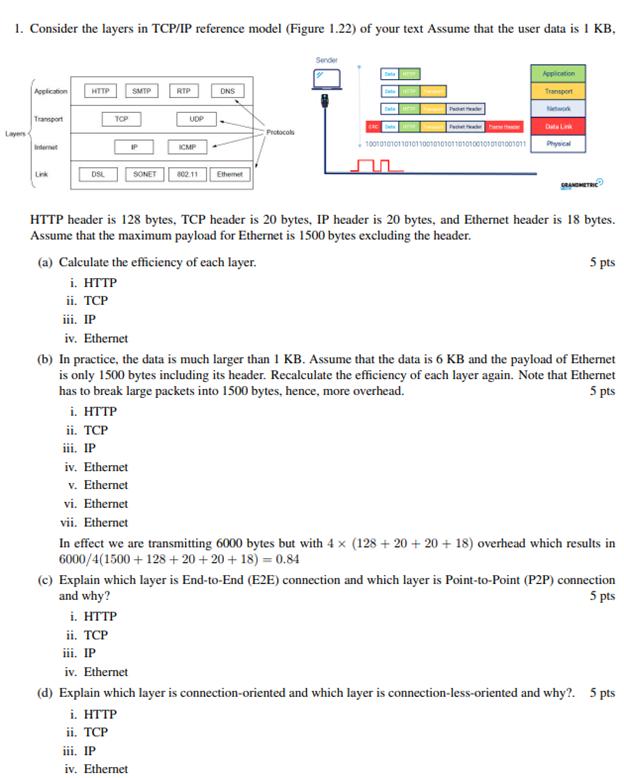
1. Consider the layers in TCP/IP reference model (Figure 1.22) of your text Assume that the user data is I KB, Layers Application Transport Link HTTP DSL TOP IP iii. IP iv. Ethernet SMTP RTP iv. Ethernet v. Ethernet vi. Ethernet vii. Ethernet UDP ICMP SONET 802.11 (a) Calculate the efficiency of each layer. i. HTTP ii. TCP ii. TCP iii. IP iv. Ethernet DNS Protocols Sender ata Packa 100101010110101100101010110101001010101001011 HTTP header is 128 bytes, TCP header is 20 bytes, IP header is 20 bytes, and Ethernet header is 18 bytes. Assume that the maximum payload for Ethernet is 1500 bytes excluding the header. Application Transport Data Link GRANDMETRIC (b) In practice, the data is much larger than 1 KB. Assume that the data is 6 KB and the payload of Ethernet is only 1500 bytes including its header. Recalculate the efficiency of each layer again. Note that Ethernet has to break large packets into 1500 bytes, hence, more overhead. 5 pts i. HTTP ii. TCP iii. IP 5 pts In effect we are transmitting 6000 bytes but with 4 x (128+20+20 + 18) overhead which results in 6000/4(1500+128 +20+20+18)= 0.84 (c) Explain which layer is End-to-End (E2E) connection and which layer is Point-to-Point (P2P) connection and why? 5 pts i. HTTP (d) Explain which layer is connection-oriented and which layer is connection-less-oriented and why?. 5 pts i. HTTP ii. TCP iii. IP iv. Ethernet
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The solution to the image a Calculate the efficiency of each layer HTTP 128 bytes 1268 bytes 100 101 ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


