Question: 1. Mechanical Equilibrium By a definition, a system is in mechanical equilibrium if the sum of the forces acting on that system is equal to
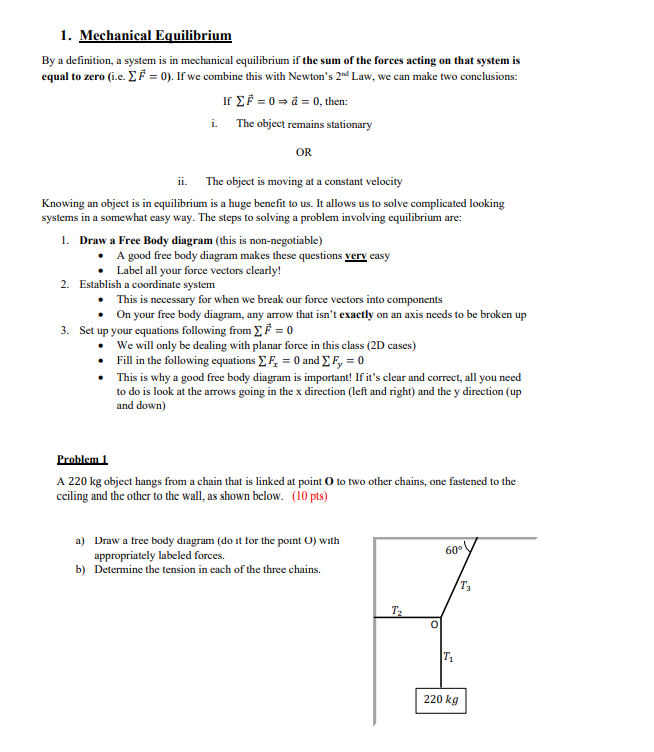
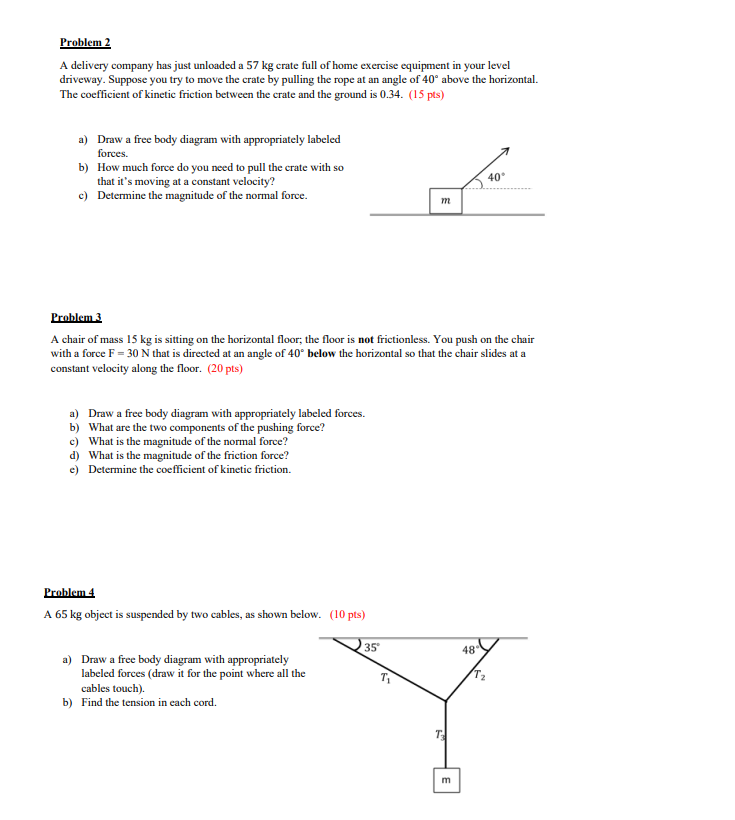
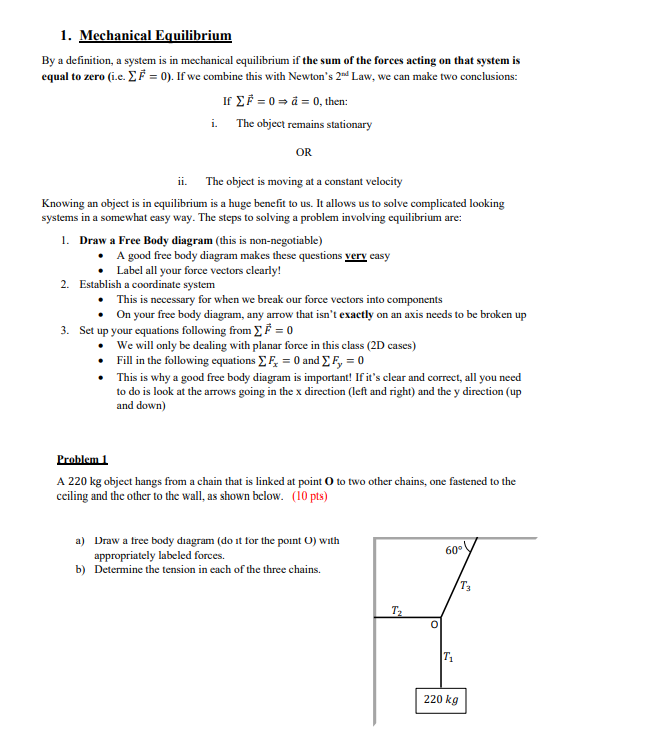
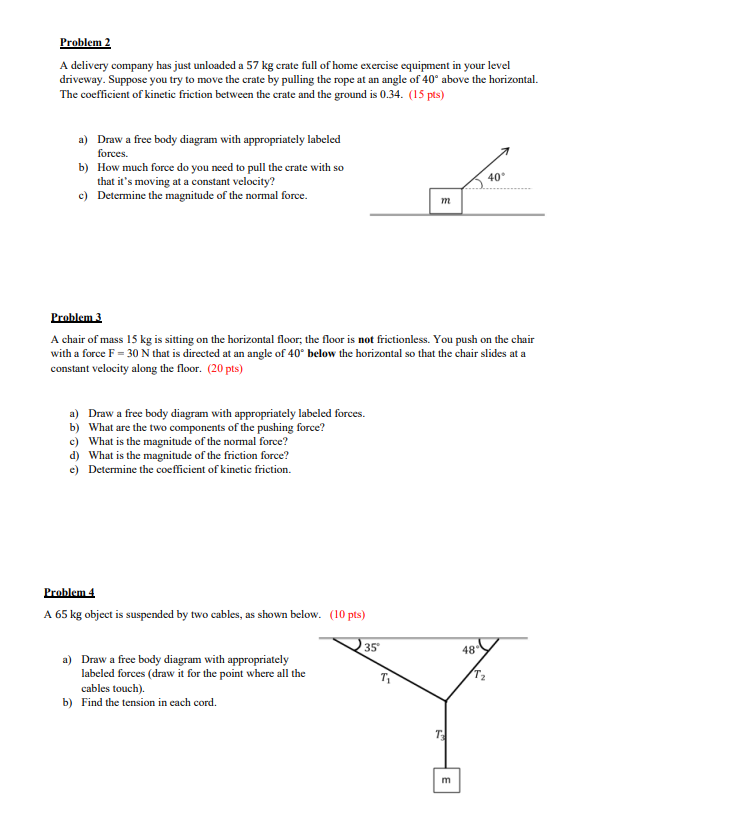
1. Mechanical Equilibrium By a definition, a system is in mechanical equilibrium if the sum of the forces acting on that system is equal to zero (i.c. EF = 0). If we combine this with Newton's 2"d Law, we can make two conclusions: If EF = 0 = a = 0, then: i. The object remains stationary OR ii. The object is moving at a constant velocity Knowing an object is in equilibrium is a huge benefit to us. It allows us to solve complicated looking systems in a somewhat easy way. The steps to solving a problem involving equilibrium are: 1. Draw a Free Body diagram (this is non-negotiable) A good free body diagram makes these questions very casy . Label all your force vectors clearly! 2. Establish a coordinate system This is necessary for when we break our force vectors into components On your free body diagram, any arrow that isn't exactly on an axis needs to be broken up 3. Set up your equations following from E F = 0 We will only be dealing with planar force in this class (2D cases) . Fill in the following equations _ F, = 0 and ) Fy = 0 This is why a good free body diagram is important! If it's clear and correct, all you need to do is look at the arrows going in the x direction (left and right) and the y direction (up and down) Problem 1 A 220 kg object hangs from a chain that is linked at point O to two other chains, one fastened to the ceiling and the other to the wall, as shown below. (10 pts) a) Draw a free body diagram (do it for the point O) with appropriately labeled forces. b) Determine the tension in each of the three chains. T2 O T1 220 kgProblem 2 A delivery company has just unloaded a 57 kg crate full of home exercise equipment in your level driveway. Suppose you try to move the crate by pulling the rope at an angle of 40 above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ground is 0.34. (15 pts) a) Draw a free body diagram with appropriately labeled forces. b) How much force do you need to pull the crate with so that it's moving at a constant velocity? 40 c) Determine the magnitude of the normal force. Problem 3 A chair of mass 15 kg is sitting on the horizontal floor; the floor is not frictionless. You push on the chair with a force F = 30 N that is directed at an angle of 40" below the horizontal so that the chair slides at a constant velocity along the floor. (20 pts) a) Draw a free body diagram with appropriately labeled forces. b) What are the two components of the pushing force? c) What is the magnitude of the normal force? d) What is the magnitude of the friction force? e) Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction. Problem 4 A 65 kg object is suspended by two cables, as shown below. (10 pts) 35 48- a) Draw a free body diagram with appropriately labeled forces (draw it for the point where all the cables touch). b) Find the tension in each cord. m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


