Question: 1 . Suppose a 4 0 0 0 bytes TCP message ( including the TCP header ) is passed to IP for delivery across two
Suppose a bytes TCP message including the TCP header is passed to IP for delivery across two networks of the Internet. The first network has an MTU of bytes; the second has an MTU of bytes. Each networks MTU gives the size of the largest IP datagram that can be carried in a linklayer frame.
a Give the sizes, offsets, values of offset fields in the IP headers of the sequence of fragments delivered to the network layer at the destination host. Assume all IP headers are bytes. Note, the IP requires that fragmentation should always happen on byte boundaries.
b Path MTU is the smallest MTU of any link on the current path route between two hosts. Assume that we could discover the path MTU of the path used, and that we use this value as the MTU for all the path segments. Give the sizes of the sequence of IP packets delivered to the network layer at the destination host.
IP addresses. Company X and Company Y both connect to the same ISP. Company X is assigned the prefix and Company Y is assigned the prefix The ISP has a single port router: port connects to Company X port connects to Company Y and port connects to the rest of the Internet.
a Draw and complete as best you can the contents of the forwarding table in the ISPs router.
b What aggregated prefix does the router advertize to the rest of the Internet so that packets can reach both Company X and Company Y
Suppose a route has built up the routing table shown in the following table.
SubnetNumber
SubnetMask
Next hop
Interface
Interface
R
R
Default
R
The router can deliver packets directly over interfaces and or it can forward packets to routers R R or R Describe what the router does with a packet addressed to each of the following destinations:
a
b
c
d
e
f
The following table is a routing table using CIDR. Address bytes are in hexadecimal.
NetMaskLength
Next hop
C
A
CE
B
C
C
C
D
E
F
G
State to what next hop the following will be delivered.
a CEA
b CE
c C
dE
eA
f CE
g CAE
An organization has a class C network and wants to form subnets for six departments, which host as follows:
A hosts
B hosts
C hosts
D hosts
E hosts
F hosts
G hosts
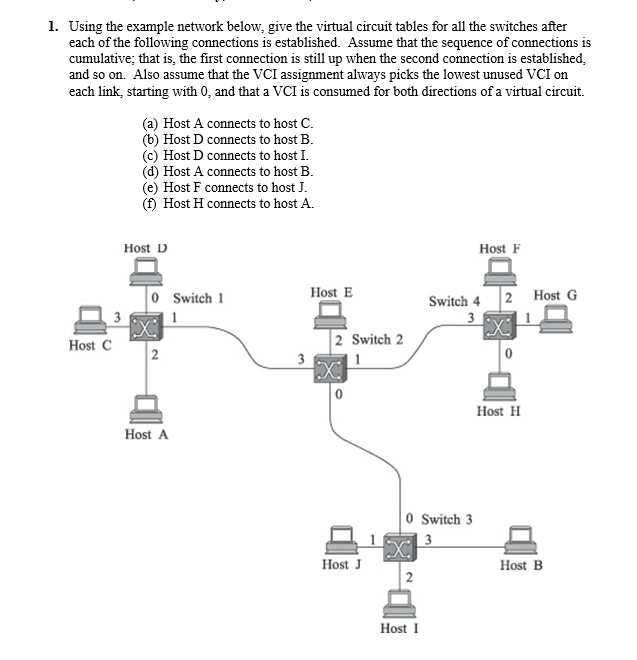
There are hosts in all. Design a possible arrangement of subnets to make each department in a different subnet. For each subnet, give subnet number, subnet mask and range of IP addresses. Using the example network below, give the virtual circuit tables for all the switches after each of the following connections is established. Assume that the sequence of connections is cumulative; that is the first connection is still up when the second connection is established, and so on Also assume that the VCI assignment always picks the lowest unused VCI on each link, starting with and that a VCI is consumed for both directions of a virtual circuit.
a Host A connects to host C
b Host D connects to host B
c Host D connects to host I.
d Host A connects to host B
e Host F connects to host J
f Host H connects to host A Consider the arrangement of learning bridges shown in the following figure. Assuming all are initially empty, give the forwarding tables for each of the bridges mathrmBmathrmB after the following transmissions:
A sends to B ; B sends to A ; A sends to X
X sends to A ; D sends to Y ; E sends to underlineunderlineD Linkstate routing protocols
This question explores how to set the configurable link weights in linkstate routing protocols like OSPF inside a single Autonomous System AS to achieve ASwide goals.
a How should the network operators set the link weights if their goal is to minimize the number of hops each packet traverses to reach its destination?
b How should the operators set the link weights to minimize the endtoend delay the traffic experiences? Assume the network is lightly loaded, so queuing delay is insignificant.
c In the picture below, the nodes are routers, the edges are links, and the integers correspond to the link weight on each direction of the link. That is the link a b and the link b a both have weight Put arrows on the edges to show the shortest path from every node to the destination node mathbfd That is show the "sink tree" leading to node mathbfd
d Suppose the link ih is overloaded with traffic. Identify a sing
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


