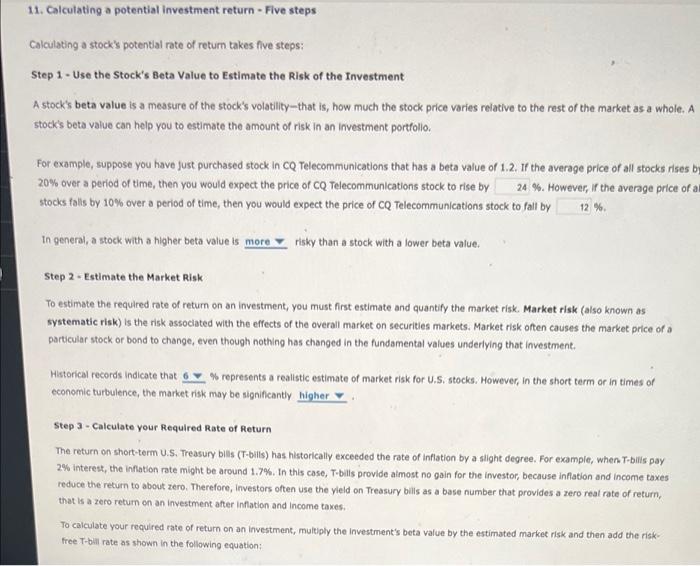
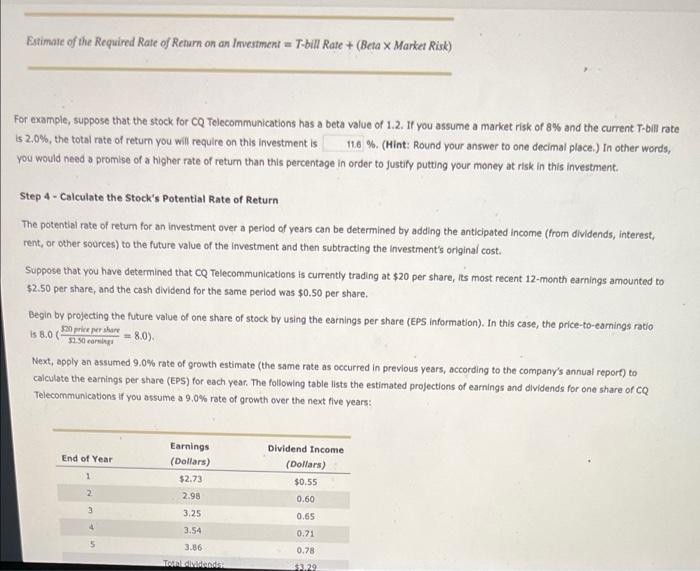
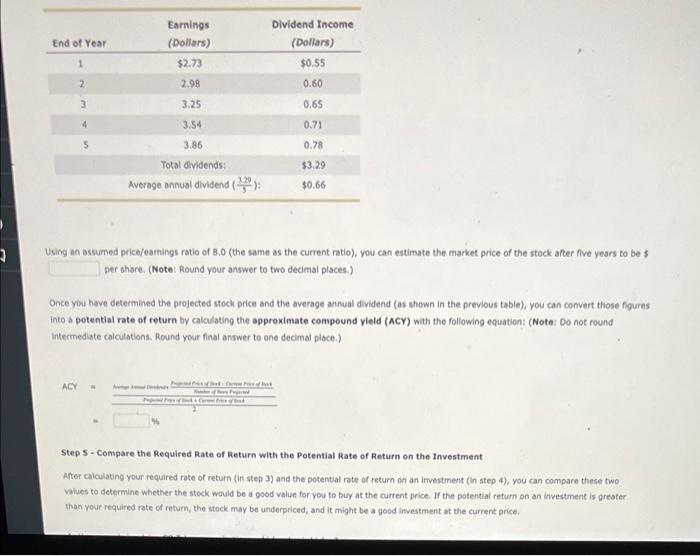
11. Calculating a potential investment return - Five steps Calculating a stock's potential rate of return takes five steps: Step 1 - Use the Stock's Beta Value to Estimate the risk of the Investment A stock's beta value is a measure of the stock's volatility-that is, how much the stock price varies relative to the rest of the market as a whole. A stock's beta value can help you to estimate the amount of risk in an Investment portfolio For example, suppose you have just purchased stock in CQ Telecommunications that has a beta value of 1.2. If the average price of all stocks rises by 20% over a period of time, then you would expect the price of CQ Telecommunications stock to rise by 24 %. However, if the average price of a stocks foils by 10% over a period of time, then you would expect the price of CQ Telecommunications stock to fall by 12 % In general, a stock with a higher beta value is more risky than a stock with a lower beta value. Step 2 - Estimate the Market Risk To estimate the required rate of return on an investment, you must first estimate and quantify the market risk. Market risk (also known as systematic risk) is the risk associated with the effects of the overall market on securities markets. Market risk often causes the market price of a particular stock or bond to change, even though nothing has changed in the fundamental values underlying that investment. Historical records indicate that 6 represents a realistic estimate of market risk for U.S. stocks. However, in the short term or in times of economic turbulence, the market risk may be significantly higher Step 3 - Calculate your Required Rate of Return The return on short-term U.S. Treasury bills (T-bills) has historically exceeded the rate of inflation by a slight degree. For example, when T-bills pay 2% Interest, the inflation rate might be around 1.7%. In this case, T-bills provide almost no gain for the investor, because inflation and Income taxes reduce the return to about zero. Therefore, Investors often use the yield on Treasury bills as a base number that provides a zero reat rate of return, that is a zero return on an investment after inflation and income taxes. To calculate your required rate of return on an investment, multiply the investment's beta value by the estimated market risk and then add the risk free T-bill rate as shown in the following equation: Estimate of the Required Rate of Return on an Investment T-bill Rate +(Beta x Market Risk) For example, suppose that the stock for CQ Telecommunications has a beta value of 1.2. If you assume a market risk of 8% and the current T-bil rate is 2,0%, the total rate of return you will require on this investment is 116 %. (Hint: Round your answer to one decimal place.) In other words, you would need a promise of a higher rate of return than this percentage in order to justify putting your money at risk in this investment. Step 4 - Calculate the Stock's Potential Rate of Return The potential rate of return for an investment over a period of years can be determined by adding the anticipated income (from dividends, interest, rent, or other sources) to the future value of the investment and then subtracting the Investment's original cost. Suppose that you have determined that CQ Telecommunications is currently trading at $20 per share, its most recent 12-month earnings amounted to $2.50 per share, and the cash dividend for the same period was $0.50 per share. Begin by projecting the future value of one share of stock by using the earnings per share (EPS Information). In this case, the price-to-earnings ratio $20 price perstore - 8.0). Next, apply an assumed 9.0% rate of growth estimate (the same rate as occurred in previous years, according to the company's annual report) to calculate the earnings per share (EPS) for each year. The following table lists the estimated projections of earnings and dividends for one share of CQ Telecommunications if you assume a 9,0% rate of growth over the next five years: is 8.0 $2.50 carti End of Year Earnings (Dollars) $2.73 1 Dividend Income (Dollars) $0.55 0.60 2 3 4 2.98 3.25 3.54 3.86 TA 0.65 0.71 0.78 $329 End of Year Earnings (Dollars) $2.73 Dividend Income (Dollars) $0.55 1 2 2.98 0.60 3 3.25 0.65 0.71 3.54 3.86 0.78 Total dividends: $3.29 Average annual dividend (47: $0.66 3 Using an assumed price/earnings ratio of 8.0 (the same as the current ratio), you can estimate the market price of the stock after five years to be $ per share. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal places.) Once you have determined the projected stock price and the average annual dividend (as shown in the previous table), you can convert those figures into a potential rate of return by calculating the approximate compound yield (ACY) with the following equation: (Note: Do not round Intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to one decimal place.) ACY Step 5 - Compare the required Rate of Return with the potential Rate of Return on the Investment Alter calculating your required rate of return (in step 3) and the potential rate of return on an investment (in step 4), you can compare these two values to determine whether the stock would be a good value for you to buy at the current price. If the potential return on an investment is greater than your required rate of return, the stock may be underpriced, and it might be a good investment at the current price Using an assumed price/earnings ratio of 8.0 (the same as the current ratio), you can estimate the market price of the stock after five years to be per share. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal places.) Once you have determined the projected stock price and the average annual dividend (as shown in the previous table), you can convert those figures into a potential rate of return by calculating the approximate compound yield (ACY) with the following equation: (Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to one decimal place) Chet ACY M % Step 5. Compare the required Rate of Return with the potential Rate of Return on the Investment After calculating your required rate of return (in step 3) and the potential rate of return on an investment in step 4), you can compare these two values to determine whether the stock would be a good value for you to buy at the current price. If the potential return on an investment is greater than your required rate of retum, the stock may be underpriced, and it might be a good investment at the current price. In the example involving CQ Telecommunications, which value is higher The required rate of return (from step 3) mestock's potential rate of retum (from step 4) Therefore, CQ Telecommunications stock a good investment (that is, an undervalued Investment) at the current market price of $20 per share