1,2,3,4.marketing.
1.
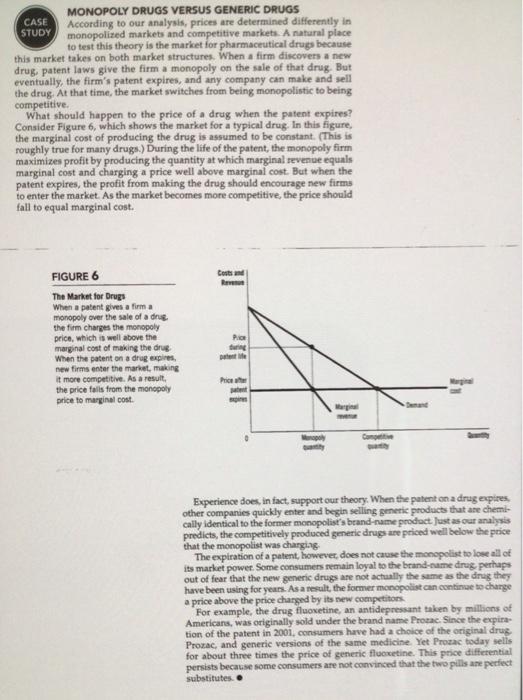
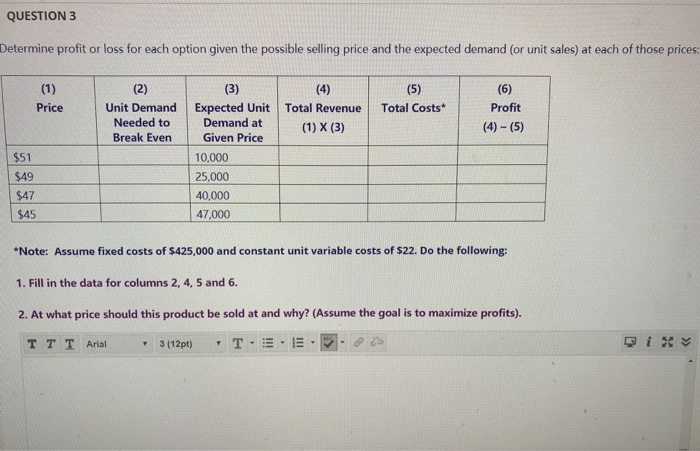
CASE STUDY QUESTIONS TO BE ANSWERED (1) Explain how this case study titled "Monopoly drugs versus generic drugs" is related to some of the economic concepts examined in this course (ECON 21 1). (2) What is the importance of this case study to consumers. producers and government? In your view which of these three economic agents is affected most by the issues discussed in this case study and why? (3) From your own point of view or personal experience would you consider "brand-name drugs" and "generic drugs" as perfect substitutes? Why? (4) If the length of time that a patent is protected is reduced what could be some of the impact on society?MONOPOLY DRUGS VERSUS GENERIC DRUGS CASE According to our analysis, prices are determined differently In STUDY monopolized markets and competitive markets. A natural place to test this theory is the market for pharmaceutical drugs because this market takes on both market structures. When a firm discovers a new drug, patent laws give the firm a monopoly on the sale of that drug. But eventually, the firm's patent expires, and any company can make and sell the drug. At that time, the market switches from being monopolistic to being competitive. What should happen to the price of a drug when the patent expires? Consider Figure 6, which shows the market for a typical drug. In this figure, the marginal cost of producing the drug is assumed to be constant. (This is roughly true for many drugs.) During the life of the patent, the monopoly firm maximizes profit by producing the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost and charging a price well above marginal cost. But when the patent expires, the profit from making the drug should encourage new firms to enter the market. As the market becomes more competitive, the price should fall to equal marginal cost. FIGURE 6 The Market for Drugs When a patent gives a firm a monopoly over the sale of a drug. the firm changes the monopoly price, which is well above the marginal cost of making the drug When the patent on a drug expire, new firms enter the market, making it more competitive. As a result, Prion she the price falls from the monopoly price to marginal cost. Experience does, in fact, support our theory: When the pubent on a drug expires other companies quickly enter and begin selling generic products that are chemi- cally identical to the former monopolist's brand-name product. Just as our analysis predicts, the competitively produced generic drugs are priced well below the price that the monopolist was charging The expiration of a patent, however, does not cause the monopolist to lose all of its market power. Some consumers remain loyal to the brand-name drug. perhaps out of fear that the new generic drugs are not actually the same as the drug they have been using for years. As a result, the former monopolist can continue to change price above the price charged by its new competitors. For example, the drug fluoxetine, an antidepressant taken by millions of Americana, was originally sold under the brand name Prozac. Since the expir tion of the patent in 2001, consumers have had a choice of the original drug. Prozac, and generic versions of the same medicine. Yet Prozac today sells for about three times the price of generic fluoxetine. This price differential persists because some consumers are not convinced that the two pills are perfect substitutes.QUESTION 3 Determine profit or loss for each option given the possible selling price and the expected demand (or unit sales) at each of those prices: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) Price Unit Demand Expected Unit Total Revenue Total Costs* Profit Needed to Demand at (1) X (3) (4) - (5) Break Even Given Price $51 10,000 $49 25,000 $47 40,000 $45 47,000 Note: Assume fixed costs of $425,000 and constant unit variable costs of $22. Do the following: 1. Fill in the data for columns 2, 4, 5 and 6. 2. At what price should this product be sold at and why? (Assume the goal is to maximize profits). T TT Arial 3 (12pt)5. A winery increased the price of it's Merlot from $15 a bottle to $19 a bottle. After this price change, demand went down from 7400 bottles to 6950 bottles. Calculate the elasticity of demand. a. What is the co-efficient of elasticity? b. Does this represent elastic or inelastic demand for this wine? Explain. 6. A washing machine company has just introduced a revolutionary new washer that will use less water and reduce energy costs. It will take some time for competitors to offer a competing product. There is a viable segment of the market who will respond positively to the benefits this product offers. Should the company use a price skimming or penetration pricing strategy when introducing this machine? Explain your answer.other improvements in information technology have enabled marketers to better understand the needs of customers on a one- to-one basis. Similar value card programs are evident in many different industries. Consumers receive rewards for purchasing virtually every type of product-from grocery stores to drive- through coffee retailers. Questions 1. Visit the CVS/pharmacy website (http://www.cvs.com). What other benefits does CVS provide to ExtraCare customers? Provide examples of both utilitarian and hedonic value. 2. Suppose a major competitor launches its own customer value card program. How might CVS respond? What recommendations would you give CVS to improve the ExtraCare program? 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of not requiring personal information from customers for participating in the ExtraCare program? 4. What ethical issues would CVS need to consider before changing their ExtraCare policy to require an address and phone number? CHAPTER 2: VALUE AND THE CONSUMER BEHAVIOR VALUE FRAMEWORK 39