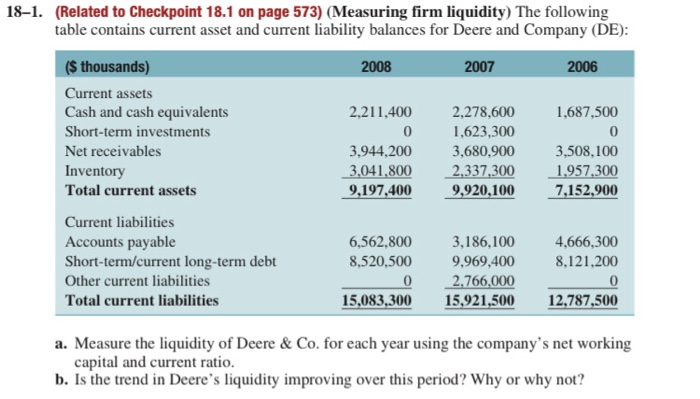
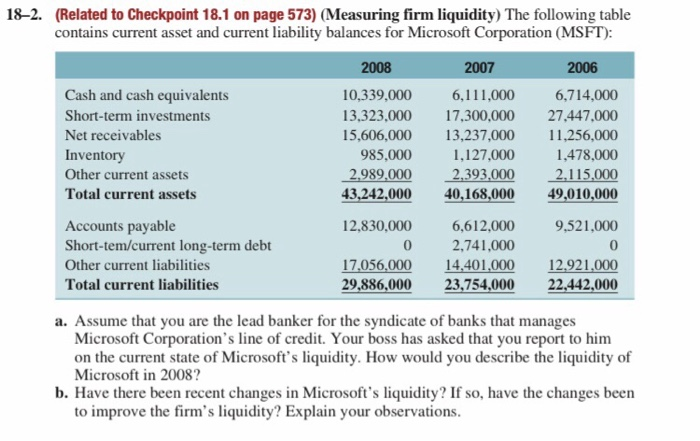
18-1. (Related to Checkpoint 18.1 on page 573) (Measuring firm liquidity) The following table contains current asset and current liability balances for Deere and Company (DE): 2008 2007 2006 1,687,500 ($ thousands) Current assets Cash and cash equivalents Short-term investments Net receivables Inventory Total current assets 2,211,400 0 3,944,200 3,041,800 9,197,400 2,278,600 1,623,300 3,680,900 2,337,300 9,920,100 3,508,100 1,957,300 7,152,900 Current liabilities Accounts payable Short-term/current long-term debt Other current liabilities Total current liabilities 6,562,800 8,520,500 4,666,300 8,121,200 3,186,100 9.969,400 2,766,000 15,921,500 0 15,083,300 12,787,500 a. Measure the liquidity of Deere & Co. for each year using the company's net working capital and current ratio. b. Is the trend in Deere's liquidity improving over this period? Why or why not? 182. (Related to Checkpoint 18.1 on page 573) (Measuring firm liquidity) The following table contains current asset and current liability balances for Microsoft Corporation (MSFT): 2008 2007 2006 Cash and cash equivalents Short-term investments Net receivables Inventory Other current assets Total current assets 10.339.000 13,323,000 15,606,000 985,000 2.989,000 43,242,000 6,111,000 17,300,000 13,237,000 1,127.000 2,393,000 40,168,000 6,714,000 27.447.000 11,256,000 1,478,000 2,115,000 49,010,000 9.521.000 Accounts payable Short-tem/current long-term debt Other current liabilities Total current liabilities 12,830,000 0 17,056,000 29,886,000 6,612,000 2,741,000 14,401,000 23,754,000 12.921,000 22,442,000 a. Assume that you are the lead banker for the syndicate of banks that manages Microsoft Corporation's line of credit. Your boss has asked that you report to him on the current state of Microsoft's liquidity. How would you describe the liquidity of Microsoft in 2008? b. Have there been recent changes in Microsoft's liquidity? If so, have the changes been to improve the firm's liquidity? Explain your observations. 18-5. (Related to Checkpoint 18.2 on page 580) (Calculating the cash conversion cycle) Network Solutions just introduced a new, fully automated manufacturing plant that produces 2,000 wireless routers per day with materials costs of $50 per router and no other costs. The average number of days a router is held in inventory before being sold is 45 days. In addition, the company generally pays its suppliers in 30 days, while collecting from its customers after 25 days. a. What is the cash conversion cycle? b. What would happen to the cash conversion cycle if the company could stretch its payments to suppliers from 30 days to 50 days? c. How much would working capital financing be reduced if the company stretched its payments to suppliers from 30 days to 50 days? 18-6. (Related to Checkpoint 18.2 on page 580) (Calculating the operating and cash conver- sion cycle) Carraway Seed Company Inc. has for many years cultivated and sold what are known as heritage plants and seeds. For example, the company has sought out older varieties of tomato plants that are no longer grown by commercial vegetable farmers because they either take too long to mature, do not ship well, or do not hold up for long on the store shelf. The company has recently been considering ways to reduce its in- vestment in working capital in order to make itself more profitable. At present the firm has an inventory conversion period of 90 days and offers credit terms of 30 days that the majority of its customers take full advantage of. The company purchases its inven- tory items on credit terms that allow it 45 days to pay but has always followed a policy of making cash payments for invoices as soon as they are received, so the accounts payable deferral period is typically only five days. a. What are Carraway's operating and cash conversion cycles? b. If Carraway were to decide to take full advantage of its credit terms and delay pay- ment until the last possible date, how would this impact its cash conversion cycle? c. What would be your recommendation to the company with regard to its working capital management practices and why