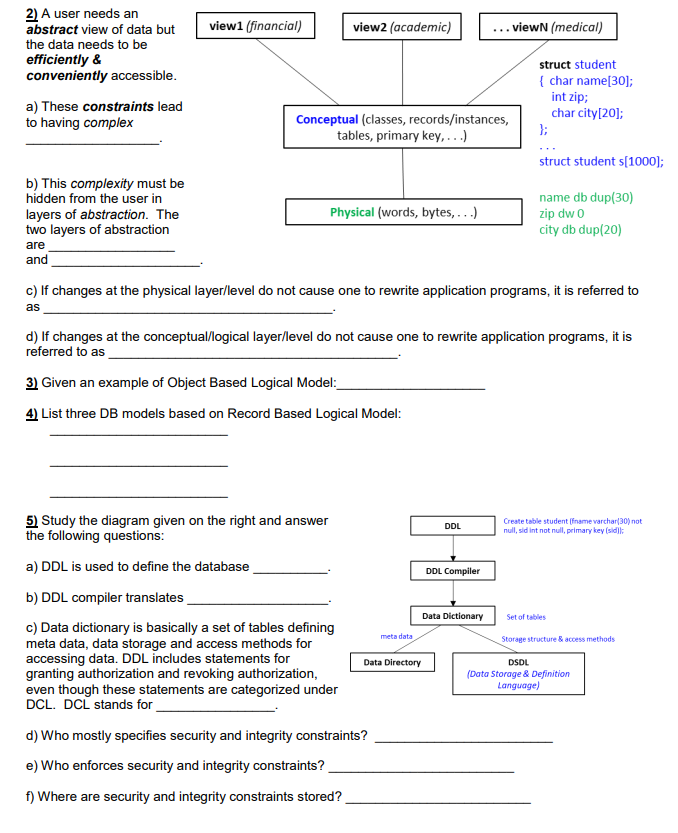
2) A user needs an abstract view of data but viewN (medical) view1 (financial) view2 (academic) the data needs to be efficiently & conveniently accessible. struct student { char name[30]; int zip; char city[20]; a) These constraints lead to having complex Conceptual (classes, records/instances, }; tables, primary key, ...) struct student s[1000); b) This complexity must be hidden from the user in layers of abstraction. The two layers of abstraction name db dup(30) zip dw 0 city db dup(20) Physical (words, bytes,...) are and c) If changes at the physical layer/level do not cause one to rewrite application programs, it is referred to as d) If changes at the conceptual/logical layer/level do not cause one to rewrite application programs, it is referred to as 3) Given an example of Object Based Logical Model: 4) List three DB models based on Record Based Logical Model: 5) Study the diagram given on the right and answer the following questions: Create table student (fname varchar(30) not null, sid int not null, primary key (sidi): DDL a) DDL is used to define the database DDL Compiler b) DDL compiler translates Data Dictionary Set of tables c) Data dictionary is basically a set of tables defining meta data, data storage and access methods for accessing data. DDL includes statements for granting authorization and revoking authorization, even though these statements are categorized under DCL. DCL stands for meta data Storage structure & access methods Data Directory DSDL (Data Storage & Definition Language) d) Who mostly specifies security and integrity constraints? e) Who enforces security and integrity constraints? f) Where are security and integrity constraints stored? 2) A user needs an abstract view of data but viewN (medical) view1 (financial) view2 (academic) the data needs to be efficiently & conveniently accessible. struct student { char name[30]; int zip; char city[20]; a) These constraints lead to having complex Conceptual (classes, records/instances, }; tables, primary key, ...) struct student s[1000); b) This complexity must be hidden from the user in layers of abstraction. The two layers of abstraction name db dup(30) zip dw 0 city db dup(20) Physical (words, bytes,...) are and c) If changes at the physical layer/level do not cause one to rewrite application programs, it is referred to as d) If changes at the conceptual/logical layer/level do not cause one to rewrite application programs, it is referred to as 3) Given an example of Object Based Logical Model: 4) List three DB models based on Record Based Logical Model: 5) Study the diagram given on the right and answer the following questions: Create table student (fname varchar(30) not null, sid int not null, primary key (sidi): DDL a) DDL is used to define the database DDL Compiler b) DDL compiler translates Data Dictionary Set of tables c) Data dictionary is basically a set of tables defining meta data, data storage and access methods for accessing data. DDL includes statements for granting authorization and revoking authorization, even though these statements are categorized under DCL. DCL stands for meta data Storage structure & access methods Data Directory DSDL (Data Storage & Definition Language) d) Who mostly specifies security and integrity constraints? e) Who enforces security and integrity constraints? f) Where are security and integrity constraints stored







