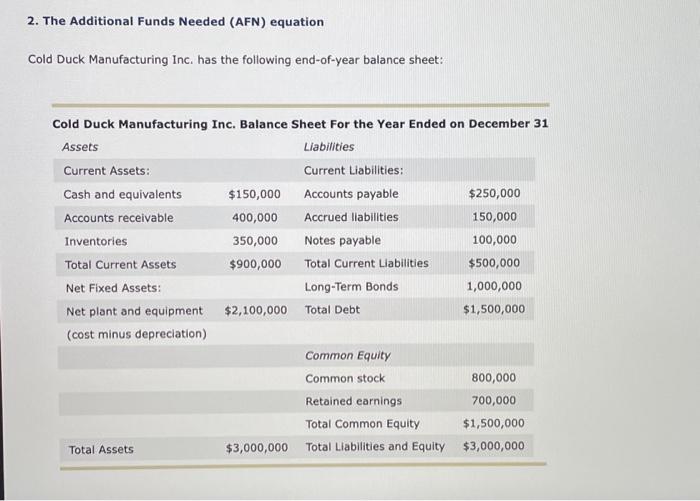
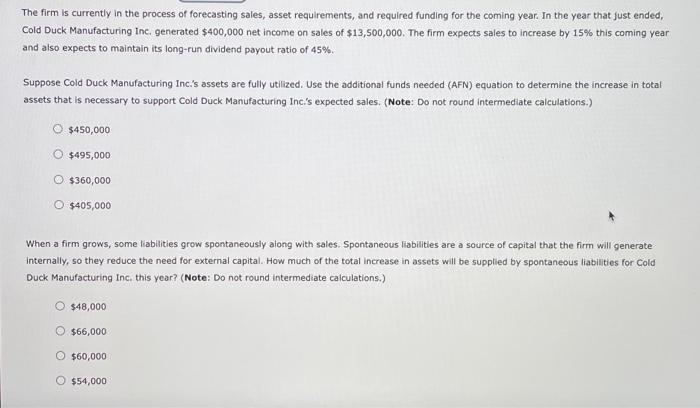
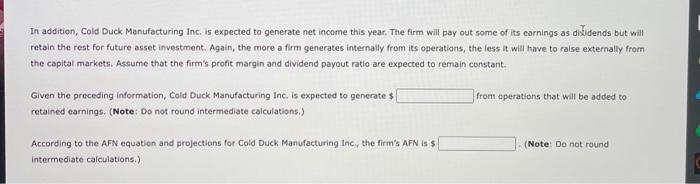
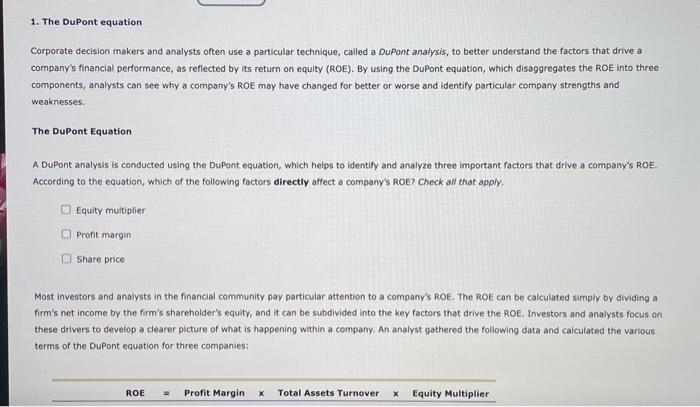
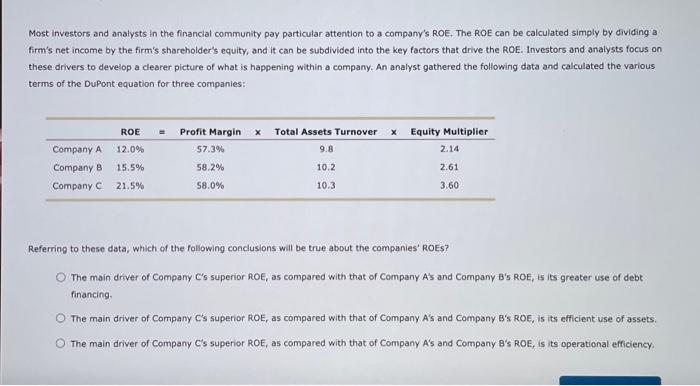
2. The Additional Funds Needed (AFN) equation Cold Duck Manufacturing Inc. has the following end-of-year balance sheet: The firm is currently in the process of forecasting sales, asset requirements, and required funding for the coming year. In the year that just ended, Cold Duck Manufacturing ine. generated $400,000 net income on sales of $13,500,000. The firm expects sales to increase by 15% this coming year and also expects to maintain its long-run dividend payout ratio of 45%. Suppose Cold Duck Manufacturing Inc.'s assets are fully utilized. Use the additional funds needed (AFN) equation to determine the increase in total assets that is necessary to support Cold Duck Manufacturing Inc.'s expected sales. (Note: Do not round intermediate calculations.) $450,000$495,000$360,000$405,000 When a firm grows, some liablities grow spontaneously along with sales. Spontaneous liabilities are a source of capital that the firm will generate internally, so they reduce the need for external capital. How much of the total increase in assets will be supplied by spontaneous liabilities for Cold Duck Manufacturing Inc, this year? (Note: Do not round intermediate calculations.) $48,000$66,000$60,000$54,000 In addition, Cold Duck Manufacturing Inc. is expected to generate net income this year. The firm will pay out some of its earnings as dividends but will retain the rest for future asset investment, Again, the more a firm generates internally from its operations, the less it wili have to raise externally from the capital markets. Assume that the firm's profit margin and dividend payout ratio are expected to remain constant. Given the preceding information, Cold Duck Manufacturing Inc. is expected to generate $ from operations that will be added to retained earnings. (Note: Do not round intermediate calculations.) According to the AFN equation and projections for Cold Duck Manufacturing lnc.y the firm's AFN is $ (Note: Do not round intermediate calculations.) Corporate decision makers and analysts often use a particular technique, called a DuPont analysis, to better understand the factors that drive a company's financial performance, as reflected by its return on equity (ROE). By using the DuPont equation, which disaggregates the ROE into three components, analysts can see why a company's ROE may have changed for better or worse and identify particular company strengths and weaknesses. The DuPont Equation A DuPont analysis is conducted using the DuPont equation, which helps to identify and analyze three important factors that drive a company's ROE. According to the equation, which of the following factors directly affect a company's ROE? Check all that apply. Equity multiplier Proft margin Share price Most investors and analysts in the financial community pay particular attention to a company's ROE. The ROE can be calculated simply by dividing a firm's net income by the firm's shareholder's equity, and it can be subdivided into the key factors that drive the ROE. Investors and analysts focus on these drivers to develop a clearer plcture of what is happening within a company. An analyst gathered the following data and calculated the various terms of the Dupont equation for three companies: Most investors and analysts in the financlal community pay particular attention to a company's ROE. The ROE can be calculated simply by dividing a firm's net income by the firm's shareholder's equity, and it can be subdivided into the key factors that drive the RoE. Investors and analysts focus on these drivers to develop a clearer picture of what is happening within a company. An analyst gathered the following data and calculated the various terms of the Dupont equation for three companies: Referring to these data, which of the following conclusions will be true about the companies' ROEs? The main driver of Company C's superior ROE, as compared with that of Company A's and Company B's ROE, is its greater use of debt financing. The main driver of Company C's superior ROE, as compared with that of Company A's and Company B's ROE, is its efficient use of assets: The main driver of Company C's superior ROE, as compared with that of Company A's and Company B's ROE, is its operational efficiency