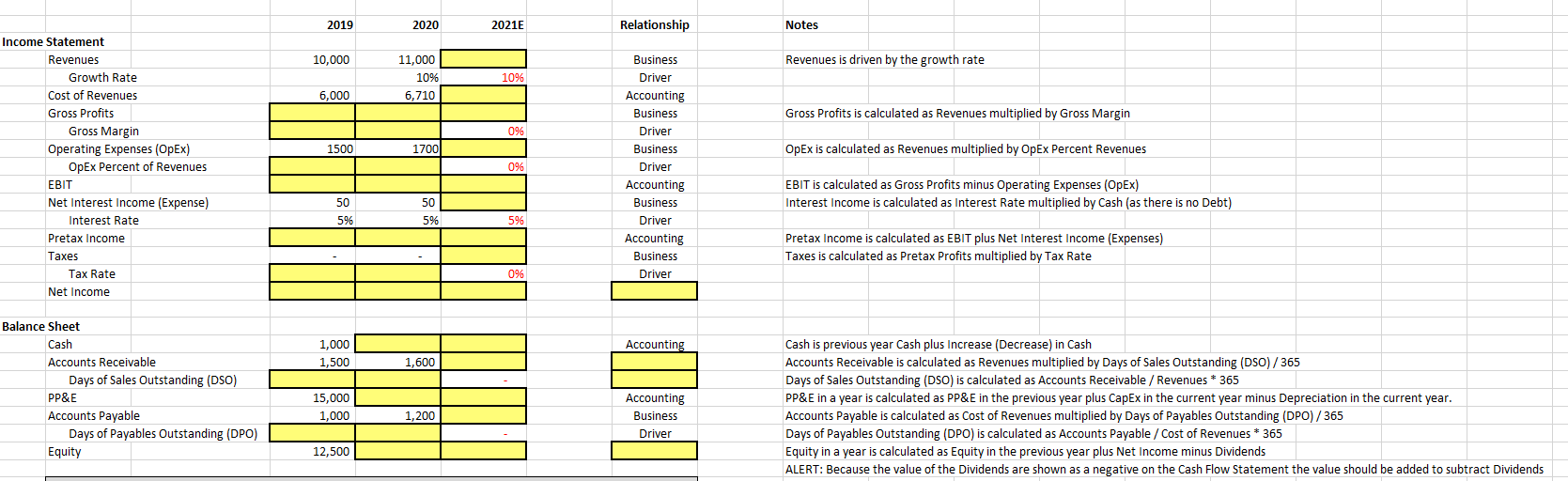
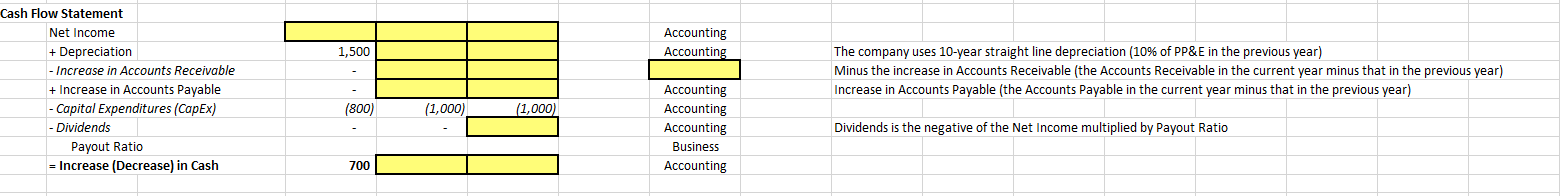
2019 2020 2021E Relationship Notes 10,000 Revenues is driven by the growth rate 11,000 10% 6,710 10% 6,000 Gross Profits is calculated as Revenues multiplied by Gross Margin 0% 1500 1700 OpEx is calculated as Revenues multiplied by OpEx Percent Revenues Income Statement Revenues Growth Rate Cost of Revenues Gross Profits Gross Margin Operating Expenses (Opex) OpEx Percent of Revenues EBIT Net Interest Income (Expense) Interest Rate Pretax Income Taxes Tax Rate Net Income 0% Business Driver Accounting Business Driver Business Driver Accounting Business Driver Accounting Business Driver EBIT is calculated as Gross Profits minus Operating Expenses (Opex) Interest Income is calculated as Interest Rate multiplied by Cash (as there is no Debt) 50 50 5% 5% 5% Pretax Income is calculated as EBIT plus Net Interest Income (Expenses) Taxes is calculated as Pretax Profits multiplied by Tax Rate 0% Accounting 1,000 1,500 1,600 Balance Sheet Cash Accounts Receivable Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO) PP&E Accounts Payable Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO) Equity 15,000 1,000 1,200 Accounting Business Driver Cash is previous year Cash plus Increase (Decrease) in Cash Accounts Receivable is calculated as Revenues multiplied by Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO)/365 Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO) is calculated as Accounts Receivable / Revenues * 365 PP&E in a year is calculated as PP&E in the previous year plus CapEx in the current year minus Depreciation in the current year. Accounts Payable is calculated as Cost of Revenues multiplied by Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO)/365 Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO) is calculated as Accounts Payable / Cost of Revenues * 365 Equity in a year is calculated as Equity in the previous year plus Net Income minus Dividends ALERT: Because the value of the Dividends are shown as a negative on the Cash Flow Statement the value should be added to subtract Dividends 12,500 Accounting Accounting 1,500 Cash Flow Statement Net Income + Depreciation - Increase in Accounts Receivable + Increase in Accounts Payable - Capital Expenditures (CapEx) - Dividends Payout Ratio = Increase (Decrease) in Cash The company uses 10-year straight line depreciation (10% of PP&E in the previous year) Minus the increase in Accounts Receivable (the Accounts Receivable in the current year minus that in the previous year) Increase in Accounts Payable (the Accounts Payable in the current year minus that in the previous year) (800) (1,000) (1,000) Accounting Accounting Accounting Business Accounting Dividends is the negative of the Net Income multiplied by Payout Ratio 700 2019 2020 2021E Relationship Notes 10,000 Revenues is driven by the growth rate 11,000 10% 6,710 10% 6,000 Gross Profits is calculated as Revenues multiplied by Gross Margin 0% 1500 1700 OpEx is calculated as Revenues multiplied by OpEx Percent Revenues Income Statement Revenues Growth Rate Cost of Revenues Gross Profits Gross Margin Operating Expenses (Opex) OpEx Percent of Revenues EBIT Net Interest Income (Expense) Interest Rate Pretax Income Taxes Tax Rate Net Income 0% Business Driver Accounting Business Driver Business Driver Accounting Business Driver Accounting Business Driver EBIT is calculated as Gross Profits minus Operating Expenses (Opex) Interest Income is calculated as Interest Rate multiplied by Cash (as there is no Debt) 50 50 5% 5% 5% Pretax Income is calculated as EBIT plus Net Interest Income (Expenses) Taxes is calculated as Pretax Profits multiplied by Tax Rate 0% Accounting 1,000 1,500 1,600 Balance Sheet Cash Accounts Receivable Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO) PP&E Accounts Payable Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO) Equity 15,000 1,000 1,200 Accounting Business Driver Cash is previous year Cash plus Increase (Decrease) in Cash Accounts Receivable is calculated as Revenues multiplied by Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO)/365 Days of Sales Outstanding (DSO) is calculated as Accounts Receivable / Revenues * 365 PP&E in a year is calculated as PP&E in the previous year plus CapEx in the current year minus Depreciation in the current year. Accounts Payable is calculated as Cost of Revenues multiplied by Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO)/365 Days of Payables Outstanding (DPO) is calculated as Accounts Payable / Cost of Revenues * 365 Equity in a year is calculated as Equity in the previous year plus Net Income minus Dividends ALERT: Because the value of the Dividends are shown as a negative on the Cash Flow Statement the value should be added to subtract Dividends 12,500 Accounting Accounting 1,500 Cash Flow Statement Net Income + Depreciation - Increase in Accounts Receivable + Increase in Accounts Payable - Capital Expenditures (CapEx) - Dividends Payout Ratio = Increase (Decrease) in Cash The company uses 10-year straight line depreciation (10% of PP&E in the previous year) Minus the increase in Accounts Receivable (the Accounts Receivable in the current year minus that in the previous year) Increase in Accounts Payable (the Accounts Payable in the current year minus that in the previous year) (800) (1,000) (1,000) Accounting Accounting Accounting Business Accounting Dividends is the negative of the Net Income multiplied by Payout Ratio 700








