Question: Consider a load/store machine with ALU instructions having 3 operands; one destination register and two source registers and 16 registers R0-R15. For example, ADD

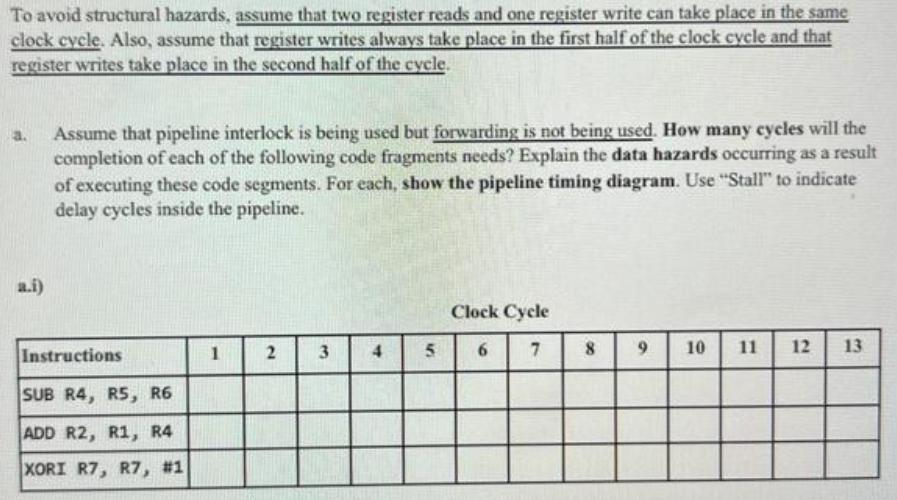

Consider a load/store machine with ALU instructions having 3 operands; one destination register and two source registers and 16 registers R0-R15. For example, "ADD R1, R2, R3" does the following RI - -R2+R3. Consider an instruction pipeline consisting of the following 5 stages. IE: Instruction fetch: Fetch the instruction from memory and update PC ID: Instruction decode and register fetch o Decode Instruction o Fetch register values (operands) o . Compute possible branch target address by adding offset in instruction to PC (PC-Relative addressing is used for branches) EX: Execute (ALU instruction), calculate effective addr. (Load/Store), or evaluate branch condition (Branch instruction) MEM: Read the data from memory (for Load/Store) WB: Write the data back to the register file (for ALU or Load) or to PC (for a taken branch) To avoid structural hazards, assume that two register reads and one register write can take place in the same clock cycle. Also, assume that register writes always take place in the first half of the clock cycle and that register writes take place in the second half of the cycle. To avoid structural hazards, assume that two register reads and one register write can take place in the same clock cycle. Also, assume that register writes always take place in the first half of the clock cycle and that register writes take place in the second half of the cycle. a. a.i) Assume that pipeline interlock is being used but forwarding is not being used. How many cycles will the completion of each of the following code fragments needs? Explain the data hazards occurring as a result of executing these code segments. For each, show the pipeline timing diagram. Use "Stall" to indicate delay cycles inside the pipeline. Instructions SUB R4, R5, R6 ADD R2, R1, R4 XORI R7, R7, #1 1 2 3 4 5 Clock Cycle 7 6 8 9 10 11 12 13 The above code segment needs Explanation of the data hazard: cycles.
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The given code segment will need 12 cycles With three stall cycles due to data dep... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


