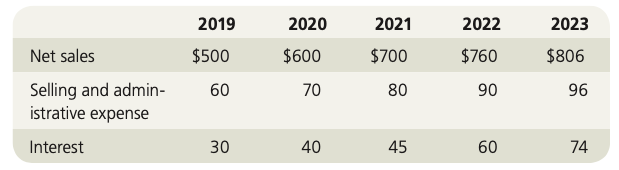266 Build a Model: Merger Analysis
Start with the partial model in the file Ch26 P07 Build a Model.xlsx on the textbooks Web site. Wansley Portal Inc., a large Internet service provider, is evaluating the possible acquisition of Alabama Connections Company (ACC), a regional Internet service provider. Wansleys analysts project the following post-merger data for ACC (in thousands of dollars):
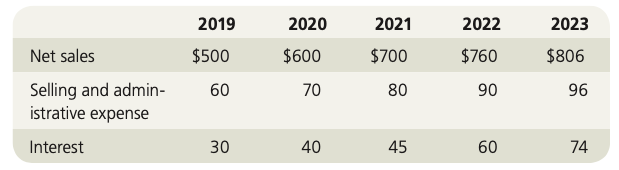
If the acquisition is made, it will occur on January 1, 2019. All cash flows shown in the income statements are assumed to occur at the end of the year. ACC currently has a capital structure of 30% debt, which costs 9%, but Wansley would increase that over time to 40%, costing 10%, if the acquisition were made. ACC, if independent, would pay taxes at 30%, but its income would be taxed at 35% if it were consolidated. ACCs current market-determined beta is 1.4. The cost of goods sold, which includes depreciation, is expected to be 65% of sales, but it could vary somewhat. Required gross investment in operating capital is approximately equal to the depreciation charged, so there will be no investment in net operating capital. The risk-free rate is 7%, and the market risk premium is 6.5%. Wansley currently has $400,000 in debt outstanding. Use the compressed APV model to answer the following questions.
a. What is the unlevered cost of equity? b. What are the horizon value of the tax shields and the horizon value of the unlevered operations? What are the value of ACCs operations and the value of ACCs equity to Wansleys shareholders?
Excel File
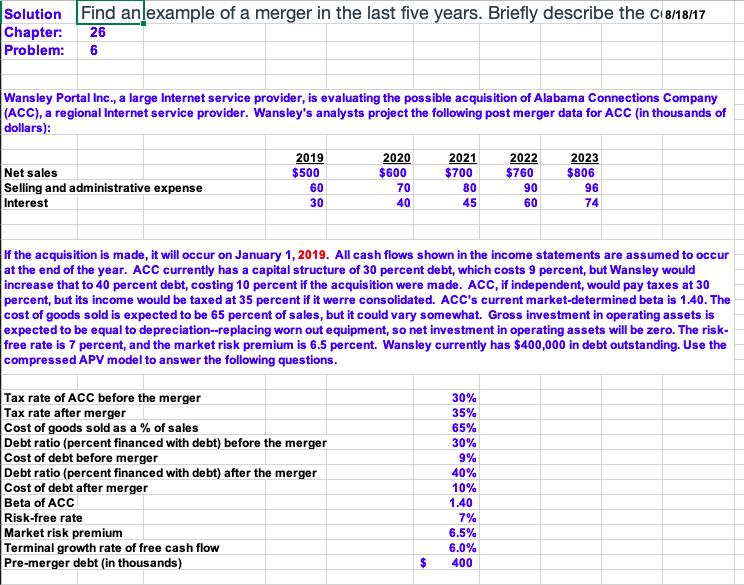
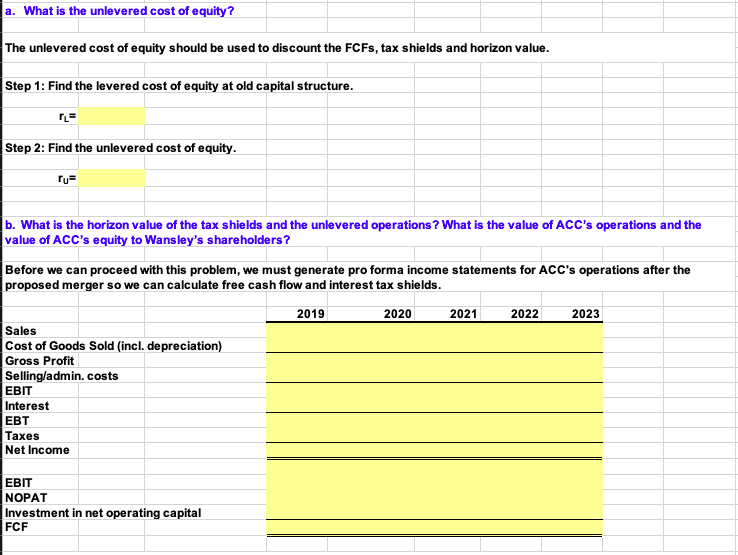
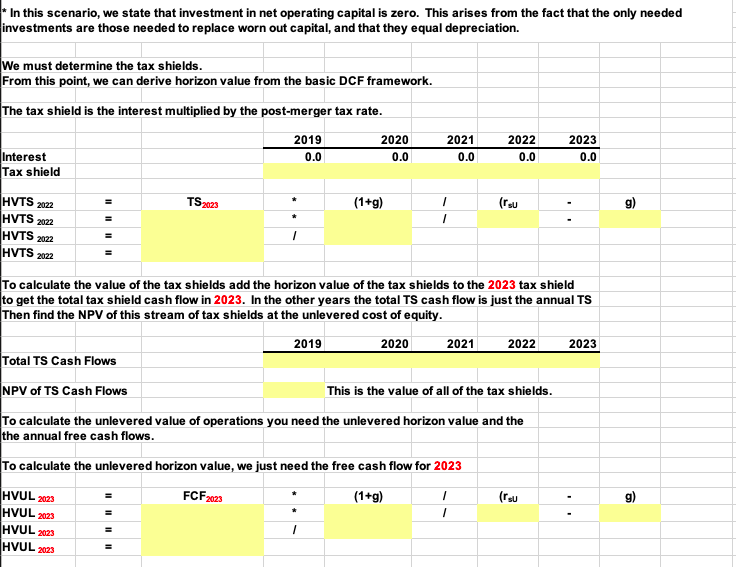
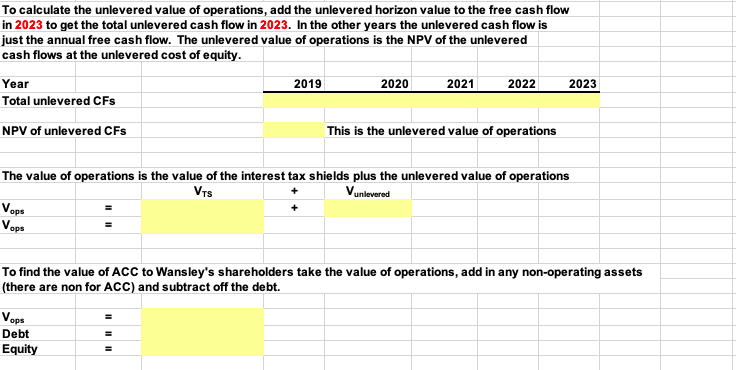
2019 Net sales $500 Selling and admin- 60 istrative expense Interest - 30 2020 $600 70 40 2021 $700 80 45 2022 $760 90 60 2023 $806 96 74 Solution Chapter: Problem: Find anlexample of a merger in the last five years. Briefly describe the C18/18/17 26 Wansley Portal Inc., a large Internet service provider, is evaluating the possible acquisition of Alabama Connections Company (ACC), a regional Internet service provider. Wansley's analysts project the following post merger data for ACC (in thousands of dollars): 2019 $500 60 30 Net sales Selling and administrative expense Interest 2020 $600 70 40 2023 $806 2021 $700 80 45 2022 $760 90 60 96 74 If the acquisition is made, it will occur on January 1, 2019. All cash flows shown in the income statements are assumed to occur at the end of the year. ACC currently has a capital structure of 30 percent debt, which costs 9 percent, but Wansley would increase that to 40 percent debt, costing 10 percent if the acquisition were made. ACC, if independent, would pay taxes at 30 percent, but its income would be taxed at 35 percent if it werre consolidated. ACC's current market-determined beta is 1.40. The cost of goods sold is expected to be 65 percent of sales, but it could vary somewhat. Gross investment in operating assets is expected to be equal to depreciation--replacing worn out equipment, so net investment in operating assets will be zero. The risk- free rate is 7 percent, and the market risk premium is 6.5 percent. Wansley currently has $400,000 in debt outstanding. Use the compressed APV model to answer the following questions. 30% 35% 65% 30% 9% Tax rate of ACC before the merger Tax rate after merger Cost of goods sold as a % of sales Debt ratio (percent financed with debt) before the merger Cost of debt before merger Debt ratio (percent financed with debt) after the merger Cost of debt after merger Beta of ACC Risk-free rate Market risk premium Terminal growth rate of free cash flow Pre-merger debt (in thousands) 40% 10% 1.40 7% 6.5% 6.0% 400 a. What is the unlevered cost of equity? The unlevered cost of equity should be used to discount the FCFs, tax shields and horizon value. Step 1: Find the levered cost of equity at old capital structure. Step 2: Find the unlevered cost of equity. ru b. What is the horizon value of the tax shields and the unlevered operations? What is the value of ACC's operations and the value of ACC's equity to Wansley's shareholders? Before we can proceed with this problem, we must generate pro forma income statements for ACC's operations after the proposed merger so we can calculate free cash flow and interest tax shields. 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Sales Cost of Goods Sold (incl. depreciation) Gross Profit Selling/admin. costs EBIT Interest EBT Taxes Net Income NOPAT Investment in net operating capital FCF In this scenario, we state that investment in net operating capital is zero. This arises from the fact that the only needed investments are those needed to replace worn out capital, and that they equal depreciation. We must determine the tax shields. From this point, we can derive horizon value from the basic DCF framework. The tax shield is the interest multiplied by the post-merger tax rate. 2019 0.0 2020 0.0 2021 0.0 2022 0.0 2023 0.0 Interest Tax shield TS2003 * (1+g) HVTS 2022 HVTS 2022 HVTS 2022 HVTS 2022 To calculate the value of the tax shields add the horizon value of the tax shields to the 2023 tax shield to get the total tax shield cash flow in 2023. In the other years the total TS cash flow is just the annual TS Then find the NPV of this stream of tax shields at the unlevered cost of equity. 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Total TS Cash Flows NPV of TS Cash Flows This is the value of all of the tax shields. To calculate the unlevered value of operations you need the unlevered horizon value and the the annual free cash flows. To calculate the unlevered horizon value, we just need the free cash flow for 2023 FCF 2023 (1+g) (rsu HVUL 2023 HVUL 2023 HVUL 2023 HVUL 2023 To calculate the unlevered value of operations, add the unlevered horizon value to the free cash flow in 2023 to get the total unlevered cash flow in 2023. In the other years the unlevered cash flow is just the annual free cash flow. The unlevered value of operations is the NPV of the unlevered cash flows at the unlevered cost of equity. 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Year Total unlevered CFS NPV of unlevered CFS This is the unlevered value of operations The value of operations is the value of the interest tax shields plus the unlevered value of operations Vunlevered Vops Vops To find the value of ACC to Wansley's shareholders take the value of operations, add in any non-operating assets (there are non for ACC) and subtract off the debt. Vops Debt Equity