
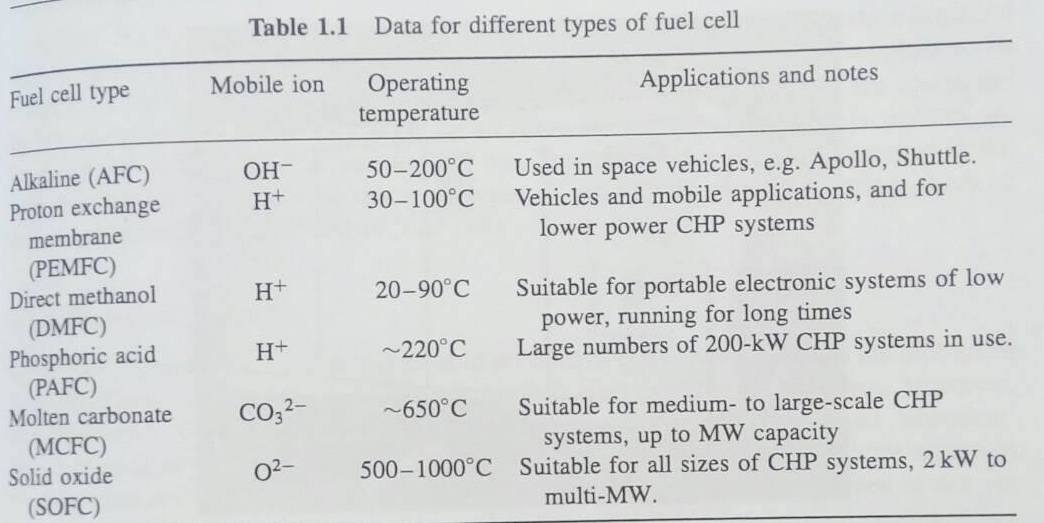
3. (1) According to Table 1.1, solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is suitable for all sizes of combined heat and power (CHP) systems, varied from 2kW to multi-MW. A SOFC delivers 500-kW electricity and 480-kW waste heat at 800C as well. The waste heat is supplied to a residential house at 25C in winter when the ambient temperature is at -23C. Based on the concept of 'pinch' technology, decide the optimum arrangement of adding other units so as to minimize exergy loss. And, determine the maximum heat tha may be supplied to the house, in kW. (2) If the waste heat is converted to additional electric power by a bottoming power engine placed outside the house, determine the maximum total electric power that may be obtained from the total system (SOFC + bottoming cycle), in kW. Table 1.1 Data for different types of fuel cell Mobile ion Applications and notes Fuel cell type Operating temperature OH 50-200C 30-100C H+ Used in space vehicles, e.g. Apollo, Shuttle. Vehicles and mobile applications, and for lower power CHP systems H+ 20-90C Alkaline (AFC) Proton exchange membrane (PEMFC) Direct methanol (DMFC) Phosphoric acid (PAFC) Molten carbonate (MCFC) Solid oxide (SOFC) Suitable for portable electronic systems of low power, running for long times Large numbers of 200-kW CHP systems in use. H+ ~220C CO32- ~650C Suitable for medium- to large-scale CHP systems, up to MW capacity 500-1000C Suitable for all sizes of CHP systems, 2 kW to multi-MW. 02- 3. (1) According to Table 1.1, solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is suitable for all sizes of combined heat and power (CHP) systems, varied from 2kW to multi-MW. A SOFC delivers 500-kW electricity and 480-kW waste heat at 800C as well. The waste heat is supplied to a residential house at 25C in winter when the ambient temperature is at -23C. Based on the concept of 'pinch' technology, decide the optimum arrangement of adding other units so as to minimize exergy loss. And, determine the maximum heat tha may be supplied to the house, in kW. (2) If the waste heat is converted to additional electric power by a bottoming power engine placed outside the house, determine the maximum total electric power that may be obtained from the total system (SOFC + bottoming cycle), in kW. Table 1.1 Data for different types of fuel cell Mobile ion Applications and notes Fuel cell type Operating temperature OH 50-200C 30-100C H+ Used in space vehicles, e.g. Apollo, Shuttle. Vehicles and mobile applications, and for lower power CHP systems H+ 20-90C Alkaline (AFC) Proton exchange membrane (PEMFC) Direct methanol (DMFC) Phosphoric acid (PAFC) Molten carbonate (MCFC) Solid oxide (SOFC) Suitable for portable electronic systems of low power, running for long times Large numbers of 200-kW CHP systems in use. H+ ~220C CO32- ~650C Suitable for medium- to large-scale CHP systems, up to MW capacity 500-1000C Suitable for all sizes of CHP systems, 2 kW to multi-MW. 02








