Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
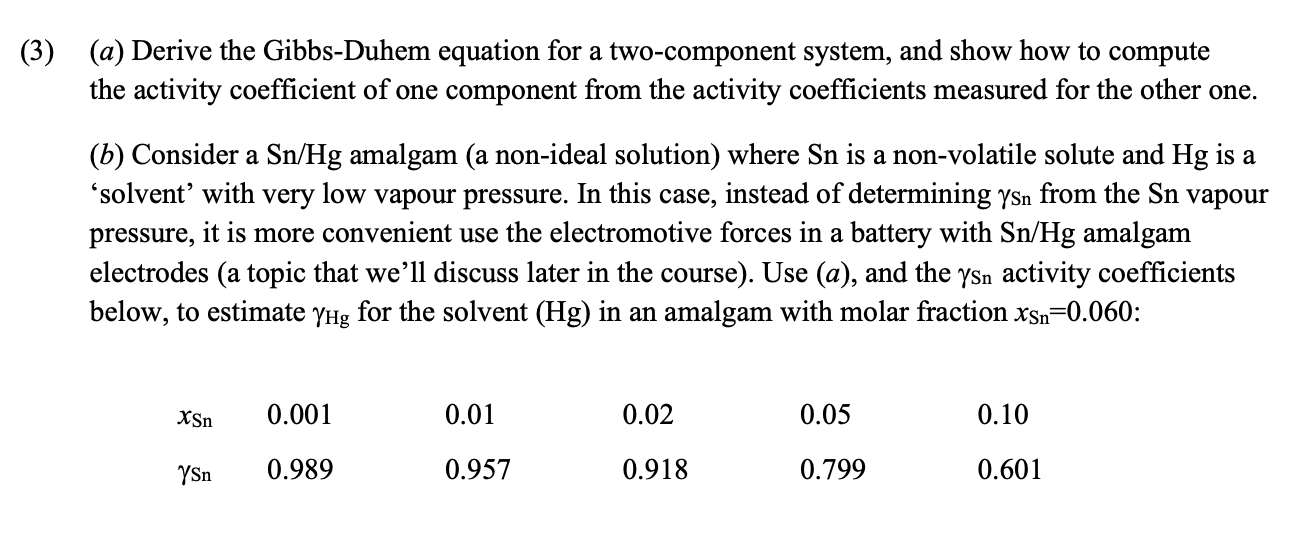
( 3 ) ( a ) Derive the Gibbs - Duhem equation for a two - component system, and show how to compute the activity
a Derive the GibbsDuhem equation for a twocomponent system, and show how to compute
the activity coefficient of one component from the activity coefficients measured for the other one.
b Consider a amalgam a nonideal solution where is a nonvolatile solute and is a
'solvent' with very low vapour pressure. In this case, instead of determining from the vapour
pressure, it is more convenient use the electromotive forces in a battery with amalgam
electrodes a topic that we'll discuss later in the course Use a and the activity coefficients
below, to estimate for the solvent in an amalgam with molar fraction :
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


