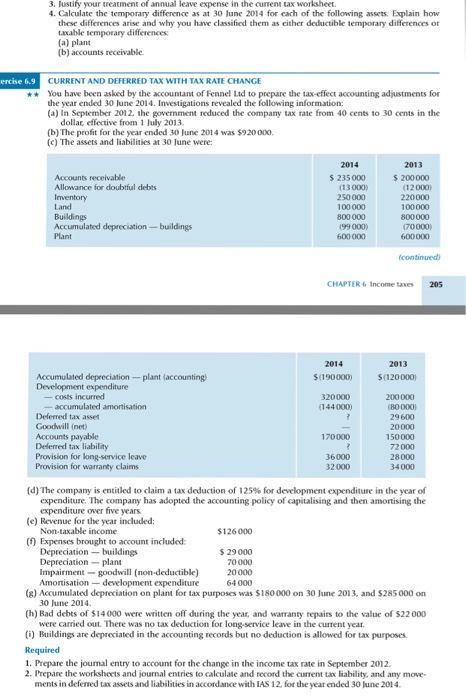
3, Justify your treatment of annual leave expense in the ourment tax worksheet . Calculate the temporary difference as at 30 lune 2014 for cach of the following assets. Explain how these differences arise and why you have classified them as either deductible temporary differences or taxable temporary d (a) plant (b) accounts receivable differences ercise 6.9 CURRENT AND DEFERRED TAX WITH TAX RATE CHANGE You have been asked by the accountant of Fennel Ltd to prepare the tax-effect accounting adjustments for the year ended 30 June 2014. Investigations revealed the following information: (a) In September 2012, the government reduced the company tax rate from 40 cents to 30 cents in the dollar, effective from 1 July 2013 (b) The profit for the year ended 30 June 2014 was $920000 (c) The assets and liabilities at 30 June were 2014 2013 Accounts receivable Allowance for doubtful debts $ 235000 $ 200000 (13 000) 250000 100000 800000 (99 000) 600000 (12 000) 220000 100000 800000 70000) 600000 Land Buildings Plant CHAPTER6 Income tases 205 2014 2013 5(190000 $(120000 costs incurred 320000 (144000) Deferred tax asset Goodwill (net) Accounts payable Deferred tax liability Provision for lkong-service leave Provision for warranty claims 170000 72000 36000 34000 (d) The company is entitled to daim a tax deduction of 125% for development expenditure in the year of expenditure. The company has adopted the accounting policy of capitalising and then amortising the expenditure over five years (e) Revenue for the year included: Non-taxable income (f) Expenses brought to account included Depreciation $ 29000 70000 20000 64 000 Impairment- goodwill (non-deductible) (g) Accumulated depreciation on plant for tax purposes was $180000 on 30 June 2013, and $285 000 on 30 June 2014 (h) Bad debts of $14000 were written off during the year, and warranty repairs to the value of $22 000 were carried out. There was no tax deduction for long-service leave in the current year (i) Buildings are depreciated in the accounting records but no deduction is allowed for tax purposes. Required 1. Prepare the journal entry to account for the change in the income tax rate in September 2012 2. Prepare the worksheets and journal entries to calculate and record the current tax liability, and any move ments in deferned tax assets and liabilities in accordance with IAS 12, for the year ended 30 June 2014. 3, Justify your treatment of annual leave expense in the ourment tax worksheet . Calculate the temporary difference as at 30 lune 2014 for cach of the following assets. Explain how these differences arise and why you have classified them as either deductible temporary differences or taxable temporary d (a) plant (b) accounts receivable differences ercise 6.9 CURRENT AND DEFERRED TAX WITH TAX RATE CHANGE You have been asked by the accountant of Fennel Ltd to prepare the tax-effect accounting adjustments for the year ended 30 June 2014. Investigations revealed the following information: (a) In September 2012, the government reduced the company tax rate from 40 cents to 30 cents in the dollar, effective from 1 July 2013 (b) The profit for the year ended 30 June 2014 was $920000 (c) The assets and liabilities at 30 June were 2014 2013 Accounts receivable Allowance for doubtful debts $ 235000 $ 200000 (13 000) 250000 100000 800000 (99 000) 600000 (12 000) 220000 100000 800000 70000) 600000 Land Buildings Plant CHAPTER6 Income tases 205 2014 2013 5(190000 $(120000 costs incurred 320000 (144000) Deferred tax asset Goodwill (net) Accounts payable Deferred tax liability Provision for lkong-service leave Provision for warranty claims 170000 72000 36000 34000 (d) The company is entitled to daim a tax deduction of 125% for development expenditure in the year of expenditure. The company has adopted the accounting policy of capitalising and then amortising the expenditure over five years (e) Revenue for the year included: Non-taxable income (f) Expenses brought to account included Depreciation $ 29000 70000 20000 64 000 Impairment- goodwill (non-deductible) (g) Accumulated depreciation on plant for tax purposes was $180000 on 30 June 2013, and $285 000 on 30 June 2014 (h) Bad debts of $14000 were written off during the year, and warranty repairs to the value of $22 000 were carried out. There was no tax deduction for long-service leave in the current year (i) Buildings are depreciated in the accounting records but no deduction is allowed for tax purposes. Required 1. Prepare the journal entry to account for the change in the income tax rate in September 2012 2. Prepare the worksheets and journal entries to calculate and record the current tax liability, and any move ments in deferned tax assets and liabilities in accordance with IAS 12, for the year ended 30 June 2014