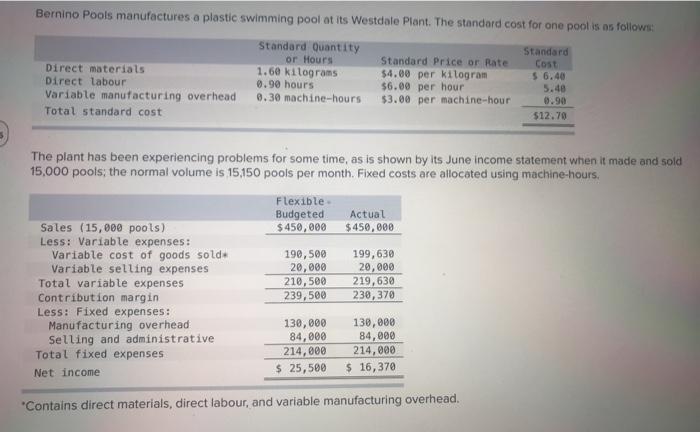
$ 3.0 Shipping expenses The static (i.e., planning) budget for March was based on producing and selling 30,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 34,500 units and incurred the following costs: 15:08 a. Purchased 150,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $9.2 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-labourers worked 62,000 hours at a rate of $17 per hour. c. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was $390,400. And fixed manufacturing overhead was $594,000. d. Total advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses were $279,000, $645,000, and $122,000, respectively. ok Tences Required: What amounts of advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses would be included in the company's flexible budget for March? Preble Company Flexible Budget For the Month Ended March 31 Units sold (9) Expenses Advertising $ Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses 34,500 270,000 170,000 122,000 It is the company's policy to close all variances to cost of goods sold on a monthly basis Required: 1. Compute the following variances for June: a. Direct materials price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Material price variance Material quantity variance b. Direct labour rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e.. zero variance).) Labour rate variance Labour efficiency variance Submit Save & Exit Saved Help b. Direct labour rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (ie.. zero variance)) Labour rate variance Labour efficiency variance c. Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Variable overhead spending variance Variable overhead efficiency variance Bernino Pools manufactures a plastic swimming pool at its Westdale Plant. The standard cost for one pool is as follows: Standard Quantity Standard or Hours Standard Price or Rate Cost Direct materials 1.60 kilograms $4.00 per kilogram 5 6.40 Direct labour 0.90 hours $6.00 per hour 5.40 Variable manufacturing overhead 0.30 machine-hours $3.00 per machine-hour 0.90 Total standard cost $12.70 The plant has been experiencing problems for some time, as is shown by its June income statement when it made and sold 15,000 pools; the normal volume is 15,150 pools per month. Fixed costs are allocated using machine-hours. Flexible Budgeted $450,000 Actual $ 450,000 Sales (15,000 pools) Less: Variable expenses: Variable cost of goods sold Variable selling expenses Total variable expenses Contribution margin Less: Fixed expenses: Manufacturing overhead Selling and administrative Total fixed expenses Net income 190,500 20,000 210,500 239,500 199,630 20,000 219,630 238,370 130,800 84,000 214,000 $ 25,500 130,000 84,000 214,000 $ 16,370 "Contains direct materials, direct labour, and variable manufacturing overhead. $ 3.0 Shipping expenses The static (i.e., planning) budget for March was based on producing and selling 30,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 34,500 units and incurred the following costs: 15:08 a. Purchased 150,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $9.2 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-labourers worked 62,000 hours at a rate of $17 per hour. c. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was $390,400. And fixed manufacturing overhead was $594,000. d. Total advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses were $279,000, $645,000, and $122,000, respectively. ok Tences Required: What amounts of advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses would be included in the company's flexible budget for March? Preble Company Flexible Budget For the Month Ended March 31 Units sold (9) Expenses Advertising $ Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses 34,500 270,000 170,000 122,000 It is the company's policy to close all variances to cost of goods sold on a monthly basis Required: 1. Compute the following variances for June: a. Direct materials price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Material price variance Material quantity variance b. Direct labour rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e.. zero variance).) Labour rate variance Labour efficiency variance Submit Save & Exit Saved Help b. Direct labour rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (ie.. zero variance)) Labour rate variance Labour efficiency variance c. Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Variable overhead spending variance Variable overhead efficiency variance Bernino Pools manufactures a plastic swimming pool at its Westdale Plant. The standard cost for one pool is as follows: Standard Quantity Standard or Hours Standard Price or Rate Cost Direct materials 1.60 kilograms $4.00 per kilogram 5 6.40 Direct labour 0.90 hours $6.00 per hour 5.40 Variable manufacturing overhead 0.30 machine-hours $3.00 per machine-hour 0.90 Total standard cost $12.70 The plant has been experiencing problems for some time, as is shown by its June income statement when it made and sold 15,000 pools; the normal volume is 15,150 pools per month. Fixed costs are allocated using machine-hours. Flexible Budgeted $450,000 Actual $ 450,000 Sales (15,000 pools) Less: Variable expenses: Variable cost of goods sold Variable selling expenses Total variable expenses Contribution margin Less: Fixed expenses: Manufacturing overhead Selling and administrative Total fixed expenses Net income 190,500 20,000 210,500 239,500 199,630 20,000 219,630 238,370 130,800 84,000 214,000 $ 25,500 130,000 84,000 214,000 $ 16,370 "Contains direct materials, direct labour, and variable manufacturing overhead