Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
398 DONNELLAN, GE, AND WENK Results A series of one-way multivariate analyses of variance (MANOVAs) and analyses of variance (ANOVAS) were per- formed on

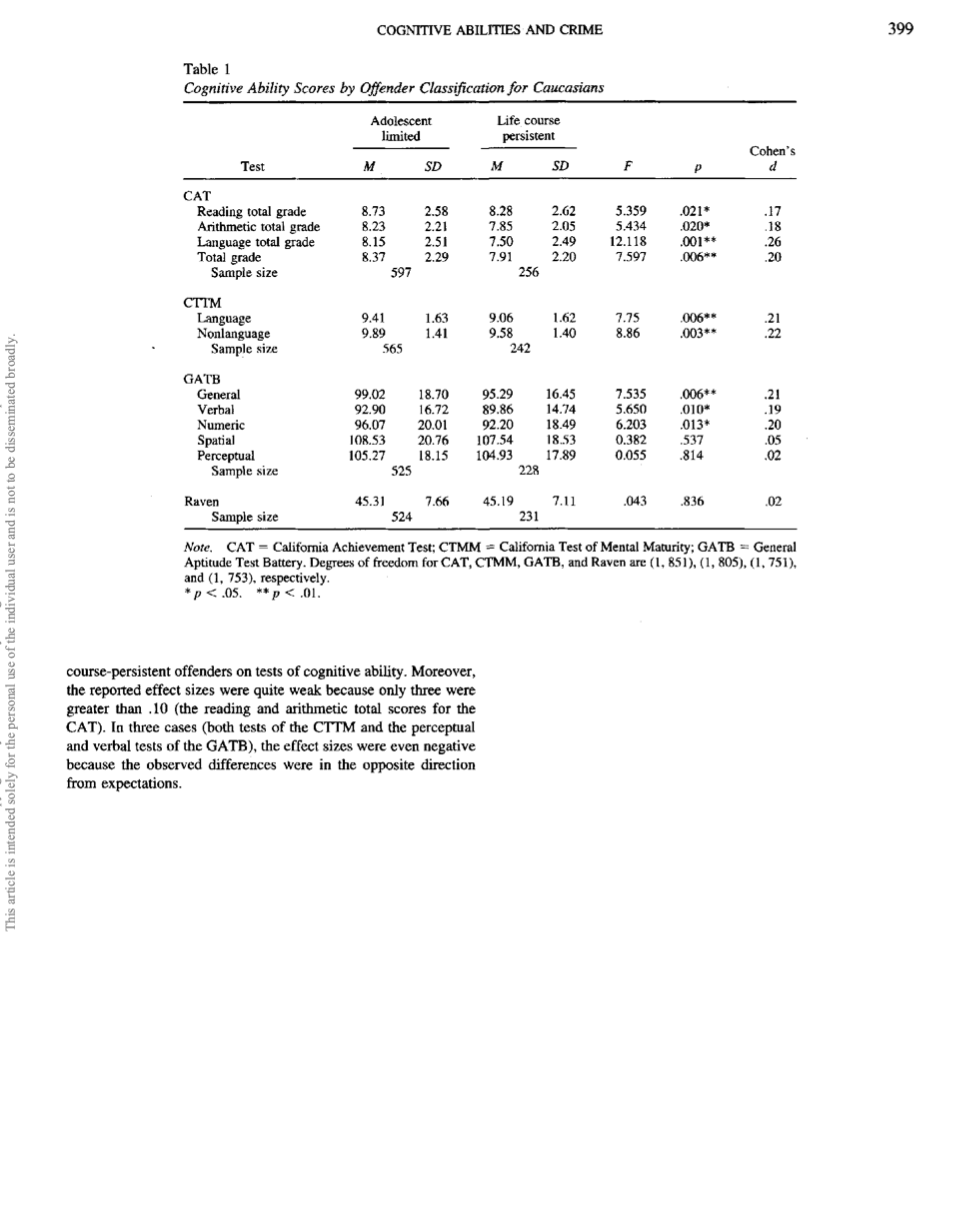
398 DONNELLAN, GE, AND WENK Results A series of one-way multivariate analyses of variance (MANOVAs) and analyses of variance (ANOVAS) were per- formed on the tests of cognitive ability separately for each ethnic group. Conducting separate analyses for each ethnic group has the dual benefits of controlling for the impact of ethnicity on test scores and offering easier interpretations of the results. Within each ethnic group, three separate MANOVAs were run on each test battery of cognitive ability (CAT, CTTM, and GATB), whereas a separate ANOVA was conducted on the Raven test. These separate analyses on the various test batteries were intended to maximize the sample size available for each analysis. Table 1 provides the results of the analyses for Caucasian offenders. The results for Caucasians provide support for Moffitt's (1993a) proposal, as shown in Table 1. In 9 of 12 tests studied, adolescent- limited offenders had significantly higher scores on tests of cog- nitive ability than life-course-persistent offenders. The nonsignif- icant results were found in the spatial and perceptual tests of the GATB and in the Raven test. It is important to note that the observed effect sizes for the significant results were small (d values ranged from .17 to .26) using Cohen's (1988) designations. However, this information should not be surprising because crim- inal careers are an example of a multiply determined behavior and large effect sizes are not to be expected (Ahadi & Diener, 1989). The results for Hispanics are displayed in Table 2. Overall, there was modest support for Moffitt's proposal in the Hispanic sub- sample, because in 6 of the 12 tests of cognitive ability, there were significant differences between offender categories. The nonsig- nificant differences were found for the reading and arithmetic tests of the CAT, both tests of the CTTM, the spatial test of the GATB, and the Raven test. Once again, the observed effect sizes for the significant results were small, according to Cohen's (1988) desig- nations (d values ranged from .22 to .36). In contrast, the results for African Americans offer no support for Moffitt's theory. As shown in Table 3, there were no signifi- cant differences between adolescent-limited offenders and life- This article is intended solely for the personal use of the individual user and is not to be disseminated broadly. Table 1 COGNITIVE ABILITIES AND CRIME Cognitive Ability Scores by Offender Classification for Caucasians Adolescent limited Life course persistent M SD M SD F Cohen's Test d CAT Reading total grade 8.73 2.58 8.28 2.62 5.359 .021* .17 Arithmetic total grade 8.23 2.21 7.85 2.05 5.434 .020* .18 Language total grade 8.15 2.51 7.50 2.49 12.118 .001** .26 Total grade 8.37 2.29 7.91 2.20 7.597 .006** .20 1288 Sample size 597 256 CTTM Language 9.41 1.63 9.06 1.62 7.75 .006** Nonlanguage 9.89 1.41 9.58 1.40 8.86 .003** .22 122 .21 Sample size 565 242 GATB General Verbal 99.02 18.70 95.29 16.45 7.535 .006** .21 92.90 16.72 89.86 14.74 5.650 .010* .19 Numeric 96.07 20.01 92.20 18.49 6.203 .013* .20 Spatial 108.53 20.76 107.54 18.53 0.382 .537 .05 Perceptual 105.27 18.15 104.93 17.89 0.055 .814 .02 Sample size 525 228 Raven 45.31 7.66 45.19 7.11 .043 .836 .02 Sample size Note. CAT 524 231 22288 California Achievement Test; CTMM California Test of Mental Maturity; GATB = General Aptitude Test Battery. Degrees of freedom for CAT, CTMM, GATB, and Raven are (1, 851), (1, 805), (1, 751), and (1, 753), respectively. *p
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


