Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
4. A copper ore grading 0.70% copper (average) is crushed for heap leaching. A sample of the crushed ore (989.2 g) was passed through
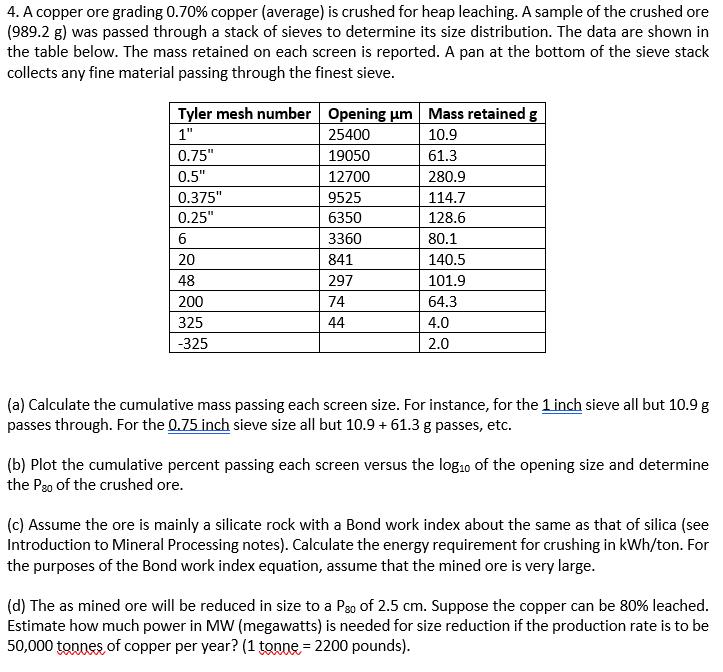
4. A copper ore grading 0.70% copper (average) is crushed for heap leaching. A sample of the crushed ore (989.2 g) was passed through a stack of sieves to determine its size distribution. The data are shown in the table below. The mass retained on each screen is reported. A pan at the bottom of the sieve stack collects any fine material passing through the finest sieve. Tyler mesh number Opening m Mass retained g 1" 25400 10.9 0.75" 19050 61.3 0.5" 12700 280.9 0.375" 9525 114.7 0.25" 6350 128.6 6 3360 80.1 20 841 140.5 48 297 101.9 200 74 64.3 325 44 4.0 -325 2.0 (a) Calculate the cumulative mass passing each screen size. For instance, for the 1 inch sieve all but 10.9 g passes through. For the 0.75 inch sieve size all but 10.9 + 61.3 g passes, etc. (b) Plot the cumulative percent passing each screen versus the log10 of the opening size and determine the P20 of the crushed ore. (c) Assume the ore is mainly a silicate rock with a Bond work index about the same as that of silica (see Introduction to Mineral Processing notes). Calculate the energy requirement for crushing in kWh/ton. For the purposes of the Bond work index equation, assume that the mined ore is very large. (d) The as mined ore will be reduced in size to a Pso of 2.5 cm. Suppose the copper can be 80% leached. Estimate how much power in MW (megawatts) is needed for size reduction if the production rate is to be 50,000 tonnes of copper per year? (1 tonne = 2200 pounds).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


