Question
4. A television network earns an average of $1.6 million (1600k) each season from a hit program and loses an average of $400k each season
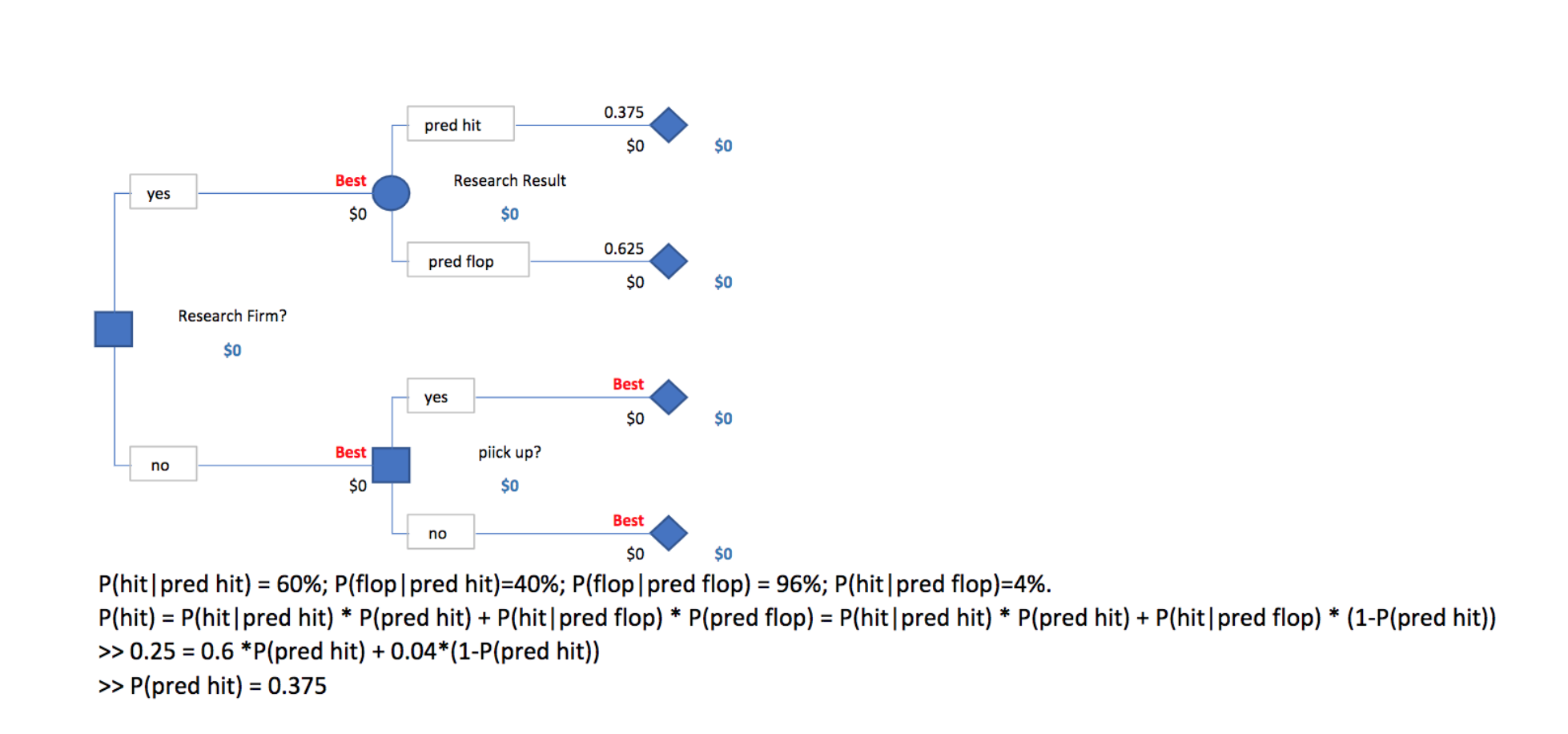
4. A television network earns an average of $1.6 million (1600k) each season from a hit program and loses an average of $400k each season on a program that turns out to be a flop. Of all programs picked up by this network in recent years, 25% turn out to be hits and 75% turn out to be flops. At a cost of $160k dollars, a market research firm will analyze a pilot episode of a prospective program and issue a report predicting whether the given program will end up being a hit. If the market researchers' prediction is a hit, there is 60% chance that the program is actually going to be a hit. If the market researchers' prediction is a flop, then the program is actually going to be a flop with 96% probability. Please note that the television network has the option of not picking the program at all. (a) Draw the decision tree, compute the EMVs of all nodes, and decide the optimal decision. (b) What is the expected value of Sample Information (EVSI)? (c) What is the Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI)?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


