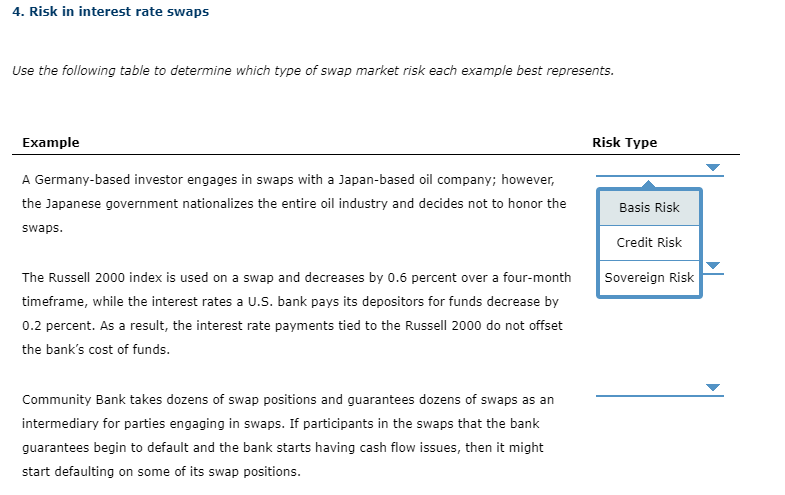


4. Risk in interest rate swaps Use the following table to determine which type of swap market risk each example best represents. Example Risk Type A Germany-based investor engages in swaps with a Japan-based oil company; however, the Japanese government nationalizes the entire oil industry and decides not to honor the Basis Risk swaps. Credit Risk Sovereign Risk The Russell 2000 index is used on a swap and decreases by 0.6 percent over a four-month timeframe, while the interest rates a U.S. bank pays its depositors for funds decrease by 0.2 percent. As a result, the interest rate payments tied to the Russell 2000 do not offset the bank's cost of funds. Community Bank takes dozens of swap positions and guarantees dozens of swaps as an intermediary for parties engaging in swaps. If participants in the swaps that the bank guarantees begin to default and the bank starts having cash flow issues, then it might start defaulting on some of its swap positions. 4. Risk in interest rate swaps Use the following table to determine which type of swap market risk each example best represents. Example Risk Type A Germany-based investor engages in swaps with a Japan-based oil company; however, the Japanese government nationalizes the entire oil industry and decides not to honor the swaps. The Russell 2000 index is used on a swap and decreases by 0.6 percent over a four-month timeframe, while the interest rates a U.S. bank pays its depositors for funds decrease by 0.2 percent. As a result, the interest rate payments tied to the Russell 2000 do not offset the bank's cost of funds. Basis Risk Credit Risk Sovereign Risk Community Bank takes dozens of swap positions and guarantees dozens of swaps as an intermediary for parties engaging in swaps. If participants in the swaps that the bank guarantees begin to default and the bank starts having cash flow issues, then it might start defaulting on some of its swap positions. 4. Risk in interest rate swaps Use the following table to determine which type of swap market risk each example best represents. Example Risk Type A Germany-based investor engages in swaps with a Japan-based oil company; however, the Japanese government nationalizes the entire oil industry and decides not to honor the swaps. Basis Risk The Russell 2000 index is used on a swap and decreases by 0.6 percent over a four-month timeframe, while the interest rates a U.S. bank pays its depositors for funds decrease by 0.2 percent. As a result, the interest rate payments tied to the Russell 2000 do not offset the bank's cost of funds. Credit Risk Sovereign Risk Community Bank takes dozens of swap positions and guarantees dozens of swaps as an intermediary for parties engaging in swaps. If participants in the swaps that the bank guarantees begin to default and the bank starts having cash flow issues, then it might start defaulting on some of its swap positions









