41Macroeconomics,,
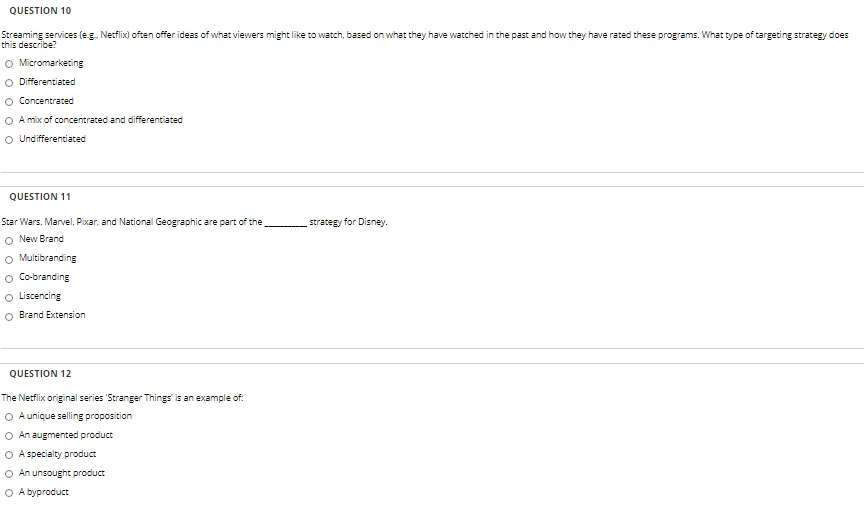
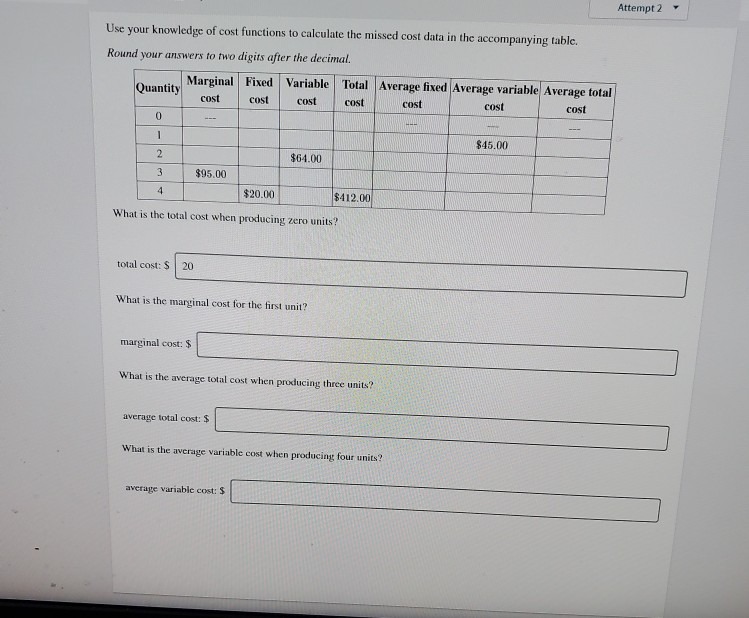
QUESTION 10 Streaming services (e g. Netflix) often offer ideas of what viewers might like to watch, based on what they have watched in the past and how they have rated these programs. What type of targeting strategy does this describe? O Micromarketing O Differentiated O Concentrated O A mix of concentrated and differentiated O Undifferentiated QUESTION 11 Star Wars, Marvel, Pixar, and National Geographic are part of the strategy for Disney. O New Brand Multibranding O Co-branding Liscencing O Brand Extension QUESTION 12 The Netflix original series 'Stranger Things' is an example of: O A unique selling proposition O An augmented product O A specialty product O An unsought product O A byproduct3. Consider a Solow economy that is on its balanced growth path (at the steady state.) Assume for simplicity that there is no technological progress. Now suppose that the rate of technological growth increases. (a) What happens to the balanced-growth-path values of capital per worker, output per worker, and consumption per worker? Sketch the paths of these variables over time as the economy moves to its new balanced growth path. (b) Describe the effect of the increase in savings rate on the path of total output over time.3. Consider a Solow economy that is on its balanced growth path (at the steady state.) Assume for simplicity that there is no technological progress. Now suppose that the rate of technological growth increases. (a) What happens to the balanced-growth-path values of capital per worker, output per worker, and consumption per worker? Sketch the paths of these variables over time as the economy moves to its new balanced growth path. (b) Describe the effect of the increase in savings rate on the path of total output over time.6. Based on your understanding of Solow growth model, graphically illustrate and the following questions. Assume that no technological progress and no population growth exist. a. What is steady-state? Because of an increase in acid rain, the rate of capital depreciation rises permanently. Given the saving rate, what are the effects on steady state capital per worker and output per worker? b. What is convergence? What prediction does the Solow growth model make about convergence? What does the empirical evidence say? Suppose every economy is in its steady state, then how could you explain the observed differences in per capita output among countries with the Solow model?6. Based on your understanding of Solow growth model, graphically illustrate and the following questions. Assume that no technological progress and no population growth exist. a. What is steady-state? Because of an increase in acid rain, the rate of capital depreciation rises permanently. Given the saving rate, what are the effects on steady state capital per worker and output per worker? b. What is convergence? What prediction does the Solow growth model make about convergence? What does the empirical evidence say? Suppose every economy is in its steady state, then how could you explain the observed differences in per capita output among countries with the Solow model?Friday 2 primake HANDOUT LAD EXERCISE TO FOLLOW LAB EXERCISE $ IN LAB BOOK 1-14 Translation is the next step in protein synthesis. Apply the principle of complimentarity to fill in the appropriate anti-codons for the IRNA molecules. Use the MRNA decoding chart from your text book (p. 118) to find the appropriate amino acid that each mRNA codon codes for. MRNA IRNA FULL NAME of N Bases N Bases Amino Acid - DEC 111 111 141 Translation takes place in this region of the cell Complete the following: During translation, the mRNA polynucleotide contributes a t tof a coding gene of a DNA molecule. Every anticodon on a tRNA polynucleotide transfers a specific from the cytoplasm of the cell to a e of the cell. (#) In real life, protein molecules are normally 1000 or more amino acids long. How many nitrogen base triplets would be required to code for a protein that contains 1000 amino acids?Attempt 2 - Use your knowledge of cost functions to calculate the missed cost data in the accompanying table. Round your answers to two digits after the decimal. Marginal Fixed Variable Quantity Total Average fixed Average variable Average total cost COST cost cost cost cost cost 0 $45.00 2 $64.00 $95.00 4 $20.00 B412.00 What is the total cost when producing zero units? total cost: $ 20 What is the marginal cost for the first unit? marginal cost: $ What is the average total cost when producing three units? average total cost: $ What is the average variable cost when producing four units? average variable cost: $