Question
5. Fiscal policy, the money market, and aggregate demand Consider a hypothetical economy in which households spend $0.50 of each additional dollar they earn and
5. Fiscal policy, the money market, and aggregate demand
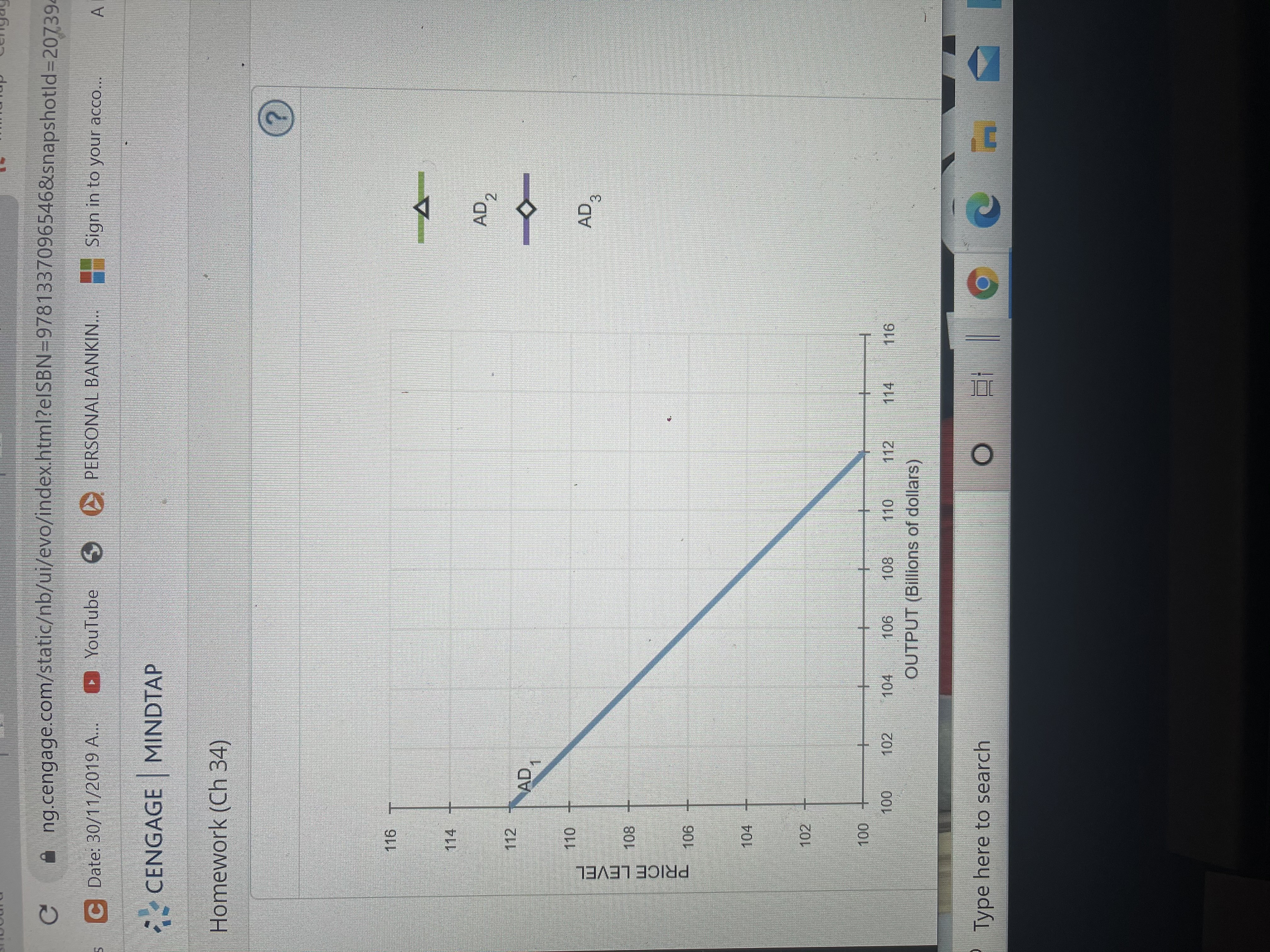
Consider a hypothetical economy in which households spend $0.50 of each additional dollar they earn and save the remaining $0.50. The following graph shows the economy's initial aggregate demand curve (AD
1
AD1).
Suppose the government increases its purchases by $3.5 billion.
Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the following graph to show the aggregate demand curve (AD
2
AD2) after the multiplier effect takes place.
Hint: Be sure the new aggregate demand curve (AD
2
AD2) is parallel toAD
1
AD1. You can see the slope ofAD
1
AD1by selecting it on the following graph.
AD
2
AD
3
100
102
104
106
108
110
112
114
116
116
114
112
110
108
106
104
102
100
PRICE LEVEL
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
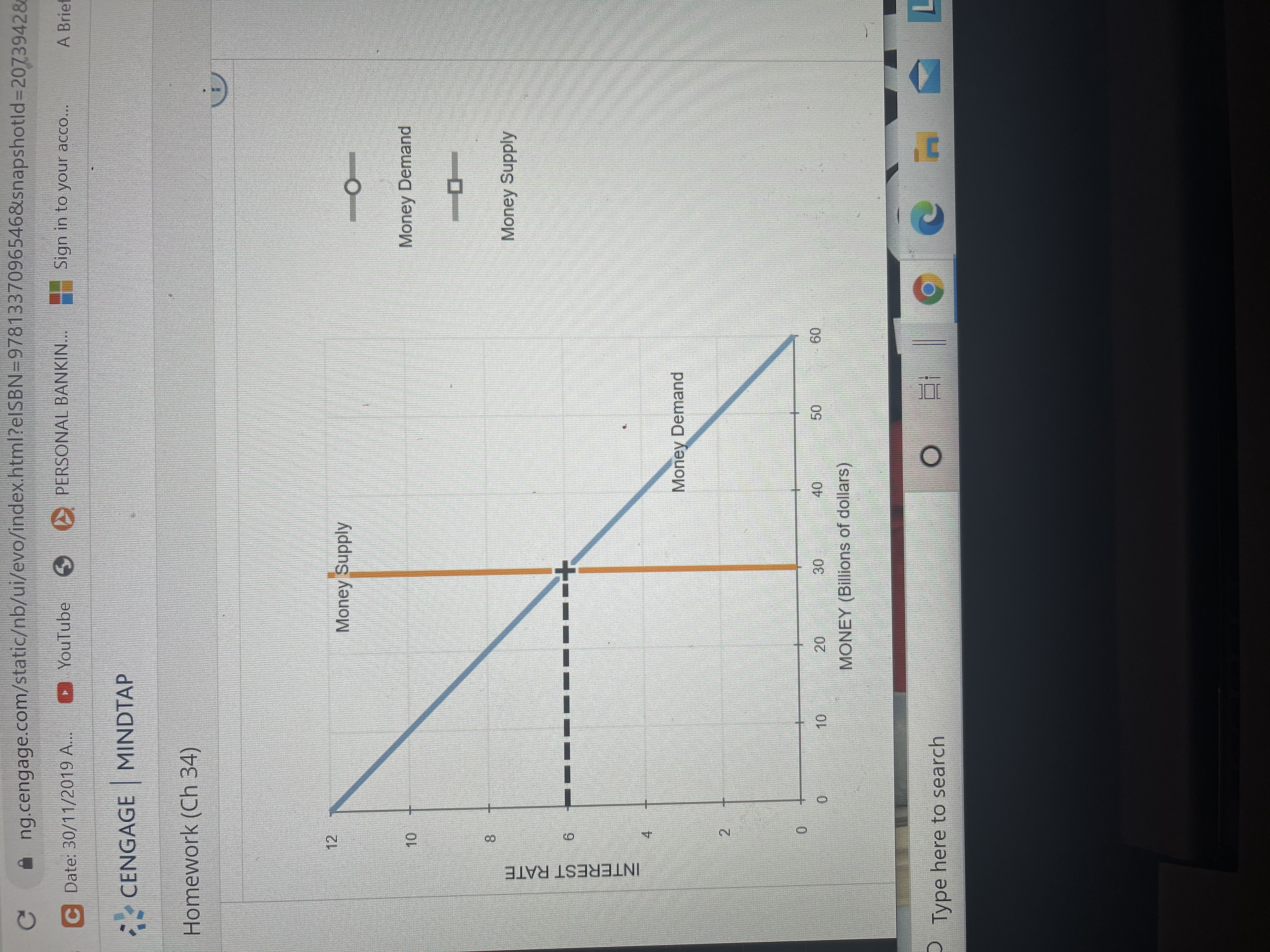
The following graph shows the money market in equilibrium at an interest rate of 6% and a quantity of money equal to $30 billion.
Show the impact of the increase in government purchases on the interest rate by shifting one or both of the curves on the following graph.
Suppose that for each one-percentage-point increase in the interest rate, the level of investment spendingdeclinesby $0.5 billion. The change in the interest rate (according to the change you made to the money market in the previous scenario) therefore causes the level of investment spending to by .
After the multiplier effect is accounted for, the change in investment spending will cause the quantity of output demanded to by at each price level. The impact of an increase in government purchases on the interest rate and the level of investment spending is known as the effect.
Use the purple line (diamond symbol) on the graph at the beginning of this problem to show the aggregate demand curve (AD
3
AD3) after accounting for the impact of the increase in government purchases on the interest rate and the level of investment spending.
Hint: Be sure your final aggregate demand curve (AD
3
AD3) is parallel toAD
1
AD1andAD
2
AD2. You can see the slopes ofAD
1
AD1andAD
2
AD2by selecting them on the graph.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


