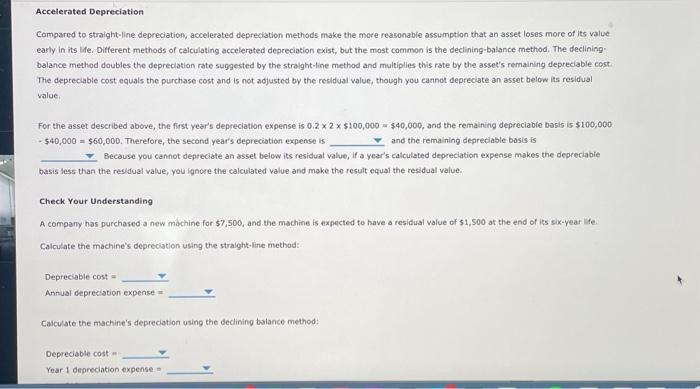
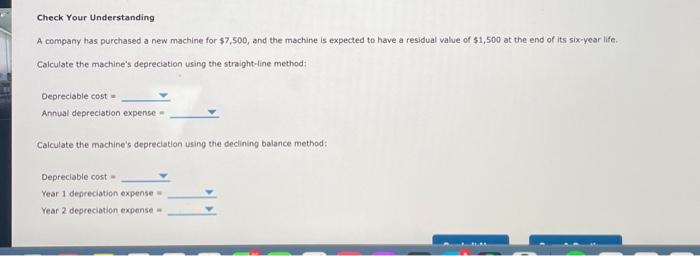
6. Depreciation methods Firms can use various methods to calculate depreciation, and it is important for you to consider these different methods when evaluating firms, The impact of different depreciation methods is stronger for asset-intensive firms. Major factors that affect the depreciation of a fored asset include the purchase cost, residual/salvage value, and estimated useful life of the asset. The purchase cost includes the astet's explicit cost plus necessary costs associated with setting up and operabing the asset (such as shipping and installation). An asset's useful ife is the benefit or amount of use the purchaser expects out of it. The residual, or salvage, value is the anticipated value of the asset at the end of its usefulte. An aswet's depreciable cost is its purchase cost minus its residual value. This figure is the amount of depreciation to be aliocated over the asset's life. and after each year, the asset'if depreciable basis declines. The useful life can be defined in several ways. In some cases, it is the length of time (in years) the asset is expected to last; in others, it could be the use received (in units produced, miles driven, hours operated, etc.). Straight-Line Depreciation Straight-line depreciation is the simplest depreciation method because it assumes assets lose value evenly throughout their lives. The annual depreciation rate is 100% divided by the useful life; for example, a five-year useful life asset has an annual depreciation rate of Iov\%h/5 in 20%. The annual depreciation expense is the depreciation rate times the depreciable cost. A five-year asset purchased for $100,000 with an expected residual value of $10,000 has an annual depreciation expense of 0,2 ( $100,000 $10,000)= After each year, the depreciation expense reduces the depreciable basis (for example, after the first year, the depreciable basis is Accelerated Depreciation Compared to straight-line depreciation, accelerated depreciation methods make the more reasonable assumption that an asset loses more of its value eatly in its life. Different methads of calculating accelerated depreciation exist, but the most common is the declining-batance method The decining. Compared to straight-line depreciation, accelerated depreciation methods make the more reasonabie assumption that an asset loses more of its value easly in its lfe. Different methods of calculating accelerated depreciation exist, but the mast common is the declining-balance method. The decliningbalance method doubles the depreciation rate suggested by the straight-line method and multiplies this rate by the asset's remaining depreciable cost. The depreciable cost equals the purchase cost and is not adjusted by the residual value, though you cannot depreclate an asset below its residual value. For the asset described above, the first year's depreciation expense is 0.22$100,000=$40,000, and the remaining depreciable basis is $100,000 540,000=$60,000. Therefore, the second year's depreciation expense is and the remaining depreciable basis is Because you cannot depreciate an asset below its residuat value, if a year's calculated depreciation expense makes the depreciabie basis less than the residual value, you ignore the calculated value and make the result equal the residual value. Check Your Understanding A compamy has purchased a new machine for $7,500, and the machine is expected to have a residual value of $1,500 at the end of its six-year life. Calculate the machine's depreciation using the straight-line method: Depreciable cost = Annual deprecistion expense = Calculate the machine's depreciation using the declining balance method: Depreciable cost = Year 1 depreciation expense = Check Your Understanding A company has purchased a new machine for $7,500, and the machine is expected to have a residual value of $1,500 at the end of its six-year life. Calculate the machine's depreciation using the straight-line method: Depreciable cost = Annual depreciation expense - Calculate the machine's depreciation using the declining balance method: Depreciable cost = Year 1 depreciation expense = Year 2 depreciation expense =