Question
61. Consolidation subsequent to date of acquisition-Equity method with noncontrolling interest, AAP, and gain on downstream intercompany equipment sale (Note: The facts in Problems 61
61. Consolidation subsequent to date of acquisition-Equity method with noncontrolling interest, AAP, and gain on downstream intercompany equipment sale (Note: The facts in Problems 61 and 62 are identical, except for the direction of the intercompany sale of equipment.) A parent company acquired its 70% interest in its subsidiary on January 1, 2014. On the acquisition date, the total fair value of the controlling interest and the noncontrolling interest was $455,000 in excess of the book value of the subsidiary's Stockholders' Equity. All of that excess was allocated to a Royalty Agreement, which had a zero book value in the subsidiary's financial statements (i.e., there is no Goodwill). The Royalty Agreement has a 7 year estimated remaining economic life on the acquisition date. Both companies use straight line amortization, with no terminal value.
In January 2017, the parent sold Equipment to the subsidiary for a cash price of $325,000. The parent acquired the equipment at a cost of $624,000 and depreciated the equipment over its 10-year useful life using the straight-line method (no salvage value). The parent had depreciated the equipment for 6 years at the time of sale. The subsidiary retained the depreciation policy of the parent and depreciated the equipment over its remaining 4 year useful life. Following are pre-consolidation financial statements of the parent and its subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2019. The parent uses the equity method to account for its Equity Investment.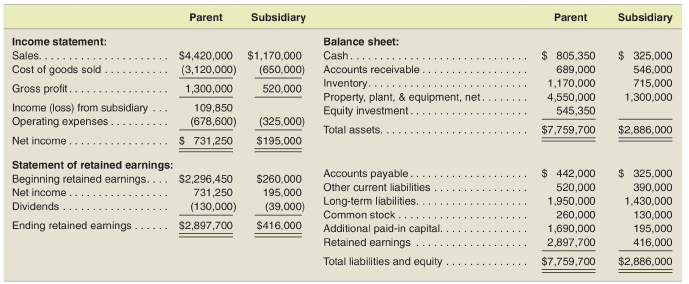
a. Disaggregate and document the activity for the 100% Acquisition Accounting Premium (AAP), the controlling interest AAP and the noncontrolling interest AAP. b. Calculate and organize the profits and losses on intercompany transactions and balances. c. Compute the pre-consolidation Equity Investment account beginning and ending balances starting with the stockholders' equity of the subsidiary. d. Reconstruct the activity in the parent's pre-consolidation Equity Investment T-account for the year of consolidation. e. Independently compute the owners' equity attributable to the noncontrolling interest beginning and ending balances starting with the owners' equity of the subsidiary. f. Independently calculate consolidated net income, controlling interest net income and noncontrolling interest net income. g. Complete the consolidating entries according to the C-E-A-D-1 sequence and complete the consolidation worksheet.
Parent Subsidiary Parent Subsidiary Balance sheet: Cash.... Income statement: Sales. $4,420,000 $1,170,000 Cost of goods sold (3,120,000) (650,000) Gross profit.. 1,300,000 520,000 Income (loss) from subsidiary 109,850 Operating expenses. (678,600) (325,000) Net income.. $ 731,250 $195,000 Statement of retained earnings: Beginning retained earnings... $2,296,450 $260,000 Net income 731,250 195,000 Dividends... (130,000) (39,000) Ending retained earnings $2,897,700 $416,000 Accounts receivable Inventory. Property, plant, & equipment, net. Equity investment. Total assets. $ 805,350 689,000 1,170,000 4,550,000 545,350 $7,759,700 $ 325,000 546,000 715,000 1,300,000 $2,886,000 Accounts payable Other current liabilities Long-term liabilities Common stock Additional paid-in capital. Retained earnings. Total liabilities and equity $ 442,000 520,000 1,950,000 260,000 1,690,000 2,897,700 $7,759,700 $ 325,000 390,000 1,430,000 130,000 195,000 416,000 $2,886,000 Parent Subsidiary Parent Subsidiary Balance sheet: Cash.... Income statement: Sales. $4,420,000 $1,170,000 Cost of goods sold (3,120,000) (650,000) Gross profit.. 1,300,000 520,000 Income (loss) from subsidiary 109,850 Operating expenses. (678,600) (325,000) Net income.. $ 731,250 $195,000 Statement of retained earnings: Beginning retained earnings... $2,296,450 $260,000 Net income 731,250 195,000 Dividends... (130,000) (39,000) Ending retained earnings $2,897,700 $416,000 Accounts receivable Inventory. Property, plant, & equipment, net. Equity investment. Total assets. $ 805,350 689,000 1,170,000 4,550,000 545,350 $7,759,700 $ 325,000 546,000 715,000 1,300,000 $2,886,000 Accounts payable Other current liabilities Long-term liabilities Common stock Additional paid-in capital. Retained earnings. Total liabilities and equity $ 442,000 520,000 1,950,000 260,000 1,690,000 2,897,700 $7,759,700 $ 325,000 390,000 1,430,000 130,000 195,000 416,000 $2,886,000Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


