Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
6-Assume that a Parent company acquires a 60% interest in its Subsidiary on January 1, 2020. On the date of acquisition, the fair value of

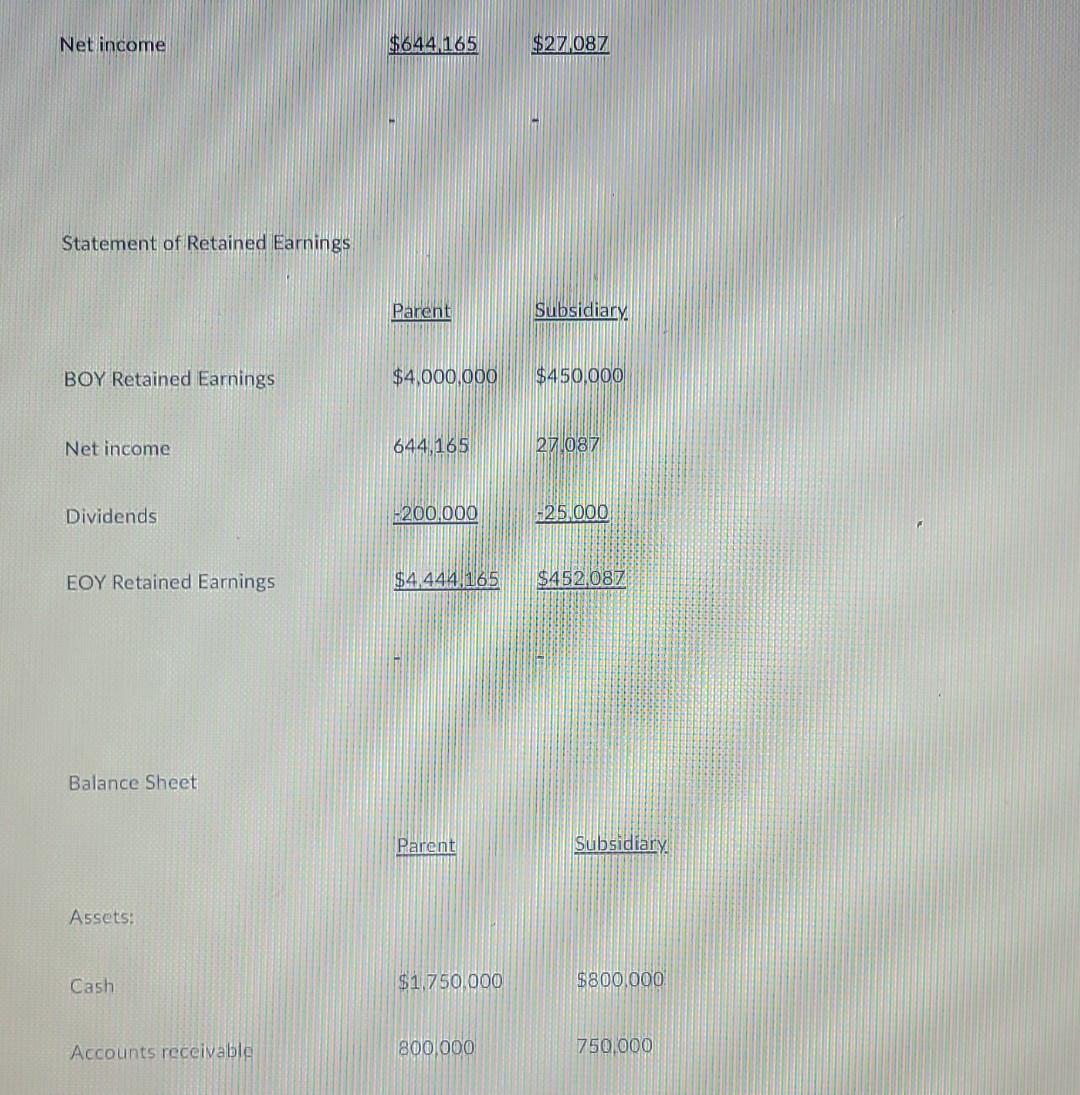
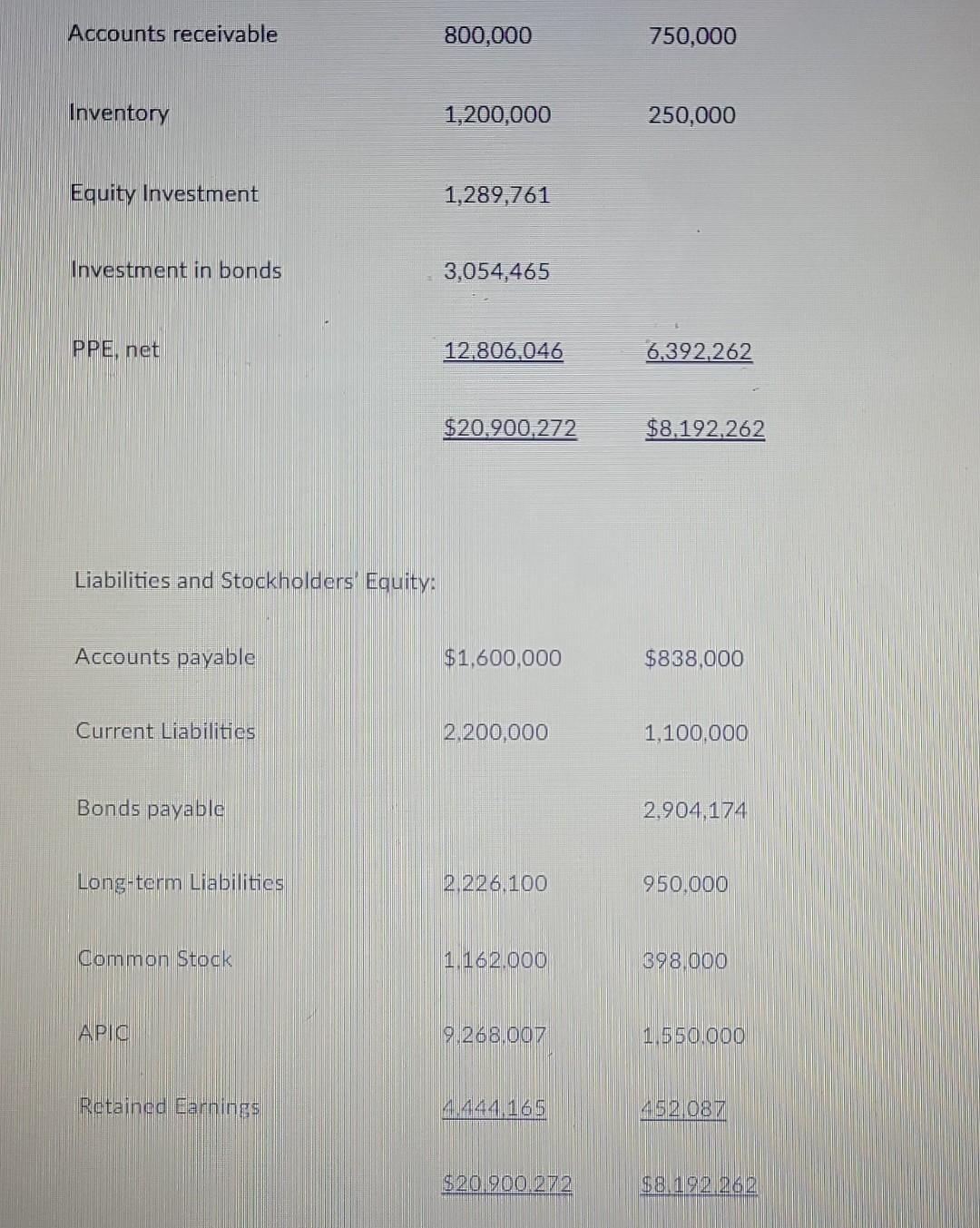
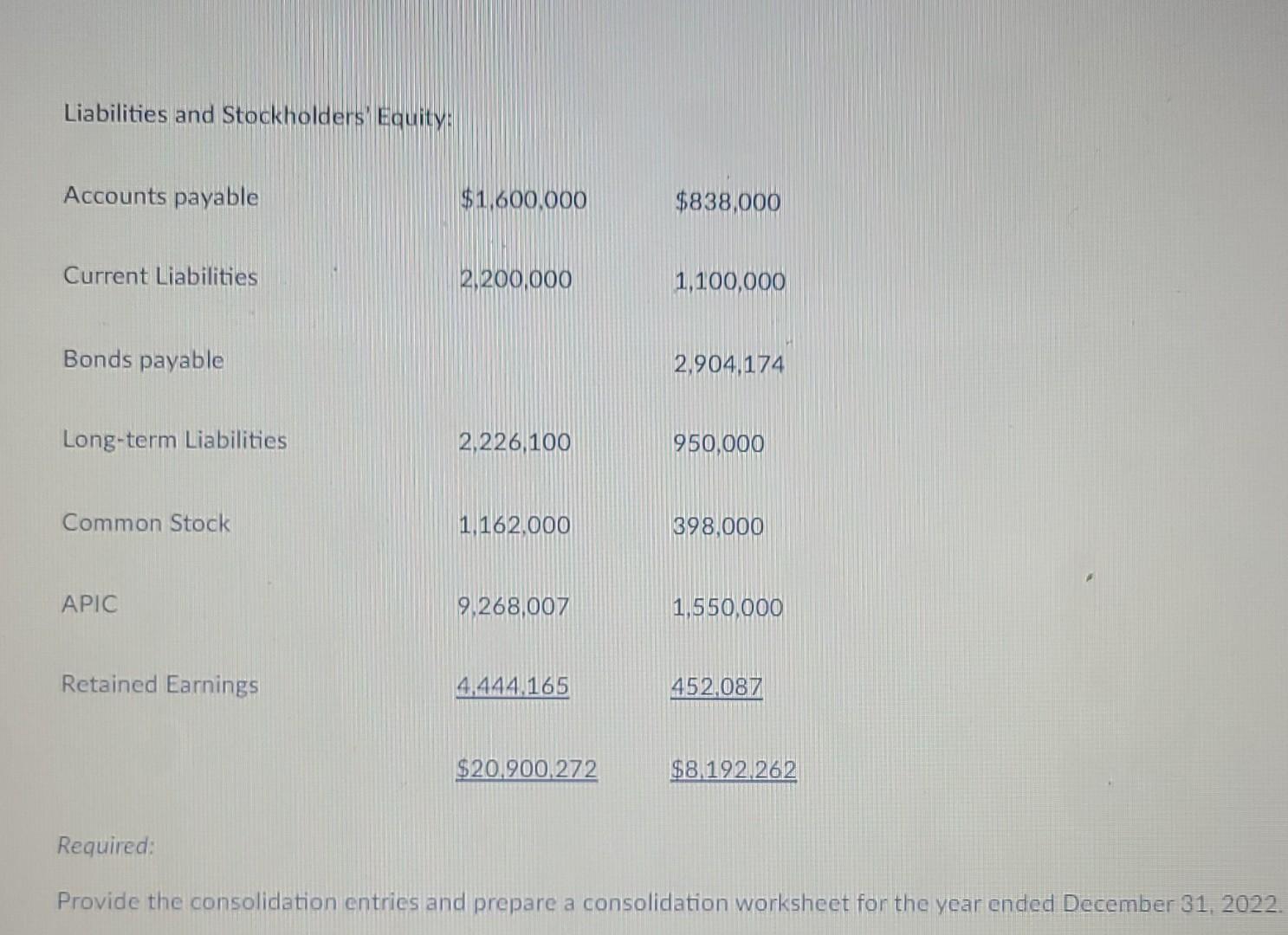
6-Assume that a Parent company acquires a 60% interest in its Subsidiary on January 1, 2020. On the date of acquisition, the fair value of the 60% controlling interest was $1,440,000 and the fair value of the 40% noncontrolling interest was $960,000. On January 1, 2020, the book value of net assets equaled $2,400,000 and the fair value of the identifiable net assets equaled the book value of identifiable net assets (i.e. there was no AAP or Goodwill). The parent uses the equity method to account for its investment in the subsidiary. On December 31, 2021, the Subsidiary company issued $3,000,000 (face) 5 percent, five-year bonds to an unaffiliated company for $2,760,436. The bonds pay interest annually on December 31, and the bond discount is amortized using the straight-line method. This results in annual bond-payable discount amortization equal to $47,913 per year. On December 31, 2023, the Parent paid $3,081,698 to purchase all of the outstanding Subsidiary company bonds. The bond premium is amortized using the straight-line method, which results in annual bond-investment premium amortization equal to $27,233 per year. The Parent and the Subsidiary report the following financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2024: Income Statement Parent Subsidiary. Sales $1,100,000 $800,000 -440,000 -450.000 Cost of goods sold Gross Profit 660,000 350,000 Income (loss) from subsidiary 91,398 Bond interest income 122.767 -197.913 Bond interest expense -230.000 -125.000 Operating expenses Net income $644,165 $27 087 Statement of Retained Earnings Parent Subsidiary BOY Retained Earnings $4,000,000 $450,000 Net income 644,165 271087 Dividends 200.000 -25,000 EOY Retained Earnings $4,444.165 $452.087 Balance Sheet Parent Subsidiary Assets: Cash $1,750,000 $800.000 Accounts receivable 800,000 750,000 Accounts receivable 800,000 750,000 Inventory 1,200,000 250,000 Equity Investment 1,289,761 Investment in bonds 3,054,465 PPE, net 12.806,046 6,392,262 $20.900,272 $8.192.262 Liabilities and Stockholders Equity: Accounts payable $1,600,000 $838,000 Current Liabilities 2.200,000 1,100,000 Bonds payable 2,904,174 Long-term Liabilities 2. 2 26.100 950.000 Common Stock 1.162.000 398.000 APIG 9.268.007 1.550.000 Retained Earnings 44144.165 452 087 $20.900/2712 $8.192.262 Liabilities and Stockholders Equity: Accounts payable $1,600,000 $838,000 Current Liabilities 2,200,000 1,100,000 Bonds payable 2,904,174 Long-term Liabilities 2,226,100 950,000 Common Stock 1,162,000 398,000 APIC 9,268,007 1,550,000 Retained Earnings 4.444.165 452,087 $20.900,272 $8.192.262 Required: Provide the consolidation entries and prepare a consolidation worksheet for the year ended December 31, 2022
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


