Question: 7. [-/11 Points] DETAILS PRIVITERASTATS2 12.E.025. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER Iconic memory is a type of memory that holds visual information for
![7. [-/11 Points] DETAILS PRIVITERASTATS2 12.E.025. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/09/66e126fd02211_61266e126fc56a17.jpg)
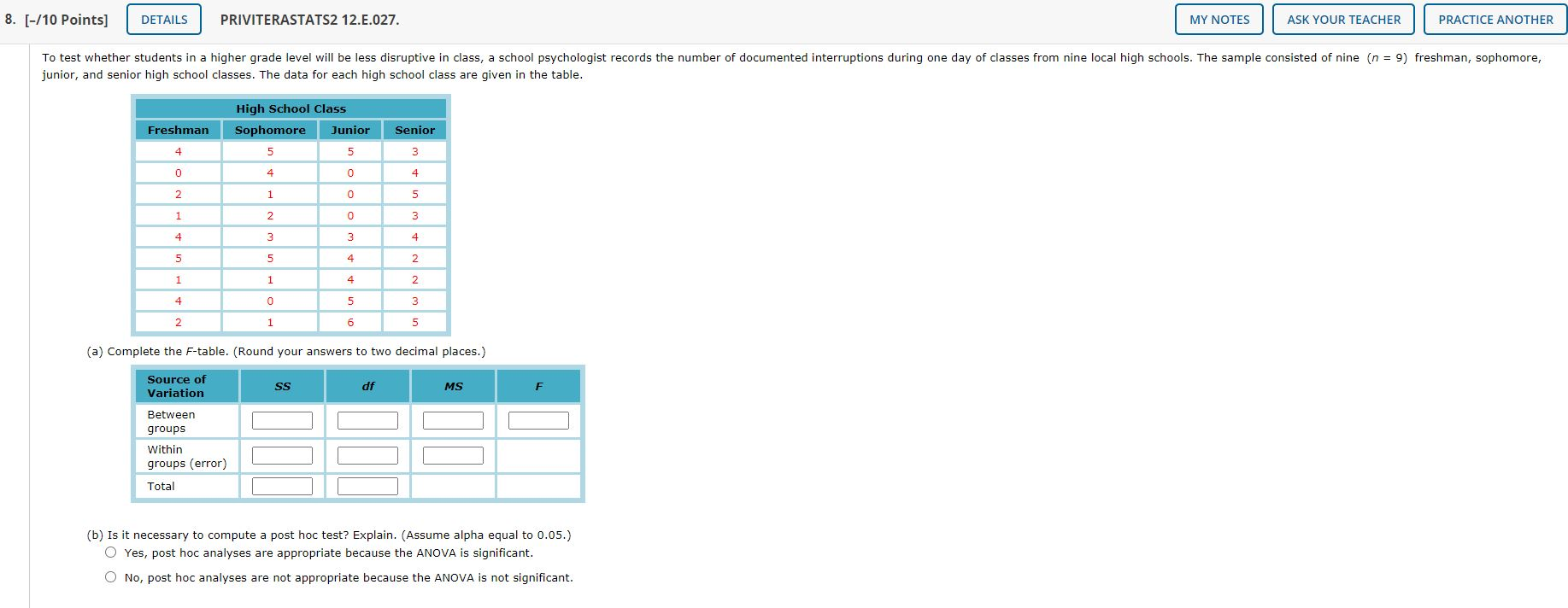
7. [-/11 Points] DETAILS PRIVITERASTATS2 12.E.025. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER Iconic memory is a type of memory that holds visual information for about half a second (0.5 seconds). To demonstrate this type of memory, participants were shown three rows of four letters for 50 milliseconds. They were then asked to recall as many letters as possible, with a 0-, 0.5-, or 1.0-second delay before responding. Researchers hypothesized that longer delays would result in poorer recall. The number of letters correctly recalled is given in the table. Delay Before Recall 0 0.5 1 10 9 4 5 8 5 6 3 1 7 6 8 11 5 9 5 2 (a) Complete the F-table. (Round your values for MS and F to two decimal places.) Source of Variation SS df MS F Between groups Within groups (error) Total (b) Compute Tukey's HSD post hoc test and interpret the results. (Assume alpha equal to 0.05. Round your answer to two decimal places.) The critical value is for each pairwise comparison. Which of the comparisons had significant differences? (Select all that apply.) The null hypothesis of no difference should be retained because none of the pairwise comparisons demonstrate a significant difference. Recall following no delay was significantly different from recall following a one second delay. Recall following a half second delay was significantly different from recall following a one second delay. Recall following no delay was significantly different from recall following a half second delay. 8. [-/10 Points] DETAILS PRIVITERASTATS2 12.E.027. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER To test whether students in a higher grade level will be less disruptive in class, a school psychologist records the number of documented interruptions during one day of classes from nine local high schools. The sample consisted of nine (n = 9) freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior high school classes. The data for each high school class are given in the table. Freshman High School Class Sophomore Junior 5 5 Senior 4 3 0 4 0 4 2 1 0 5 1 2 0 3 4 3 3 4 5 5 4 2 1 1 4 2 4 0 5 6 3 5 2 1 (a) Complete the F-table. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) SS df MS F Source of Variation Between groups Within groups (error) Total (b) Is it necessary to compute a post hoc test? Explain. (Assume alpha equal to 0.05.) Yes, post hoc analyses are appropriate because the ANOVA is significant. No, post hoc analyses are not appropriate because the ANOVA is not significant. 7. [-/11 Points] DETAILS PRIVITERASTATS2 12.E.025. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER Iconic memory is a type of memory that holds visual information for about half a second (0.5 seconds). To demonstrate this type of memory, participants were shown three rows of four letters for 50 milliseconds. They were then asked to recall as many letters as possible, with a 0-, 0.5-, or 1.0-second delay before responding. Researchers hypothesized that longer delays would result in poorer recall. The number of letters correctly recalled is given in the table. Delay Before Recall 0 0.5 1 10 9 4 5 8 5 6 3 1 7 6 8 11 5 9 5 2 (a) Complete the F-table. (Round your values for MS and F to two decimal places.) Source of Variation SS df MS F Between groups Within groups (error) Total (b) Compute Tukey's HSD post hoc test and interpret the results. (Assume alpha equal to 0.05. Round your answer to two decimal places.) The critical value is for each pairwise comparison. Which of the comparisons had significant differences? (Select all that apply.) The null hypothesis of no difference should be retained because none of the pairwise comparisons demonstrate a significant difference. Recall following no delay was significantly different from recall following a one second delay. Recall following a half second delay was significantly different from recall following a one second delay. Recall following no delay was significantly different from recall following a half second delay. 8. [-/10 Points] DETAILS PRIVITERASTATS2 12.E.027. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER To test whether students in a higher grade level will be less disruptive in class, a school psychologist records the number of documented interruptions during one day of classes from nine local high schools. The sample consisted of nine (n = 9) freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior high school classes. The data for each high school class are given in the table. Freshman High School Class Sophomore Junior 5 5 Senior 4 3 0 4 0 4 2 1 0 5 1 2 0 3 4 3 3 4 5 5 4 2 1 1 4 2 4 0 5 6 3 5 2 1 (a) Complete the F-table. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) SS df MS F Source of Variation Between groups Within groups (error) Total (b) Is it necessary to compute a post hoc test? Explain. (Assume alpha equal to 0.05.) Yes, post hoc analyses are appropriate because the ANOVA is significant. No, post hoc analyses are not appropriate because the ANOVA is not significant
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


