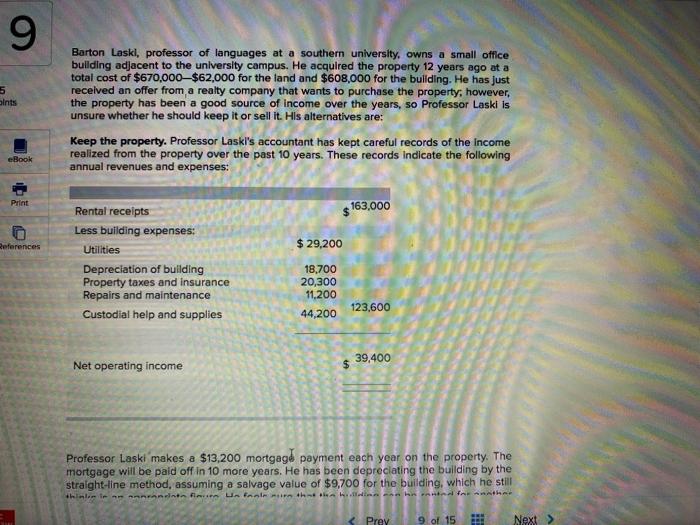
9 5 Sints Barton Laskl, professor of languages at a southern university, owns a small office building adjacent to the university campus. He acquired the property 12 years ago at a total cost of $670,000-$62,000 for the land and $608,000 for the building. He has just received an offer from a realty company that wants to purchase the property, however, the property has been a good source of income over the years, so Professor Laski is unsure whether he should keep it or sell it. His alternatives are: Keep the property. Professor Laski's accountant has kept careful records of the income realized from the property over the past 10 years. These records indicate the following annual revenues and expenses: eBook Print 163,000 References $ 29,200 Rental receipts Less building expenses: Utilities Depreciation of building Property taxes and insurance Repairs and maintenance Custodial help and supplies 18,700 20,300 11.200 44,200 123,600 39,400 Net operating income $ Professor Laski makes a $13,200 mortgage payment each year on the property. The mortgage will be paid off in 10 more years. He has been depreciating the building by the straight-line method, assuming a salvage value of $9,700 for the building, which he still him inte finns inte in the Prey 9 of 15 Next > 1.2: Ch 14 Assignment Seved 9 7.5 points eBook Professor Laski makes a $13,200 mortgage payment each year on the property. The mortgage will be paid off in 10 more years. He has been depreciating the building by the straight-line method, assuming a salvage value of $9,700 for the building, which he still thinks is an appropriate figure. He feels sure that the building can be rented for another 16 years. He also feels sure that 16 years from now the land will be worth 2.10 times what he paid for it. Sell the property. A realty company has offered to purchase the property by paying $200,000 Immediately and $21,000 per year for the next 16 years. Control of the property would go to the realty company Immediately. To sell the property, Professor Laski would need to pay the mortgage off, which could be done by making a lump-sum payment of $82,000. Professor Laski requires a 12% rate of return. (Ignore income taxes.) Click here to view Exhibit 148-1 and Exhibit 14B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Print References Required: a. Calculate the net present value of cash flows using total cost approach If he keeps the property. (Use the appropriate table to determine the discount factor(s) and round final answers to the nearest dollar amount.) Net present value b. Calculate the net present value of cash flows using total cost approach If he sells the property. (Use the appropriate table to determine the discount factor(s) and round 9 payment UI 202,wVU, RIVIESSUT LOSS 140 1QVUI TELITI. Vylu retakes.) Click here to view Exhibit 14B-1 and Exhibit 14B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables. Required: a. Calculate the net present value of cash flows using total cost approach if he keeps the property. (Use the appropriate table to determine the discount factor(s) and round final answers to the nearest dollar amount.) 7.5 points Net procent value eBook Print References b. Calculate the net present value of cash flows using total cost approach If he sells the property. (Use the appropriate table to determine the discount factor(s) and round final answers to the nearest dollar amount.) Net present value c. Would you recommend Professor Laski to keep the property or to sell? Sell the property Keep the property hlaut