Question
A 16-bit Ridiculously Simple Computer (RiSC-16) defined originally at Michigan University has the below ISA description. rA, rB, and rC represent general purpose registers in
A 16-bit Ridiculously Simple Computer (RiSC-16) defined originally at Michigan University has the below ISA description. rA, rB, and rC represent general purpose registers in the given table (A, B, C are unsigned integers encoding register numbers), except r0 is a constant (hardwired) zero register as in MIPS. There are three instruction formats available: Register-Register-Register (RRR), Register-Register-Immediate (RRI), and Register-Immediate (RI). For RRI type, the immediate (immed) operand can have a value from -64 to 63, represented using 2s complement. The immediate (immed) operand can have a value between 0 and 0x3FF (inclusive) for the RI type. The memory is short-word (16 bit) addressable.
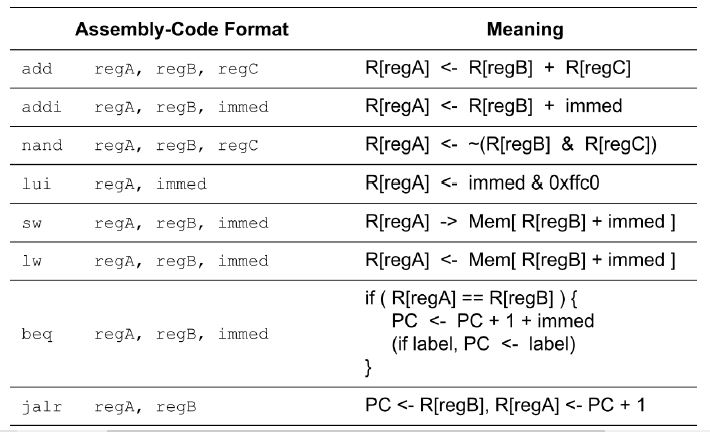
i) Considering the ISA design principles carefully, sketch a viable instruction format for each of the types RRR, RRI, and RI. Indicate the size of each field in bits, and mark any unused field with a . ii) What is the ISA design compromise made in this machine associated with the number of instructions? Explain. iii) What is the ISA design principle followed in implementing the jalr instruction (which of the available three formats might it use)? Explain.
Assembly-Code Format Meaning add addi regA, regB, immed nandregA, regB, regC lui regA, regB, regC R[regA] Mem RregB immed ] RregA] Mem RregB immed ] RregA]Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


