Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Using the data in the ideal gas tables, determine the equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction: HO = 1/2 H + OH at (a)

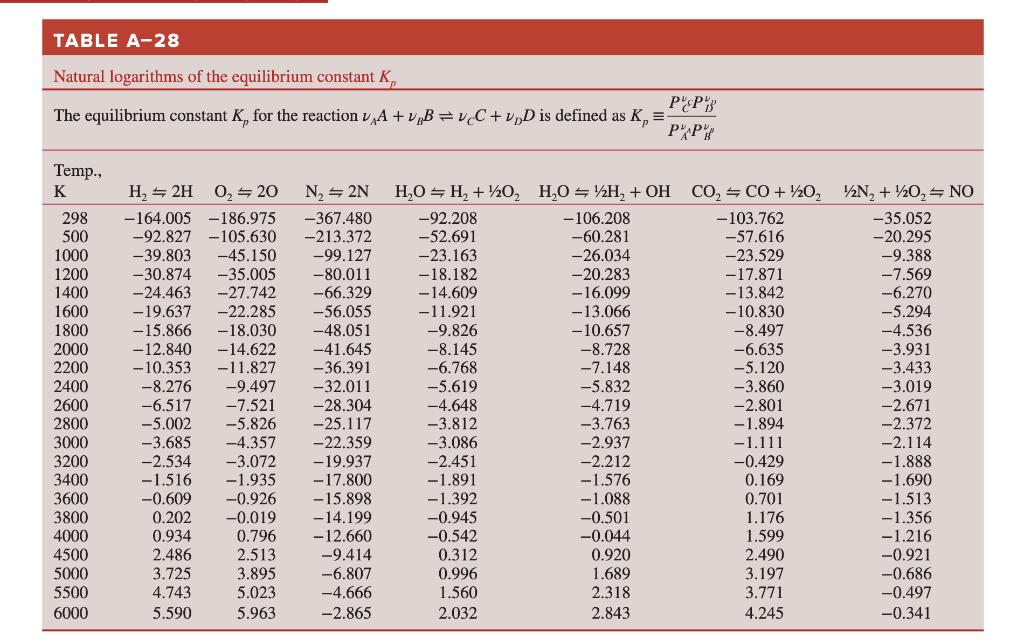
Using the data in the ideal gas tables, determine the equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction: HO = 1/2 H + OH at (a) 298 K and (b) 3000 K. Compare your results with the Kp values listed in Table A-28. TABLE A-28 Natural logarithms of the equilibrium constant K PEP PAP The equilibrium constant K, for the reaction A + B =vC+vD is defined as K = Temp., K 298 500 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 2400 2600 2800 3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000 4500 5000 5500 6000 H 2H 0 20 N = 2N -367.480 -164.005 -186.975 -92.827 -105.630 -213.372 -99.127 -39.803 -45.150 -30.874 -35.005 -80.011 -24.463 -27.742 -66.329 -19.637 -22.285 -56.055 -15.866 -18.030 -48.051 -12.840 -14.622 -41.645 -10.353 -11.827 -36.391 -8.276 -9.497 -32.011 -6.517 -7.521 -28.304 -5.002 -5.826 -25.117 -3.685 -4.357 -22.359 -2.534 -3.072 -19.937 -1.516 -1.935 -17.800 -0.609 -0.926 -15.898 0.202 -0.019 -14.199 0.934 0.796 -12.660 2.486 2.513 -9.414 3.725 3.895 -6.807 4.743 5.023 -4.666 5.590 5.963 -2.865 HO H + 1/2O HO = H + OH CO=CO+ //202 2N + 1/2O = NO -92.208 -103.762 -35.052 -52.691 -57.616 -20.295 -23.163 -23.529 -9.388 -18.182 -17.871 -7.569 -14.609 -13.842 -6.270 -11.921 -10.830 -5.294 -9.826 -8.497 -4.536 -8.145. -6.635 -3.931 -6.768 -5.120 -3.433 -5.619 -3.860 -3.019 -4.648 -2.801 -2.671 -3.812 -1.894 -2.372 -3.086 -1.111 -2.114 -2.451 -0.429 -1.888 -1.891 0.169 -1.690 -1.392 0.701 -0.945 1.176 -0.542 1.599 0.312 2.490 0.996 3.197 1.560 3.771 2.032 4.245 -106.208 -60.281 -26.034 -20.283 - 16.099 -13.066 -10.657 -8.728 -7.148 -5.832 -4.719 -3.763 -2.937 -2.212 -1.576 -1.088 -0.501 -0.044 0.920 1.689 2.318 2.843 -1.513 -1.356 -1.216 -0.921 -0.686 -0.497 -0.341
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.48 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Write the reactions at 5000 K as follows HO H OH K 1689 1 1 HO H 0 K 0...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


