Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A well-insulated, rigid gas bottle of volume V is filled from a high-pressure supply line at temperature Tin pressure Pin and at constant volumetric

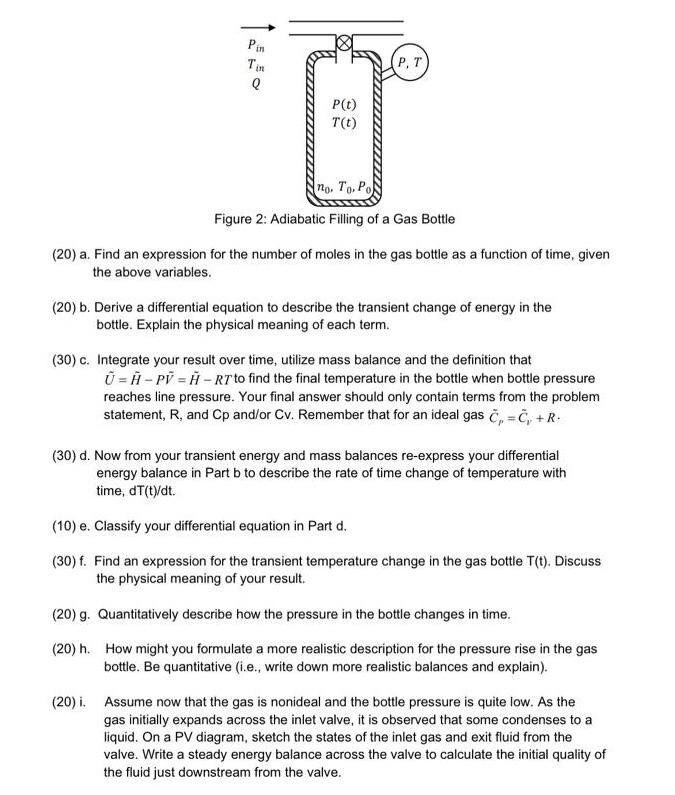
A well-insulated, rigid gas bottle of volume V is filled from a high-pressure supply line at temperature Tin pressure Pin and at constant volumetric flow rate Q, as shown in the figure below. Initially, the gas bottle is filled with a small amount of gas moles, labeled as no, at temperature, To and at low pressure, Po. The gas may be approximated as ideal and the gas in the bottle is well mixed. Heat capacities are independent of temperature. Pin Q P(t) T(t) no. To. Po Figure 2: Adiabatic Filling of a Gas Bottle (20) a. Find an expression for the number of moles in the gas bottle as a function of time, given the above variables. (20) b. Derive a differential equation to describe the transient change of energy in the bottle. Explain the physical meaning of each term. (30) c. Integrate your result over time, utilize mass balance and the definition that U=H-PV=H-RT to find the final temperature in the bottle when bottle pressure reaches line pressure. Your final answer should only contain terms from the problem statement, R, and Cp and/or Cv. Remember that for an ideal gas C=C, +R (30) d. Now from your transient energy and mass balances re-express your differential energy balance in Part b to describe the rate of time change of temperature with time, dT(t)/dt. (10) e. Classify your differential equation in Part d. (30) f. Find an expression for the transient temperature change in the gas bottle T(t). Discuss the physical meaning of your result. (20) g. Quantitatively describe how the pressure in the bottle changes in time. (20) h. How might you formulate a more realistic description for the pressure rise in the gas bottle. Be quantitative (i.e., write down more realistic balances and explain). (20) i. Assume now that the gas is nonideal and the bottle pressure is quite low. As the gas initially expands across the inlet valve, it is observed that some condenses to a liquid. On a PV diagram, sketch the states of the inlet gas and exit fluid from the valve. Write a steady energy balance across the valve to calculate the initial quality of the fluid just downstream from the valve.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


