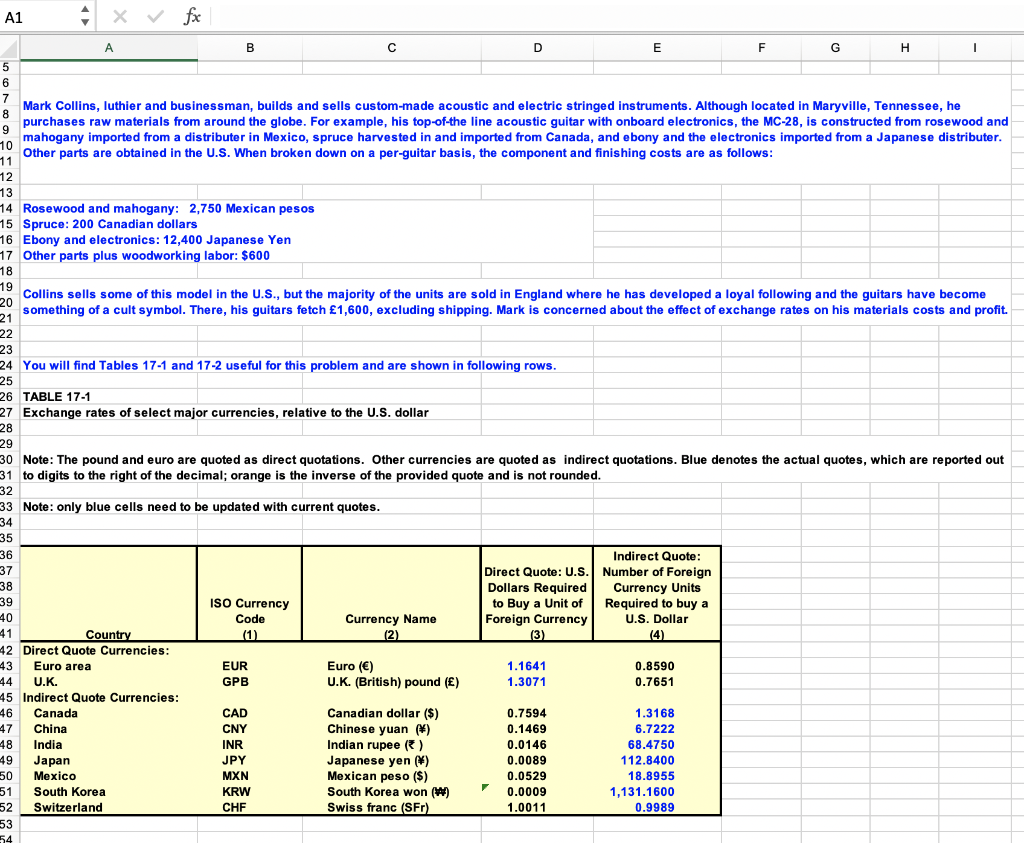
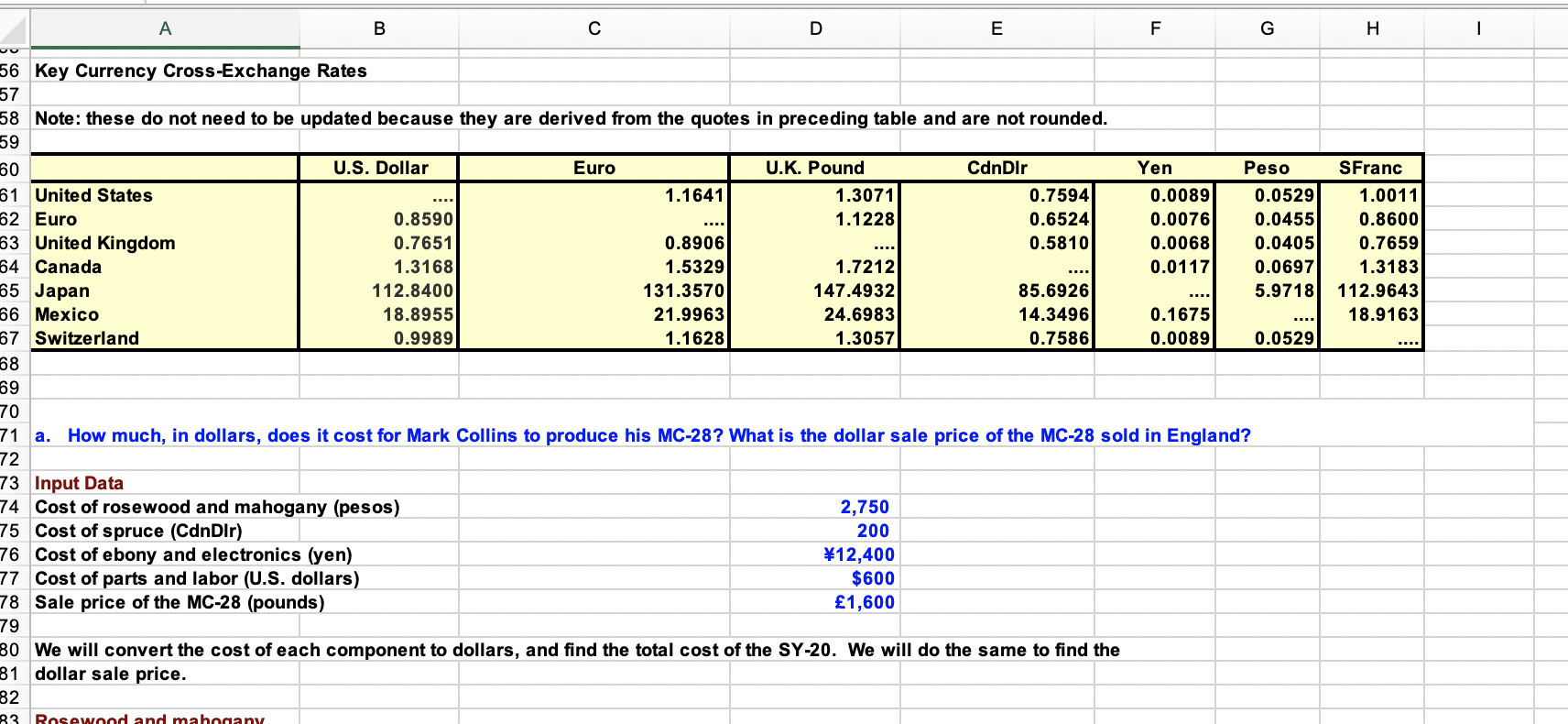
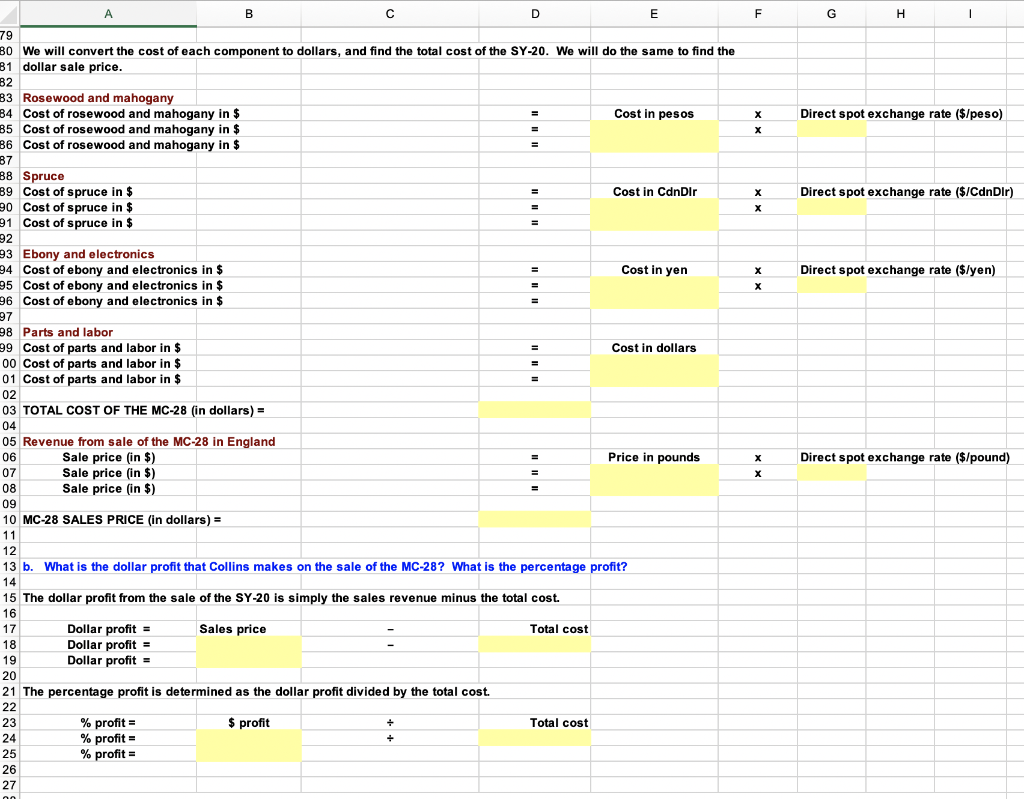
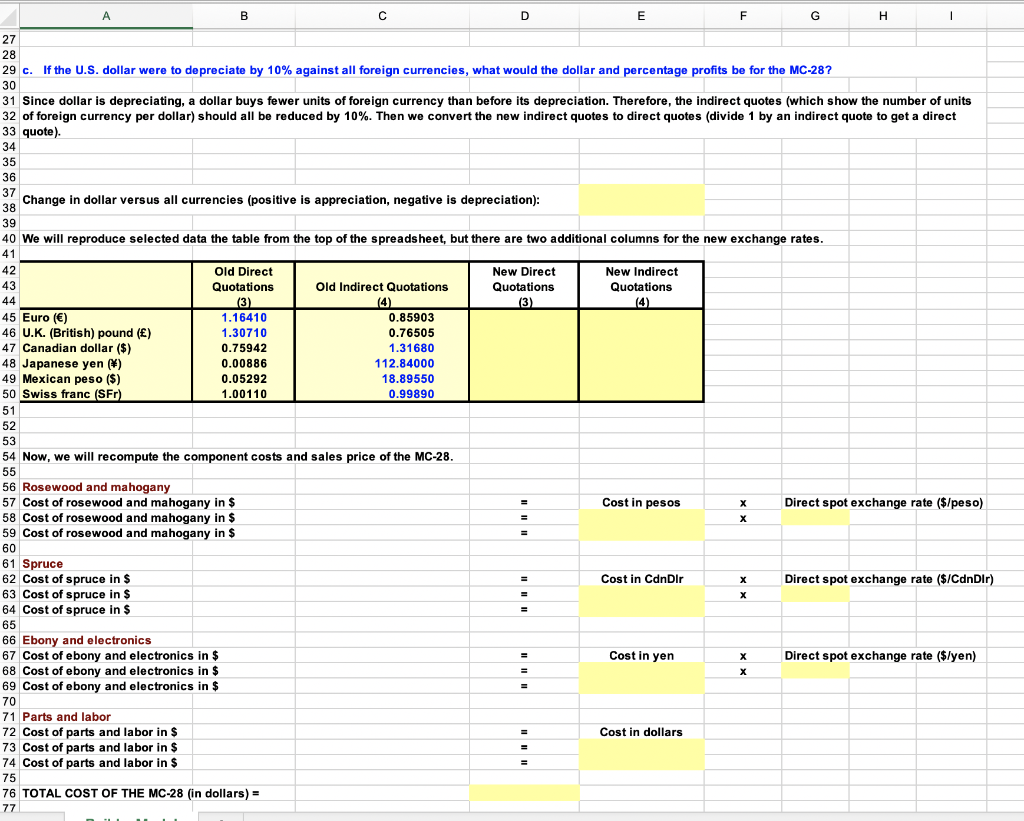
A1 xv fx A B D E F G H H I 5 5 6 7 Mark Collins, luthier and businessman, builds and sells custom-made acoustic and electric stringed instruments. Although located in Maryville, Tennessee, he 8 purchases raw materials from around the globe. For example, his top-of-the line acoustic guitar with onboard electronics, the MC-28, is constructed from rosewood and 9 mahogany imported from a distributer in Mexico, spruce harvested in and imported from Canada, and ebony and the electronics imported from a Japanese distributer. 10 11 Other parts are obtained in the U.S. When broken down on a per-guitar basis, the component and finishing costs are as follows: 11 12 12 13 13 14 Rosewood and mahogany: 2,750 Mexican pesos 15 Spruce: 200 Canadian dollars 16 Ebony and electronics: 12,400 Japanese Yen 17 Other parts plus woodworking labor: $600 18 TO 19 20 Collins sells some of this model in the U.S., but the majority of the units are sold in England where he has developed a loyal following and the guitars have become 21 64 something of a cult symbol. There, his guitars fetch 1,600, excluding shipping. Mark is concerned about the effect of exchange rates on his materials costs and profit. 22 23 24 You will find Tables 17-1 and 17-2 useful for this problem and are shown in following rows. 25 26 TABLE 17-1 27 Exchange rates of select major currencies, relative to the U.S. dollar 28 29 20 30 Note: The pound and euro are quoted as direct quotations. Other currencies are quoted as indirect quotations. Blue denotes the actual quotes, which are reported out 31 to digits to the right of the decimal; orange is the inverse of the provided quote and is not rounded. 32 33 Note: only blue cells need to be updated with current quotes. 34 35 36 Indirect Quote: 37 Direct Quote: U.S. Number of Foreign 38 Dollars Required Currency Units 39 ISO Currency to Buy a Unit of Required to buy a 40 Code Currency Name Foreign Currency U.S. Dollar 41 Country (1) ) (2) ) (3) (4) 42 Direct Quote Currencies: 43 Euro area * EUR Euro () 1.1641 0.8590 14 U.K. GPB U.K. (British) pound () 12 1.3071 0.7651 45 Indirect Quote Currencies: 46 Canada CAD 0.7594 Canadian dollar ($) . 1.3168 47 China CNY Chinese yuan () 0.1469 6.7222 48 India INR Indian rupee () 0.0146 68.4750 49 Japan JPY Japanese yen () 0.0089 112.8400 50 Mexico MXN Mexican Peso ($) 0.0529 18.8955 51 South Korea KRW South Korea won (W) 0.0009 1,131.1600 52 Switzerland CHF Swiss franc (SFr) 1.0011 0.9989 53 54 A B C D E F G H 1 SFranc 1.0011 0.8600 0.7659 1.3183 112.9643 18.9163 56 Key Currency Cross-Exchange Rates 57 58 Note: these do not need to be updated because they are derived from the quotes in preceding table and are not rounded. 59 60 U.S. Dollar Euro U.K. Pound CdnDir Yen Peso 61 United States 1.1641 1.3071 0.7594 0.0089 0.0529 62 Euro 0.8590 1.1228 0.6524 0.0076 0.0455 63 United Kingdom 0.7651 0.8906 0.5810 0.0068 0.0405 64 Canada 1.3168 1.5329 1.7212 0.0117 0.0697 65 Japan 112.8400 131.3570 147.4932 85.6926 5.9718 66 Mexico 18.8955 21.9963 24.6983 14.3496 0.1675 67 Switzerland 0.9989 1.1628 1.3057 0.7586 0.0089 0.0529 68 69 70 71 a. How much, in dollars, does it cost for Mark Collins to produce his MC-28? What is the dollar sale price of the MC-28 sold in England? 72 73 Input Data 74 Cost of rosewood and mahogany (pesos) 2,750 75 Cost of spruce (Cdndlr) 200 76 Cost of ebony and electronics (yen) 12,400 77 Cost of parts and labor (U.S. dollars) $600 78 Sale price of the MC-28 (pounds) 1,600 79 80 We will convert the cost of each component to dollars, and find the total cost of the SY-20. We will do the same to find the 81 dollar sale price. 82 33 Rosewood and mahogany F G H I = Direct spot exchange rate ($/peso) X X Direct spot exchange rate ($/CdnDir) II III X Direct spot exchange rate ($/yen) III = A B D E 79 BO We will convert the cost of each component to dollars, and find the total cost of the SY-20. We will do the same to find the 81 dollar sale price. 32 B3 Rosewood and mahogany 34 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ Cost in pesos B5 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ B6 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ 87 B8 Spruce B9 Cost of spruce in $ Cost in Candlr 90 Cost of spruce in $ 91 Cost of spruce in $ 92 24 93 Ebony and electronics 94 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ Cost in yen 95 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ 96 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ 97 98 Parts and labor 999 Cost of parts and labor in $ Cost in dollars 00 Cost of parts and labor in $ 01 Cost of parts and labor in $ 02 03 TOTAL COST OF THE MC-28 (in dollars) = 04 OE 05 Revenue from sale of the MC-28 in England 06 Sale price in $) Price in pounds 07 Sale price in $) 08 Sale price (in $) 09 10 MC-28 SALES PRICE (in dollars) = 11 12 13 b. What is the dollar profit that Collins makes on the sale of the MC-28? What is the percentage profit? 44 14 15 The dollar profit from the sale of the SY-20 is simply the sales revenue minus the total cost. 40 16 . Dollar profit Sales price Total cost 18 Dollar profit = 19 Dollar profit = 20 21 The percentage profit is determined as the dollar profit divided by the total cost. 22 23 % profit = $ profit $ Total cost 24 % profit = 25 % profit 26 27 nn = Direct spot exchange rate ($/pound) 17 ! B H E F G 1 27 28 29 c. If the U.S. dollar were to depreciate by 10% against all foreign currencies, what would the dollar and percentage profits be for the MC-28? 30 31 Since dollar is depreciating, a dollar buys fewer units of foreign currency than before its depreciation. Therefore, the indirect quotes (which show the number of units 32 of foreign currency per dollar) should all be reduced by 10%. Then we convert the new indirect quotes to direct quotes (divide 1 by an indirect quote to get a direct 33 quote) 34 35 36 37 38 Change in dollar versus all currencies (positive is appreciation, negative is depreciation): 39 40 We will reproduce selected data the table from the top of the spreadsheet, but there are two additional columns for the new exchange rates. 41 42 Old Direct New Direct New Indirect 43 Quotations Old Indirect Quotations Quotations Quotations 44 (3) (4) (3) (4) 45 Euro () 1.16410 0.85903 46 U.K. (British) pound () 1.30710 0.76505 47 Canadian dollar ($) 0.75942 1.31680 48 Japanese yen () 0.00886 112.84000 49 Mexican Peso ($) 0.05292 18.89550 50 Swiss franc (SFr) 1.00110 0.99890 51 52 53 54 Now, we will recompute the component costs and sales price of the MC-28. 55 56 Rosewood and mahogany 57 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ Cost in pesos Direct spot exchange rate ($/peso) 58 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ 59 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ 60 61 Spruce 62 Cost of spruce in $ Cost in CdnDir x Direct spot exchange rate ($/Cdndir) 63 Cost of spruce in $ 64 Cost of spruce in $ 65 66 Ebony and electronics 67 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ Costin yen Direct spot exchange rate ($/yen) 68 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ 69 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ 70 71 Parts and labor 72 Cost of parts and labor in $ Cost in dollars 73 Cost of parts and labor in $ 74 Cost of parts and labor in $ 75 76 TOTAL COST OF THE MC-28 (in dollars) = 77 II # . A B B D E F G H 1 I 85 The dollar profit from the sale of the MC-28 is simply the sales revenue minus the total cost. 86 87 Dollar profit - Sales price Total cost 88 Dollar profit 89 09 Dollar profit - 90 91 The percentage profit is determined as the dollar profit divided by the total cost. 92 93 % % profit = $ profit Total cost 94 % profit = 1 95 % profit = 96 97 7 & The total costs go up because the dollar has depreciated against the currencies' of the suppliers, making it more expensive in dollars for Collins to purchase the raw 98 * materials. However, the depreciation of the dollar versus the pound increases the dollar value of sales. The net effect is a small increase in profits for this example, 99 * but that will not always be the case. 00 201 02 d. If the U.S. dollar were to depreciate by 10% only against the pound and remained constant relative to all other foreign currencies, what would the dollar and 03 percentage profits be for the MC-28? 04 04 205 0. 06 Since dollar is depreciating relative to the pound, a dollar buys fewer pounds than before its depreciation. Therefore, the indirect quote for pounds (which shows the 07 number of pounds per dollar) should be reduced by 10%. Then we convert the new indirect quote to a direct quote (divide 1 by the indirect quote to get the direct 08 quote). The is no need to change any other direct quotes because the dollar is neither depreciation nor appreciating relative to them. 209 10 Change in dollar strength against the pound 11 12 Old Direct New Direct New Indirect 13 Quotations Old Indirect Quotations Quotations Quotations 14 (3) (4) (3) (4) 15 Euro () 1.16410 0.85903 1.16410 E16 U.K. (British) pound () 1.30710 -17 Canadian dollar ($) 0.75942 1.31680 0.75942 18 Japanese yen () 0.00886 112.84000 0.00886 19 Mexican Peso ($) 0.05292 18.89550 0.05292 -20 Swiss franc (SFr) 1.00110 0.99890 1.00110 -21 -22 -25 24 Now, we will recompute the component costs and sales price of the MC-28. -25 -26 Rosewood and mahogany -27 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ Cost in pesos Direct spot exchange rate ($/peso) 28 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ -29 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ 230 231 Spruce -32 Cost of spruce in $ Cost in CdnDir Direct spot exchange rate ($/Cdndir) 233 Cost of spruce in $ 234 Cost of spruce in $ 0.76505 23 = II III = 35 III III x x A B D E F G H 1 235 E36 Ebony and electronics 37 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ Cost in yen X Direct spot exchange rate ($/yen) 38 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ E39 Cost ebony and electronics in $ 240 -41 Parts and labor 42 Cost of parts and labor in $ Cost in dollars 43 Cost of parts and labor in $ * 44 Cost of parts and labor in $ 245 -10 15 46 TOTAL COST OF THE MC-28 (in dollars) = 247 7 48 Revenue from sale of the MC-28 in England -49 Sale price (in $) Price in pounds Direct spot exchange rate ($/pound) 50 Sale price (in $) e -51 Sale price (in $) -52 53 MC-28 SALES PRICE (in dollars) = EM -54 55 The dollar profit from the sale of the MC-28 is simply the sales revenue minus the total cost. ce -56 57 -57 Dollar profit - Sales price Total cost -58 -58 Dollar profit = -59 Dollar profit = -60 260 61 The percentage profit is determined as the dollar profit divided by the total cost. -62 263 % profit $ profit Total cost 64 % profit = et 265 % profit 86 -66 67 Because sales are made in pounds, dollar revenues increase when the dollar depreciates relative to the pound--there are fewer pounds per pound, but there are more 268 dollars per pound. 269 -69 -70 71 e. The rate of return on 90-day U.S. treasury securities 3.9% and the rate of return on 90-day U.K. risk-free securities is 5.0%. Using the spot exchange information 72 from Table 17-1, estimate the 90-day forward exchange rate. 73 - 74 Using knowledge of interest rate parity, the following problem is set up. -75 76 Spot exchange rate (direct quotation) = 77 Home nominal interest rate = 3.9% 78 Foreign nominal interest rate = 5.0% 79 Time to maturity on securities (in years) = 0.25 80 Home periodic interest rate = -81 Foreign periodic interest rate = 82 B D E F G H ULLI 283 f/ (spot exchange rate) [(1+r) / (1+r)] 284 ft (spot exchange rate) [ (1+rn) / (1+r)] 285 ft 86 287 88 f. Assuming that purchasing power parity holds, what would the sale price of the MC-28 be if it were sold in France rather than England? (Hint: assume England is the 289 home country.) 290 91 Purchasing power parity allows us to establish the following problem. 292 293 Price in pounds -94 Exchange rate (pounds per euro) = 295 Ph 96 (P) (eo) pounds per euro 297 (in pounds) (P) 98 (P) 299 300 = = X = A1 xv fx A B D E F G H H I 5 5 6 7 Mark Collins, luthier and businessman, builds and sells custom-made acoustic and electric stringed instruments. Although located in Maryville, Tennessee, he 8 purchases raw materials from around the globe. For example, his top-of-the line acoustic guitar with onboard electronics, the MC-28, is constructed from rosewood and 9 mahogany imported from a distributer in Mexico, spruce harvested in and imported from Canada, and ebony and the electronics imported from a Japanese distributer. 10 11 Other parts are obtained in the U.S. When broken down on a per-guitar basis, the component and finishing costs are as follows: 11 12 12 13 13 14 Rosewood and mahogany: 2,750 Mexican pesos 15 Spruce: 200 Canadian dollars 16 Ebony and electronics: 12,400 Japanese Yen 17 Other parts plus woodworking labor: $600 18 TO 19 20 Collins sells some of this model in the U.S., but the majority of the units are sold in England where he has developed a loyal following and the guitars have become 21 64 something of a cult symbol. There, his guitars fetch 1,600, excluding shipping. Mark is concerned about the effect of exchange rates on his materials costs and profit. 22 23 24 You will find Tables 17-1 and 17-2 useful for this problem and are shown in following rows. 25 26 TABLE 17-1 27 Exchange rates of select major currencies, relative to the U.S. dollar 28 29 20 30 Note: The pound and euro are quoted as direct quotations. Other currencies are quoted as indirect quotations. Blue denotes the actual quotes, which are reported out 31 to digits to the right of the decimal; orange is the inverse of the provided quote and is not rounded. 32 33 Note: only blue cells need to be updated with current quotes. 34 35 36 Indirect Quote: 37 Direct Quote: U.S. Number of Foreign 38 Dollars Required Currency Units 39 ISO Currency to Buy a Unit of Required to buy a 40 Code Currency Name Foreign Currency U.S. Dollar 41 Country (1) ) (2) ) (3) (4) 42 Direct Quote Currencies: 43 Euro area * EUR Euro () 1.1641 0.8590 14 U.K. GPB U.K. (British) pound () 12 1.3071 0.7651 45 Indirect Quote Currencies: 46 Canada CAD 0.7594 Canadian dollar ($) . 1.3168 47 China CNY Chinese yuan () 0.1469 6.7222 48 India INR Indian rupee () 0.0146 68.4750 49 Japan JPY Japanese yen () 0.0089 112.8400 50 Mexico MXN Mexican Peso ($) 0.0529 18.8955 51 South Korea KRW South Korea won (W) 0.0009 1,131.1600 52 Switzerland CHF Swiss franc (SFr) 1.0011 0.9989 53 54 A B C D E F G H 1 SFranc 1.0011 0.8600 0.7659 1.3183 112.9643 18.9163 56 Key Currency Cross-Exchange Rates 57 58 Note: these do not need to be updated because they are derived from the quotes in preceding table and are not rounded. 59 60 U.S. Dollar Euro U.K. Pound CdnDir Yen Peso 61 United States 1.1641 1.3071 0.7594 0.0089 0.0529 62 Euro 0.8590 1.1228 0.6524 0.0076 0.0455 63 United Kingdom 0.7651 0.8906 0.5810 0.0068 0.0405 64 Canada 1.3168 1.5329 1.7212 0.0117 0.0697 65 Japan 112.8400 131.3570 147.4932 85.6926 5.9718 66 Mexico 18.8955 21.9963 24.6983 14.3496 0.1675 67 Switzerland 0.9989 1.1628 1.3057 0.7586 0.0089 0.0529 68 69 70 71 a. How much, in dollars, does it cost for Mark Collins to produce his MC-28? What is the dollar sale price of the MC-28 sold in England? 72 73 Input Data 74 Cost of rosewood and mahogany (pesos) 2,750 75 Cost of spruce (Cdndlr) 200 76 Cost of ebony and electronics (yen) 12,400 77 Cost of parts and labor (U.S. dollars) $600 78 Sale price of the MC-28 (pounds) 1,600 79 80 We will convert the cost of each component to dollars, and find the total cost of the SY-20. We will do the same to find the 81 dollar sale price. 82 33 Rosewood and mahogany F G H I = Direct spot exchange rate ($/peso) X X Direct spot exchange rate ($/CdnDir) II III X Direct spot exchange rate ($/yen) III = A B D E 79 BO We will convert the cost of each component to dollars, and find the total cost of the SY-20. We will do the same to find the 81 dollar sale price. 32 B3 Rosewood and mahogany 34 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ Cost in pesos B5 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ B6 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ 87 B8 Spruce B9 Cost of spruce in $ Cost in Candlr 90 Cost of spruce in $ 91 Cost of spruce in $ 92 24 93 Ebony and electronics 94 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ Cost in yen 95 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ 96 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ 97 98 Parts and labor 999 Cost of parts and labor in $ Cost in dollars 00 Cost of parts and labor in $ 01 Cost of parts and labor in $ 02 03 TOTAL COST OF THE MC-28 (in dollars) = 04 OE 05 Revenue from sale of the MC-28 in England 06 Sale price in $) Price in pounds 07 Sale price in $) 08 Sale price (in $) 09 10 MC-28 SALES PRICE (in dollars) = 11 12 13 b. What is the dollar profit that Collins makes on the sale of the MC-28? What is the percentage profit? 44 14 15 The dollar profit from the sale of the SY-20 is simply the sales revenue minus the total cost. 40 16 . Dollar profit Sales price Total cost 18 Dollar profit = 19 Dollar profit = 20 21 The percentage profit is determined as the dollar profit divided by the total cost. 22 23 % profit = $ profit $ Total cost 24 % profit = 25 % profit 26 27 nn = Direct spot exchange rate ($/pound) 17 ! B H E F G 1 27 28 29 c. If the U.S. dollar were to depreciate by 10% against all foreign currencies, what would the dollar and percentage profits be for the MC-28? 30 31 Since dollar is depreciating, a dollar buys fewer units of foreign currency than before its depreciation. Therefore, the indirect quotes (which show the number of units 32 of foreign currency per dollar) should all be reduced by 10%. Then we convert the new indirect quotes to direct quotes (divide 1 by an indirect quote to get a direct 33 quote) 34 35 36 37 38 Change in dollar versus all currencies (positive is appreciation, negative is depreciation): 39 40 We will reproduce selected data the table from the top of the spreadsheet, but there are two additional columns for the new exchange rates. 41 42 Old Direct New Direct New Indirect 43 Quotations Old Indirect Quotations Quotations Quotations 44 (3) (4) (3) (4) 45 Euro () 1.16410 0.85903 46 U.K. (British) pound () 1.30710 0.76505 47 Canadian dollar ($) 0.75942 1.31680 48 Japanese yen () 0.00886 112.84000 49 Mexican Peso ($) 0.05292 18.89550 50 Swiss franc (SFr) 1.00110 0.99890 51 52 53 54 Now, we will recompute the component costs and sales price of the MC-28. 55 56 Rosewood and mahogany 57 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ Cost in pesos Direct spot exchange rate ($/peso) 58 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ 59 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ 60 61 Spruce 62 Cost of spruce in $ Cost in CdnDir x Direct spot exchange rate ($/Cdndir) 63 Cost of spruce in $ 64 Cost of spruce in $ 65 66 Ebony and electronics 67 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ Costin yen Direct spot exchange rate ($/yen) 68 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ 69 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ 70 71 Parts and labor 72 Cost of parts and labor in $ Cost in dollars 73 Cost of parts and labor in $ 74 Cost of parts and labor in $ 75 76 TOTAL COST OF THE MC-28 (in dollars) = 77 II # . A B B D E F G H 1 I 85 The dollar profit from the sale of the MC-28 is simply the sales revenue minus the total cost. 86 87 Dollar profit - Sales price Total cost 88 Dollar profit 89 09 Dollar profit - 90 91 The percentage profit is determined as the dollar profit divided by the total cost. 92 93 % % profit = $ profit Total cost 94 % profit = 1 95 % profit = 96 97 7 & The total costs go up because the dollar has depreciated against the currencies' of the suppliers, making it more expensive in dollars for Collins to purchase the raw 98 * materials. However, the depreciation of the dollar versus the pound increases the dollar value of sales. The net effect is a small increase in profits for this example, 99 * but that will not always be the case. 00 201 02 d. If the U.S. dollar were to depreciate by 10% only against the pound and remained constant relative to all other foreign currencies, what would the dollar and 03 percentage profits be for the MC-28? 04 04 205 0. 06 Since dollar is depreciating relative to the pound, a dollar buys fewer pounds than before its depreciation. Therefore, the indirect quote for pounds (which shows the 07 number of pounds per dollar) should be reduced by 10%. Then we convert the new indirect quote to a direct quote (divide 1 by the indirect quote to get the direct 08 quote). The is no need to change any other direct quotes because the dollar is neither depreciation nor appreciating relative to them. 209 10 Change in dollar strength against the pound 11 12 Old Direct New Direct New Indirect 13 Quotations Old Indirect Quotations Quotations Quotations 14 (3) (4) (3) (4) 15 Euro () 1.16410 0.85903 1.16410 E16 U.K. (British) pound () 1.30710 -17 Canadian dollar ($) 0.75942 1.31680 0.75942 18 Japanese yen () 0.00886 112.84000 0.00886 19 Mexican Peso ($) 0.05292 18.89550 0.05292 -20 Swiss franc (SFr) 1.00110 0.99890 1.00110 -21 -22 -25 24 Now, we will recompute the component costs and sales price of the MC-28. -25 -26 Rosewood and mahogany -27 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ Cost in pesos Direct spot exchange rate ($/peso) 28 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ -29 Cost of rosewood and mahogany in $ 230 231 Spruce -32 Cost of spruce in $ Cost in CdnDir Direct spot exchange rate ($/Cdndir) 233 Cost of spruce in $ 234 Cost of spruce in $ 0.76505 23 = II III = 35 III III x x A B D E F G H 1 235 E36 Ebony and electronics 37 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ Cost in yen X Direct spot exchange rate ($/yen) 38 Cost of ebony and electronics in $ E39 Cost ebony and electronics in $ 240 -41 Parts and labor 42 Cost of parts and labor in $ Cost in dollars 43 Cost of parts and labor in $ * 44 Cost of parts and labor in $ 245 -10 15 46 TOTAL COST OF THE MC-28 (in dollars) = 247 7 48 Revenue from sale of the MC-28 in England -49 Sale price (in $) Price in pounds Direct spot exchange rate ($/pound) 50 Sale price (in $) e -51 Sale price (in $) -52 53 MC-28 SALES PRICE (in dollars) = EM -54 55 The dollar profit from the sale of the MC-28 is simply the sales revenue minus the total cost. ce -56 57 -57 Dollar profit - Sales price Total cost -58 -58 Dollar profit = -59 Dollar profit = -60 260 61 The percentage profit is determined as the dollar profit divided by the total cost. -62 263 % profit $ profit Total cost 64 % profit = et 265 % profit 86 -66 67 Because sales are made in pounds, dollar revenues increase when the dollar depreciates relative to the pound--there are fewer pounds per pound, but there are more 268 dollars per pound. 269 -69 -70 71 e. The rate of return on 90-day U.S. treasury securities 3.9% and the rate of return on 90-day U.K. risk-free securities is 5.0%. Using the spot exchange information 72 from Table 17-1, estimate the 90-day forward exchange rate. 73 - 74 Using knowledge of interest rate parity, the following problem is set up. -75 76 Spot exchange rate (direct quotation) = 77 Home nominal interest rate = 3.9% 78 Foreign nominal interest rate = 5.0% 79 Time to maturity on securities (in years) = 0.25 80 Home periodic interest rate = -81 Foreign periodic interest rate = 82 B D E F G H ULLI 283 f/ (spot exchange rate) [(1+r) / (1+r)] 284 ft (spot exchange rate) [ (1+rn) / (1+r)] 285 ft 86 287 88 f. Assuming that purchasing power parity holds, what would the sale price of the MC-28 be if it were sold in France rather than England? (Hint: assume England is the 289 home country.) 290 91 Purchasing power parity allows us to establish the following problem. 292 293 Price in pounds -94 Exchange rate (pounds per euro) = 295 Ph 96 (P) (eo) pounds per euro 297 (in pounds) (P) 98 (P) 299 300 = = X =













