Question: Thames Company's inventory records for its retail division show the following at December 31: E (Click the icon to view the accounting records.) At

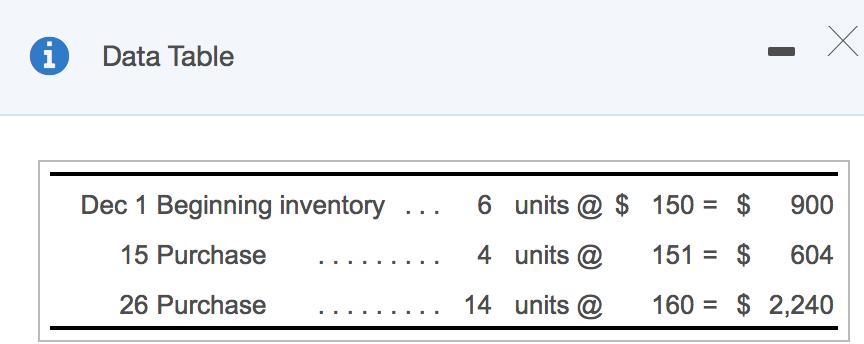
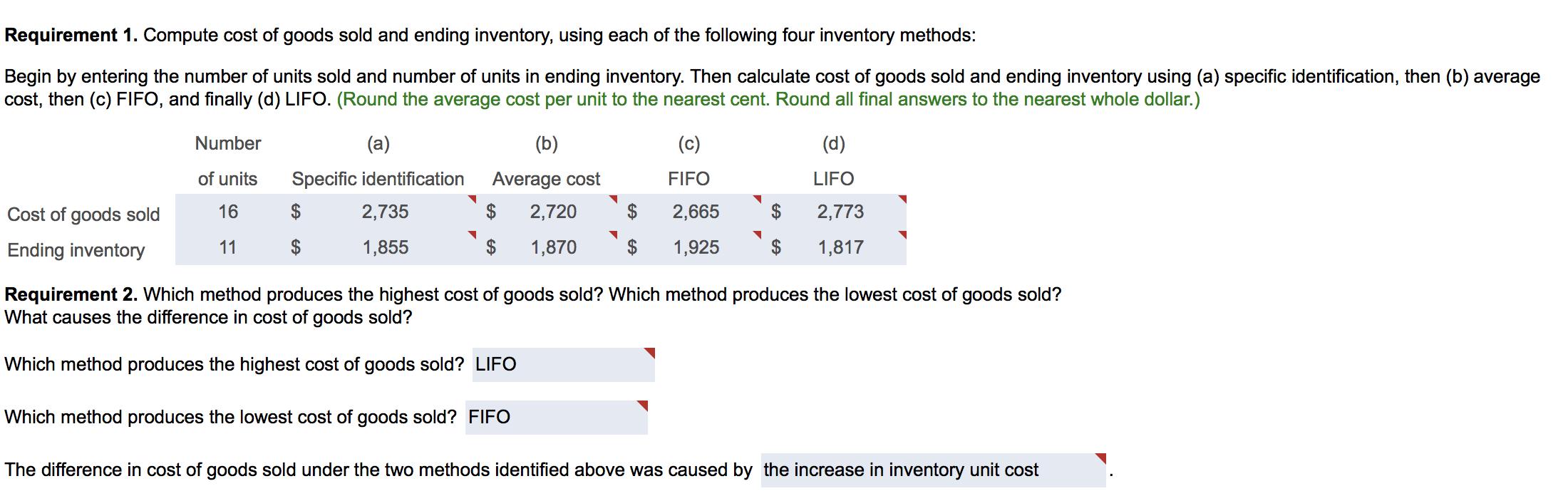
Thames Company's inventory records for its retail division show the following at December 31: E (Click the icon to view the accounting records.) At December 31, 10 of these units are on hand. Read the requirements. i Data Table Dec 1 Beginning inventory 6 units @ $ 150 = $ 900 ... 15 Purchase 4 units @ 151 = $ 604 26 Purchase 14 units @ 160 = $ 2,240 %3D Requirement 1. Compute cost of goods sold and ending inventory, using each of the following four inventory methods: Begin by entering the number of units sold and number of units in ending inventory. Then calculate cost of goods sold and ending inventory using (a) specific identification, then (b) average cost, then (c) FIFO, and finally (d) LIFO. (Round the average cost per unit to the nearest cent. Round all final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) Number (a) (b) (c) (d) of units Specific identification Average cost FIFO LIFO Cost of goods sold 16 2$ 2,735 $ 2,720 2$ 2,665 2,773 Ending inventory 11 1,855 2$ 1,870 2$ 1,925 1,817 Requirement 2. Which method produces the highest cost of goods sold? Which method produces the lowest cost of goods sold? What causes the difference in cost of goods sold? Which method produces the highest cost of goods sold? LIFO Which method produces the lowest cost of goods sold? FIFO The difference in cost of goods sold under the two methods identified above was caused by the increase in inventory unit cost
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 2 LIFO produces the highest cost of goods ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


