Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Super Skateboard Builders (SSB), Inc. was founded in 1997 by John Z-boy Boeve, the current president of the company, with the help of a

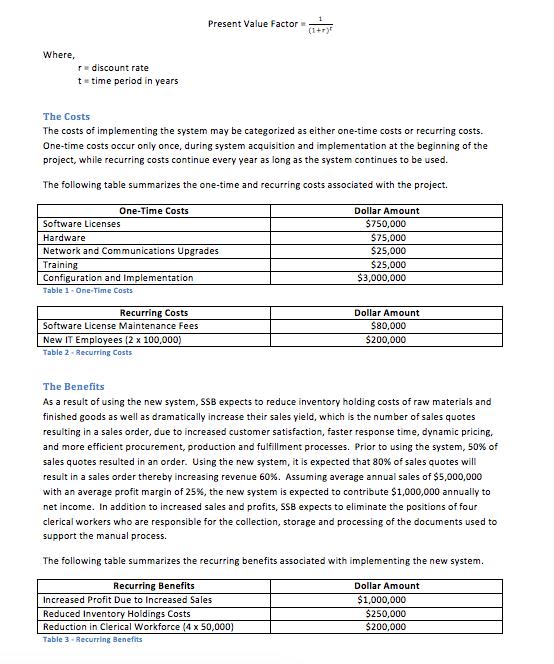

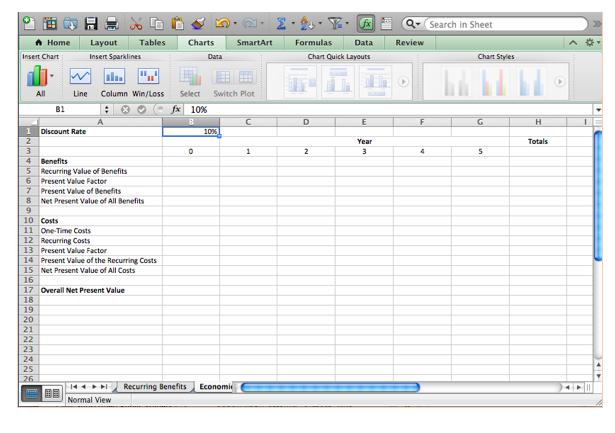

Super Skateboard Builders (SSB), Inc. was founded in 1997 by John "Z-boy" Boeve, the current president of the company, with the help of a small trust John received from his maternal grandmother, a woman who motivated John to go to college and to continue to pursue his skateboarding passion. She marveled at John's skateboarding finesse and encouraged him to find some way to earn a reasonable living by capitalizing on his passion for the sport. John used the money from the trust to buy the necessary shop and office equipment (storage bins, an assembly table, desks, etc.) and lease a small building that would adequately house a skateboard assembly operation. The Problem John recognized that the success of SSB would depend on the ability of his employees to work seamlessly together in an integrated fashion providing exceptional customer service. In the beginning when SSB was a small company with fewer than 10 employees, it was easy to provide outstanding customer service. However, as SSB grew during the next decade expanding its operations to 50 full-time employees and $5,000,000 in revenue, customer service declined, customer complaints increased, and cash flow suffered. Furthermore, the sales team was growing increasingly frustrated because they were promising products to customers they could not deliver. When John first started the company, he invested in some computer equipment and basic office software to help track important information. He was a strong believer in using the computer to store and track information related to any of life's worthwhile pursuits, especially if they were data-intensive. He purchased separate software applications to help keep track of data for each of the key functional areas in his organization - accounting, sales, and warehouse operations. While these software applications served each functional area well, they lacked integration and required significant manual intervention to perform routine business processes. For example, when the sales team submitted an order in its order tracking software application, the order had to be printed out and delivered to the warehouse and accounting departments for processing. The manual process was problematic and John felt it was one of the key reasons for the decline in customer service. Accordingly, he was considering buying an enterprise system like SAP to use throughout the organization. Your Task Before proceeding with the project, John has asked you to analyze the economic feasibility of replacing his existing suite of applications with SAP. John would like to know if the benefits realized from implementing the new system exceed the costs of buying, implementing and using the system. Therefore, you must carefully examine the cost and benefits of replacing the legacy system with SAP. To facilitate your analysis, you will create a Microsoft Excel workbook detailing the costs of purchasing, configuring, implementing, and supporting the system. The workbook should also contain a list of the projected benefits and cost savings associated with implementing the new system. Your analysis should take into account the time value of money and calculate the ROI given a 5 year life expectancy for the new system. The present value of a future cash flow may be calculated using the following formula: Where, r discount rate t time period in years One-Time Costs The Costs The costs of implementing the system may be categorized as either one-time costs or recurring costs. One-time costs occur only once, during system acquisition and implementation at the beginning of the project, while recurring costs continue every year as long as the system continues to be used. The following table summarizes the one-time and recurring costs associated with the project. Present Value Factor Software Licenses Hardware Network and Communications Upgrades Training Configuration and Implementation Table 1-One-Time Costs Recurring Costs Software License Maintenance Fees New IT Employees (2 x 100,000) Table 2. Recurring Costs (1+r) Recurring Benefits Increased Profit Due to Increased Sales Reduced Inventory Holdings Costs Reduction in Clerical Workforce (4 x 50,000) Table 3-Recurring Benefits Dollar Amount $750,000 $75,000 $25,000 $25,000 $3,000,000 Dollar Amount $80,000 $200,000 The Benefits As a result of using the new system, SSB expects to reduce inventory holding costs of raw materials and finished goods as well as dramatically increase their sales yield, which is the number of sales quotes resulting in a sales order, due to increased customer satisfaction, faster response time, dynamic pricing. and more efficient procurement, production and fulfillment processes. Prior to using the system, 50% of sales quotes resulted in an order. Using the new system, it is expected that 80% of sales quotes will result in a sales order thereby increasing revenue 60%. Assuming average annual sales of $5,000,000 with an average profit margin of 25%, the new system is expected to contribute $1,000,000 annually to net income. In addition to increased sales and profits, SSB expects to eliminate the positions of four clerical workers who are responsible for the collection, storage and processing of the documents used to support the manual process. The following table summarizes the recurring benefits associated with implementing the new system. Dollar Amount $1,000,000 $250,000 $200,000 The Deliverables Part 1 - The Excel Workbook Use Excel to create a workbook to facilitate an analysis of the economic feasibility of the project. The workbook should use fixed and variable cell references where applicable to support rapid assessment of the business case under different assumptions for interest rates, benefits and costs. The workbook should contain the following six worksheets. Table of Contents This worksheet should list the contents of the workbook along with the purpose of the workbook, the date the workbook was last modified, and the name of the person who created the workbook. One Time Costs The one-time cost worksheet lists the one-time costs for the project contained in Table 1. Recurring Costs The recurring cost worksheet lists the recurring costs of the project contained in Table 2. Recurring Benefits The recurring benefits worksheet lists the recurring benefits of the project contained in Table 3. Economic Feasibility For each year of the project calculate the recurring value of the benefits, the present value factor for the given year, the present value of the benefits, the net present value of all benefits, the one- time costs, the recurring costs, the present value factor for the given year, the present value of the recurring costs, the net present value of all costs, the overall net present value, yearly NPV cash flow, and overall NPV cash flow for the proposed project. Include a cell to capture the discount rate. The following figure illustrates the layout of the "Economic Feasibility worksheet discussed above. A Home Insert Chart 1 2 3 All B1 Line Discount Rate Layout Insert Sparklines 4 Benefits 5 Recurring Value of Benefits 6 Present Value Factor ala Column Win/Loss : 08 Tables 7 Present Value of Benefits 8 Net Present Value of All Benefits 9 10 Costs 11 One-Time Costs 12 Recurring Costs 13 Present Value Factor 14 Present Value of the Recurring Costs 15 Net Present Value of All Costs 16 17 Overall Net Present Value 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 144 Normal View Charts Data fx 10% 0 Select Switch Plot 10% 22-27 Recurring Benefits Economi SmartArt 1 Formulas Data Chart Quick Layouts D 2 E Year 3 Review 4 Search in Sheet Chart Styles 5 H Totals Break-Even Chart Create a chart graphically depicting the break-even point for the project. (Hint: Break-even occurs when the net present value of all costs equals the net present value of all benefits). Part 2 - Questions to Answer using the Excel Workbook Please answer the following questions using the workbook you created in Part 1. All questions should be answered in a separate Microsoft Word document. 1. Assume a discount rate of 10%. What is the overall net present value for the project? When will the project break-even? Should SSB move forward with the project and proceed with implementing SAP? Explain your answer. 2. Assume a discount rate of 20%. What is the overall net present value for the project? When will the project break-even? Should SSB move forward with the project and proceed with implementing SAP? Explain your answer. 3. Assume the recurring value of the benefits due to increased sales was overly optimistic and net income due to increased sales is only $500,000 instead of $1,000,000. In addition, assume the benefits due to a reduction in inventory holding costs are only $200,000 instead of $250,000. Assuming a discount rate of 10%, what is the overall net present value for the project? When will the project break- even? Should SSB move forward with the project and proceed with implementing SAP? Explain your answer. 4 Assume the recurring value of the benefits due to increased sales was overly optimistic and net income due to increased sales is only $500,000 instead of $1,000,000. In addition, assume the benefits due to a reduction in inventory holding costs are only $200,000 instead of $250,000. At what discount rate is the project economically feasible? Should SSB move forward with the project and proceed with implementing SAP? What are the implications of this change in sales to the economic feasibility of the project? Explain your answer.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.42 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


