use WOLFRAM ALPHA PROGRAM (a) On the same graph, plot the potentials Ve(r), Vy (r) and V(r) for 0.1 r 15 fm in a

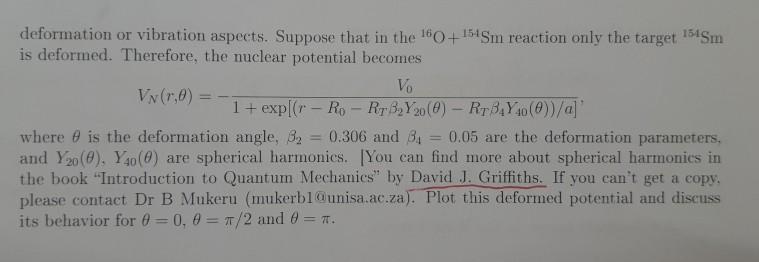

use WOLFRAM ALPHA PROGRAM (a) On the same graph, plot the potentials Ve(r), Vy (r) and V(r) for 0.1 r 15 fm in a step size of 0.5 fm for the 160+154Sm reaction. In this case you need to write a short in any programming language of your choice to obtain the numerical values to plot. (b) Discuss the behavior of these three potentials. (c) As the nucleus nucleons increase, the nucleus becomes more unstable and therefore assuming a spherical shape for heavy nuclei is less realistic. In such case one has to take into account the deformation or vibration aspects. Suppose that in the 160+154Sm reaction only the target is deformed. Therefore, the nuclear potential becomes VN (r,0) = where is the deformation angle, : 0.306 and 0.05 are the deformation parameters, and Y20(8), Y40 (0) are spherical harmonics. [You can find more about spherical harmonics in the book "Introduction to Quantum Mechanics" by David J. Griffiths. If you can't get a copy. please contact Dr B. Mukeru (mukerb1@unisa.ac.za). Plot this deformed potential and discuss its behavior for 0 = 0, 0 = /2 and 0 = . Vo 1+ exp[(r-Ro - RTSY20 (0) - RTB4Y40 (0))/a] 154Sm The potential V(r) is known to have barrier height VB associated with a barrier radius Rg, which can be obtained with the following condition dr where = =0 APAT Ap + AT r=RB r=RB (a) Use this equation to obtain RB for 160 + 154Sm and Be + 208 Pb reactions. (b) Obtain the corresponding barrier heights, given by VB = VN (RB) + ZpZre RB (c) Calculate the corresponding curvatures (2B) defined as dVN(r) + dr NB = ZpZT 7.2 is the reduced mass. 1 d V(r) 1dr2 = 0 |r=RB
Step by Step Solution
3.28 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


