Question
Adam has just graduated, and has a good job at a decent starting salary. He hopes to purchase his first new car. The car that
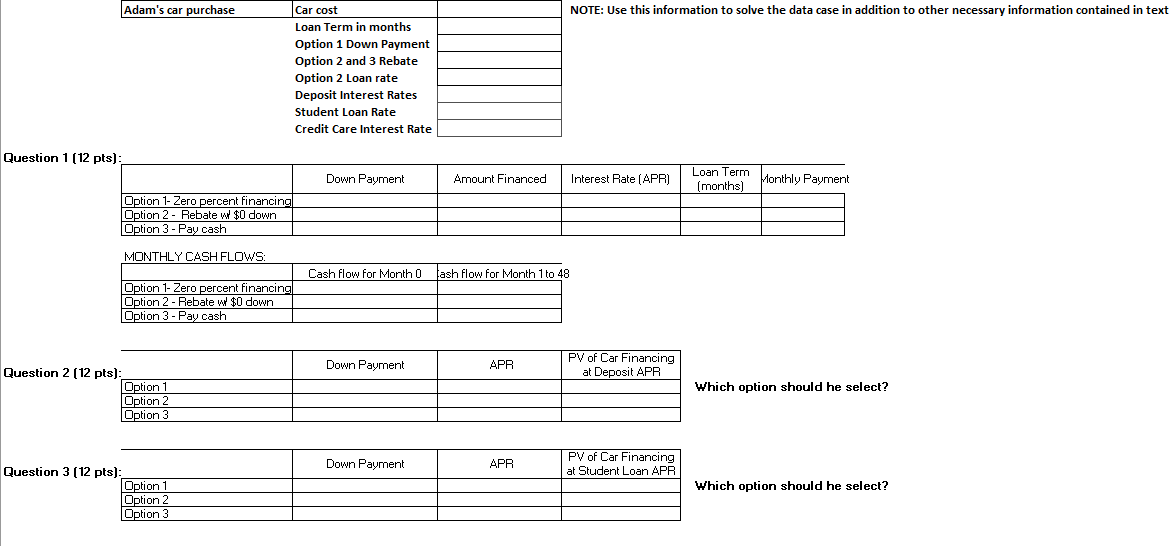
Adam has just graduated, and has a good job at a decent starting salary. He hopes to purchase his first new car. The car that Adam is considering costs $48,500. The dealer has given him three payment options:
1. Zero percent financing. Make a $5,000 down payment from his savings and finance the remainder with a 0% APR loan for 48 months. Adam has more than enough cash for the down payment, thanks to generous graduation gifts.
2. Rebate with no money down. Receive a $4,000 rebate from the car dealer and finance the rest with a standard 48-month loan, with an 4.00% APR. He likes this option, as he could think of many other uses for the $5,000 of his saving.
3. Pay cash. Get the $4,000 rebate and pay the rest with cash. While Adam doesnt have balance of the car cost in hand, he wants to evaluate this option. His parents always paid cash when they bought a family car; Adam wonders if this really was a good idea.
Adams fellow graduate, Jenna, has been trying to decide how much of her new salary she could save for retirement. Jenna is considering putting $4,100 of her annual savings in a stock fund. She just turned 22 and has a long way to go until retirement at age 65, and she considers this risk level reasonable. The fund she is looking at has earned an average of 8.25% over the past 15 years and could be expected to continue earning this amount, on average. While she has no current retirement savings, four years ago Jennas grandparents gave her a new 30-year U.S. Treasury bond with a $15,000 face value with 3.00% semiannual coupons. Jenna wants to know her retirement income if she both (1) sells her Treasury bond at its current market value and invests the proceeds in the stock fund and (2) saves an additional $4,100 at the end of each year in the stock fund from now until she retires. Once she retires, Jenna wants those savings to last until she is 96.
Questions
1. What are the cash flows associated with each of Adams three car financing options?
2. Suppose that, similar to his parents, Adam had plenty of cash in the bank so that he could easily afford to pay cash for the car without running into debt now or in the foreseeable future. If his cash earns interest at a 1.25% APR (based on monthly compounding) at the bank, what would be his best purchase option for the car?
3. In fact, Adam doesnt have sufficient cash to cover all his debts including his (substantial) student loans. The loans have a 6.0% APR, and any money spent on the car could not be used to pay down the loans. What is the best option for Adam now? (Hint: Note that having an extra $1 today saves Adam roughly $1.06 next year because he can pay down the student loans. So, 6% is Adams time value of money in this case.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


