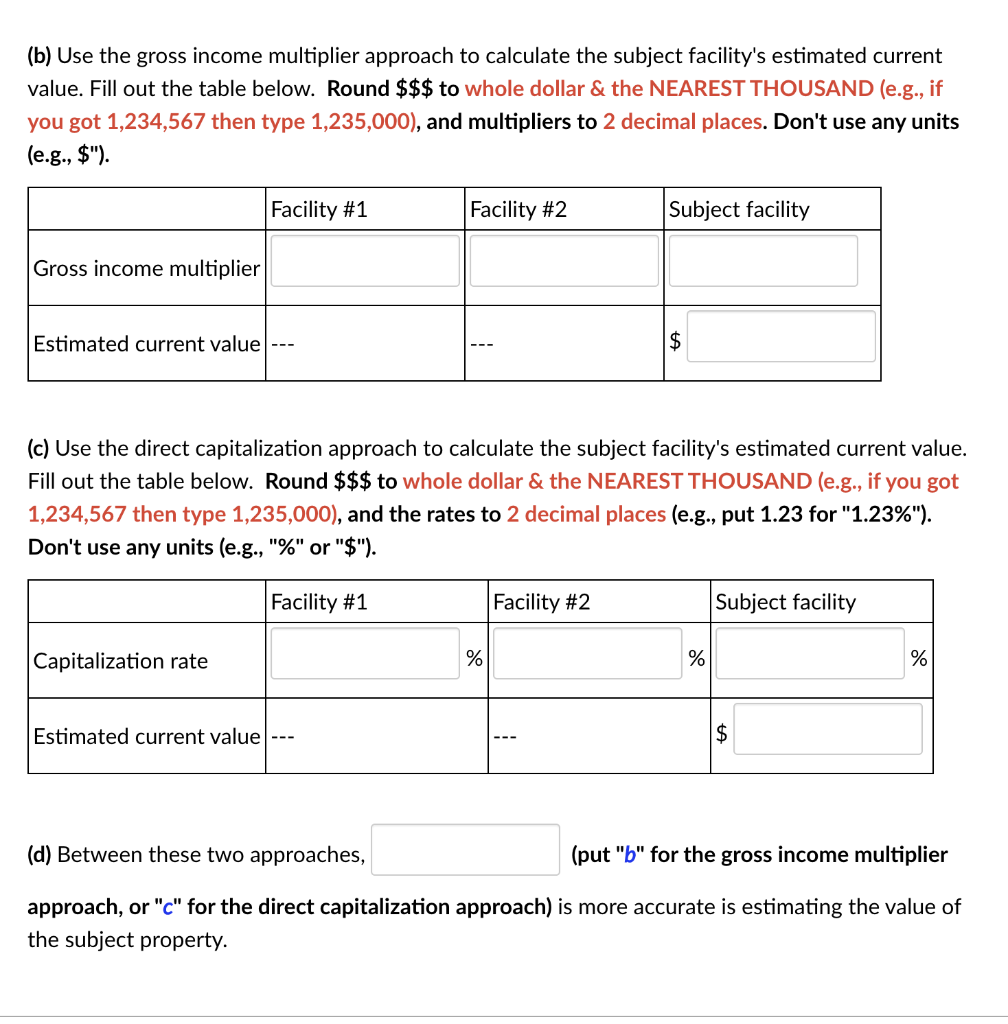
Amazonia Co. wants to buy a 650,000-square-foot distribution facility in the outskirts of the city of Cool, CA. The subject facility is presently renting for $3.90 per square foot per year. Based on recent market activity, two properties have sold within a several-mile distance from the subject facility. They are comparable in size, design, and age. One facility is 720,000 square feet and is presently being leased for $3.70 per square foot annually. The second facility contains 750,000 square feet and is being leased for $4.20 per square foot annually. It sold just a few days ago and is in very close proximity to the subject, which makes it twice as important in determining the subject's value as the first facility. Market data indicate that current vacancies and operating expenses combined (i.e., the sum of the two) should run approximately 72 percent and 82 percent of gross income for the two respective facilities, and it is 79 percent for the subject. The first facility sold for $5.9 million, and the second sold for $6.4 million. If you can, do the math in Excel with correct referencing to cells with intermediate results. This will allow you to avoid rounding errors. Otherwise, increase decimal places - the more the better! Say, 6 or even higher. (a) First, fill out the table below. Round $$$ to whole dollars. Don't use any units (e.g., "$"). Facility #1 Facility #2 Subject facility Potential gross income $ $ $ Net operating income $ $ $ (b) Use the gross income multiplier approach to calculate the subject facility's estimated current value. Fill out the table below. Round $$$ to whole dollar & the NEAREST THOUSAND (e.g., if you got 1,234,567 then type 1,235,000), and multipliers to 2 decimal places. Don't use any units (e.g., $"). un (b) Use the gross income multiplier approach to calculate the subject facility's estimated current value. Fill out the table below. Round $$$ to whole dollar & the NEAREST THOUSAND (e.g., if you got 1,234,567 then type 1,235,000), and multipliers to 2 decimal places. Don't use any units (e.g., $"). Facility #1 Facility #2 Subject facility Gross income multiplier Estimated current value $ (c) Use the direct capitalization approach to calculate the subject facility's estimated current value. Fill out the table below. Round $$$ to whole dollar & the NEAREST THOUSAND (e.g., if you got 1,234,567 then type 1,235,000), and the rates to 2 decimal places (e.g., put 1.23 for "1.23%"). Don't use any units (e.g., "%" or "$"). Facility #1 Facility #2 Subject facility Capitalization rate % % % Estimated current value $ (d) Between these two approaches, (put "b" for the gross income multiplier approach, or "c" for the direct capitalization approach) is more accurate is estimating the value of the subject property. Amazonia Co. wants to buy a 650,000-square-foot distribution facility in the outskirts of the city of Cool, CA. The subject facility is presently renting for $3.90 per square foot per year. Based on recent market activity, two properties have sold within a several-mile distance from the subject facility. They are comparable in size, design, and age. One facility is 720,000 square feet and is presently being leased for $3.70 per square foot annually. The second facility contains 750,000 square feet and is being leased for $4.20 per square foot annually. It sold just a few days ago and is in very close proximity to the subject, which makes it twice as important in determining the subject's value as the first facility. Market data indicate that current vacancies and operating expenses combined (i.e., the sum of the two) should run approximately 72 percent and 82 percent of gross income for the two respective facilities, and it is 79 percent for the subject. The first facility sold for $5.9 million, and the second sold for $6.4 million. If you can, do the math in Excel with correct referencing to cells with intermediate results. This will allow you to avoid rounding errors. Otherwise, increase decimal places - the more the better! Say, 6 or even higher. (a) First, fill out the table below. Round $$$ to whole dollars. Don't use any units (e.g., "$"). Facility #1 Facility #2 Subject facility Potential gross income $ $ $ Net operating income $ $ $ (b) Use the gross income multiplier approach to calculate the subject facility's estimated current value. Fill out the table below. Round $$$ to whole dollar & the NEAREST THOUSAND (e.g., if you got 1,234,567 then type 1,235,000), and multipliers to 2 decimal places. Don't use any units (e.g., $"). un (b) Use the gross income multiplier approach to calculate the subject facility's estimated current value. Fill out the table below. Round $$$ to whole dollar & the NEAREST THOUSAND (e.g., if you got 1,234,567 then type 1,235,000), and multipliers to 2 decimal places. Don't use any units (e.g., $"). Facility #1 Facility #2 Subject facility Gross income multiplier Estimated current value $ (c) Use the direct capitalization approach to calculate the subject facility's estimated current value. Fill out the table below. Round $$$ to whole dollar & the NEAREST THOUSAND (e.g., if you got 1,234,567 then type 1,235,000), and the rates to 2 decimal places (e.g., put 1.23 for "1.23%"). Don't use any units (e.g., "%" or "$"). Facility #1 Facility #2 Subject facility Capitalization rate % % % Estimated current value $ (d) Between these two approaches, (put "b" for the gross income multiplier approach, or "c" for the direct capitalization approach) is more accurate is estimating the value of the subject property








