Question
ASAP) Could you please show me how to set the excel for Table 1 with the answers of Questions A and B? I need to
ASAP) Could you please show me how to set the excel for Table 1 with the answers of Questions A and B? I need to set the linear programming in the "Analysis of Set #1" sheet. (First table = Set of Rates #1, Second table = Set of Rates #2)
- Excel Sheet Image captured (Table 1, needs to be submitted by next week)
Case 4: Foreign Currency Trading
Case Goal:
Determine if an arbitrage opportunity exists in foreign currency trading.
Case Overview:
Trading volume in currencies can exceed $1B per day. One type of currency trade is known as a spot currency transaction where an investor buys one currency using another currency on the spot.
To illustrate a spot transaction, consider a US company seeking to buy Japanese yen using US dollars. If each dollar was worth 89.18 yen, then one hundred US dollars would buy 8918 yen at that moment in time.
Now consider the reverse transaction. If the exchange rate from yen back to US dollars was 0.01120, the 8918 yen would buy 99.88 US dollars. The difference between the original $100 investment and the final $99.88 is the transaction cost.
Every so often the spot prices of currency are such that free money can be made. In these cases, a dollar can be invested in a set of currency transactions that returns more than a dollar at the end. In such a case the prices will quickly adjust to address this idiosyncrasy. However, if such an opportunity does arise, then it makes sense to move quickly to take advantage of it.
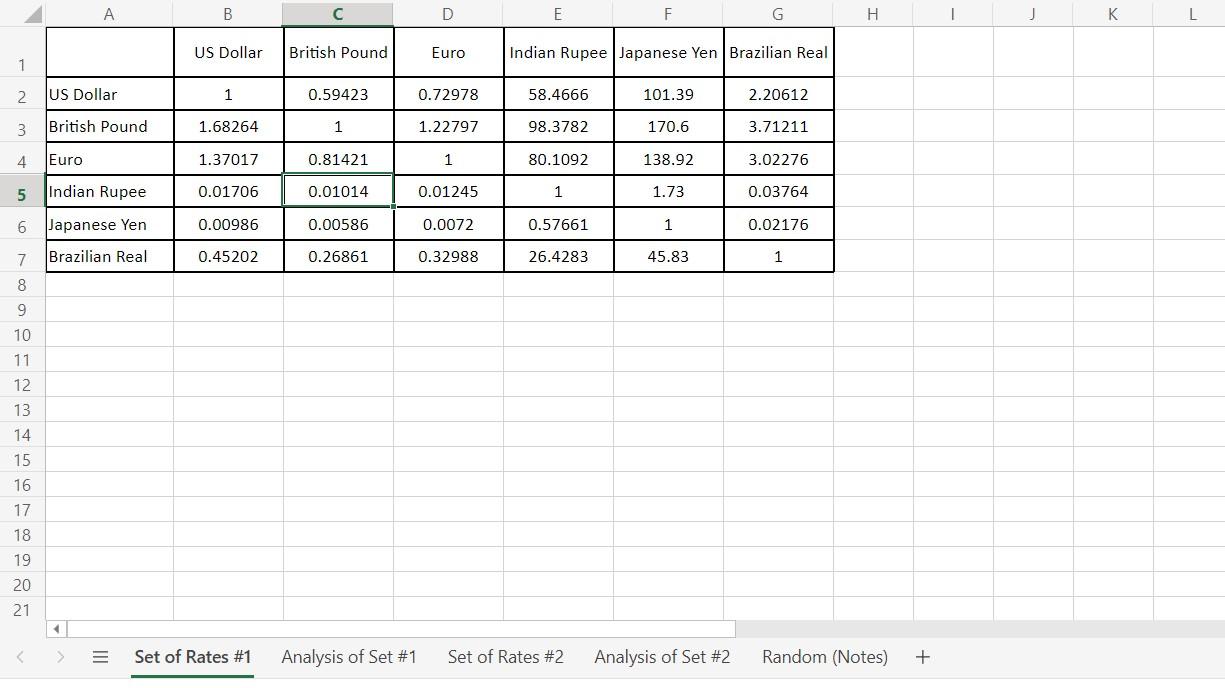
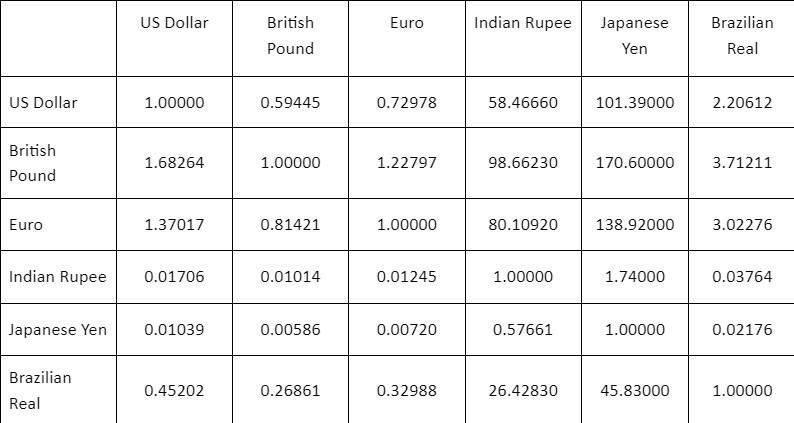
The two tables (Tables 1 and 2) provided below provide two sets of spot currency rates at certain times on given days. The left side of the table is the currency that is being traded from and the top of the table is the currency being traded to. So, for example, in the first table $1 US dollar is worth 0.66376 British Pounds at this point in time. 1 Euro is worth 56.879 Indian Rupees.
Table 1: First Set of Trading Rates
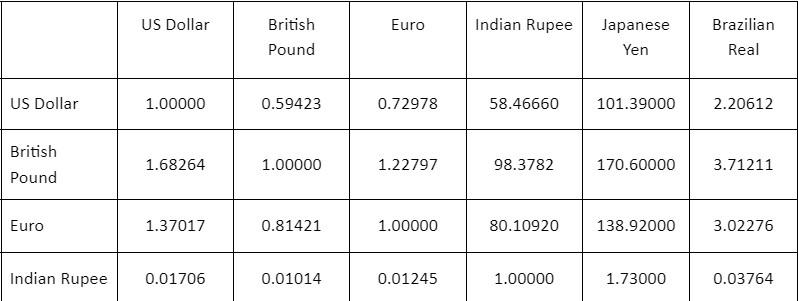
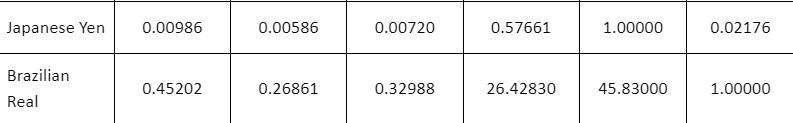
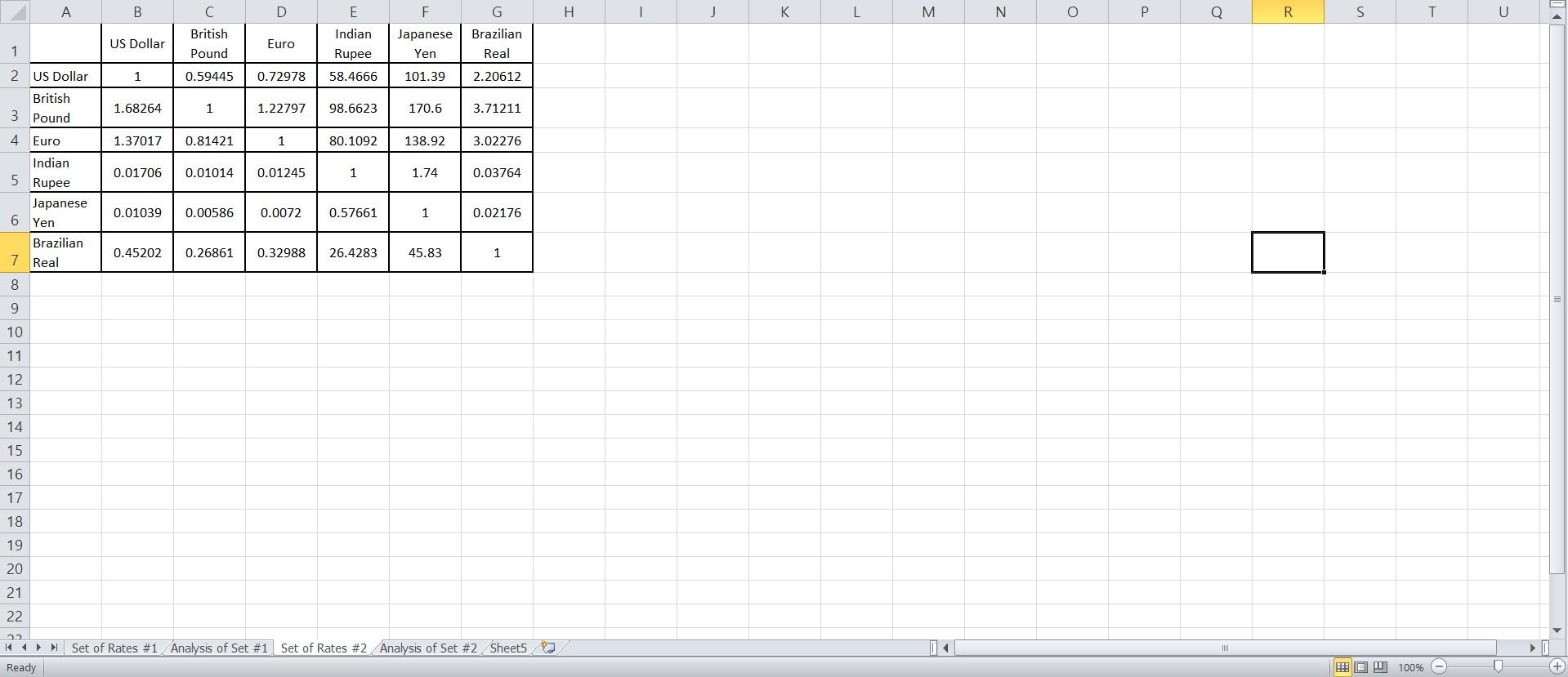
Table 2: Second Set of Trading Rates
Case Technical Details:
Linear programming should be used to model this case.
An arbitrage opportunity can exist when starting and ending in any one of the currencies to be traded. It does not need to involve all currencies available.
A constraint must be added to the linear program that bounds the final solution so that infinite money cannot be made. In every case, it is helpful to inequality constraints rather than equality constraints. Thus the amount entering a specific currency type should be greater than or equal to the amount of currency going out.
Questions for Consideration:
A. What is an arbitrage opportunity? Explain the idea and why it might be important to people in the finance industry. Provide some examples of arbitrage opportunities in practice.
B. Develop a linear program to determine if an arbitrage opportunity exists for Table 1. Note that this may require an investment in several currencies, that is, a situation where one trades from A to B from B to C, and finally from C back to A. The model should show the precise arbitrage opportunity if one exists. That is, what currencies should be used to create the opportunity?
C. Repeat this analysis for the second table, Table 2.
D. Find these six currency trading rates or another six currency trading rates online or elsewhere. Document the source of the information including the day and time for which the information was valid. Use those values to redo the problem. What results were found?
E. What are the factors that make arbitrage challenging to implement in practice? That is, why isnt everyone able to obtain free money?
F. What assumptions were made in the modeling of this arbitrage opportunity that may be unrealistic in practice? Explain.
G. Summarize and generalize the findings in this case. What are the major takeaways? What are the limitations of the analysis?
\begin{tabular}{|l|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & US Dollar & BritishPound & Euro & Indian Rupee & JapaneseYen & BrazilianReal \\ \hline US Dollar & 1.00000 & 0.59423 & 0.72978 & 58.46660 & 101.39000 & 2.20612 \\ \hline BritishPound & 1.68264 & 1.00000 & 1.22797 & 98.3782 & 170.60000 & 3.71211 \\ \hline Euro & 1.37017 & 0.81421 & 1.00000 & 80.10920 & 138.92000 & 3.02276 \\ \hline Indian Rupee & 0.01706 & 0.01014 & 0.01245 & 1.00000 & 1.73000 & 0.03764 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{l|c|c|c|c|c|c} \hline Japanese Yen & 0.00986 & 0.00586 & 0.00720 & 0.57661 & 1.00000 & 0.02176 \\ \hline BrazilianReal & 0.45202 & 0.26861 & 0.32988 & 26.42830 & 45.83000 & 1.00000 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|l|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & US Dollar & BritishPound & Euro & Indian Rupee & JapaneseYen & BrazilianReal \\ \hline US Dollar & 1.00000 & 0.59445 & 0.72978 & 58.46660 & 101.39000 & 2.20612 \\ \hline BritishPound & 1.68264 & 1.00000 & 1.22797 & 98.66230 & 170.60000 & 3.71211 \\ \hline Euro & 1.37017 & 0.81421 & 1.00000 & 80.10920 & 138.92000 & 3.02276 \\ \hline Indian Rupee & 0.01706 & 0.01014 & 0.01245 & 1.00000 & 1.74000 & 0.03764 \\ \hline Japanese Yen & 0.01039 & 0.00586 & 0.00720 & 0.57661 & 1.00000 & 0.02176 \\ \hline BrazilianReal & 0.45202 & 0.26861 & 0.32988 & 26.42830 & 45.83000 & 1.00000 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|l|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & US Dollar & BritishPound & Euro & Indian Rupee & JapaneseYen & BrazilianReal \\ \hline US Dollar & 1.00000 & 0.59423 & 0.72978 & 58.46660 & 101.39000 & 2.20612 \\ \hline BritishPound & 1.68264 & 1.00000 & 1.22797 & 98.3782 & 170.60000 & 3.71211 \\ \hline Euro & 1.37017 & 0.81421 & 1.00000 & 80.10920 & 138.92000 & 3.02276 \\ \hline Indian Rupee & 0.01706 & 0.01014 & 0.01245 & 1.00000 & 1.73000 & 0.03764 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{l|c|c|c|c|c|c} \hline Japanese Yen & 0.00986 & 0.00586 & 0.00720 & 0.57661 & 1.00000 & 0.02176 \\ \hline BrazilianReal & 0.45202 & 0.26861 & 0.32988 & 26.42830 & 45.83000 & 1.00000 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|l|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & US Dollar & BritishPound & Euro & Indian Rupee & JapaneseYen & BrazilianReal \\ \hline US Dollar & 1.00000 & 0.59445 & 0.72978 & 58.46660 & 101.39000 & 2.20612 \\ \hline BritishPound & 1.68264 & 1.00000 & 1.22797 & 98.66230 & 170.60000 & 3.71211 \\ \hline Euro & 1.37017 & 0.81421 & 1.00000 & 80.10920 & 138.92000 & 3.02276 \\ \hline Indian Rupee & 0.01706 & 0.01014 & 0.01245 & 1.00000 & 1.74000 & 0.03764 \\ \hline Japanese Yen & 0.01039 & 0.00586 & 0.00720 & 0.57661 & 1.00000 & 0.02176 \\ \hline BrazilianReal & 0.45202 & 0.26861 & 0.32988 & 26.42830 & 45.83000 & 1.00000 \\ \hline \end{tabular}Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


