Question
Assume a John (college student) manages to qualify for a loan and he purchases an apartment. John's income is 78,000 USD. Meanwhile, John is still
Assume a John (college student) manages to qualify for a loan and he purchases an apartment. John's income is 78,000 USD. Meanwhile, John is still debating with his roommate Max about the tax consequences of your capital gains and dividend income, as well as the tax implications of John's recent real estate purchase. Max insists that with a tax-deferred IRA John can still make stock market decisions, but pay zero taxes until John retires. Thanks to the power of compounding, the tax dollars John saves each year makes it worth it to keep it invested. John concedes that for a couple of years he paid more taxes, but John argues that thanks to the extra investment income he managed to make a real estate investment. Since John can now deduct mortgage and property tax payments, John's effective tax rate is less.
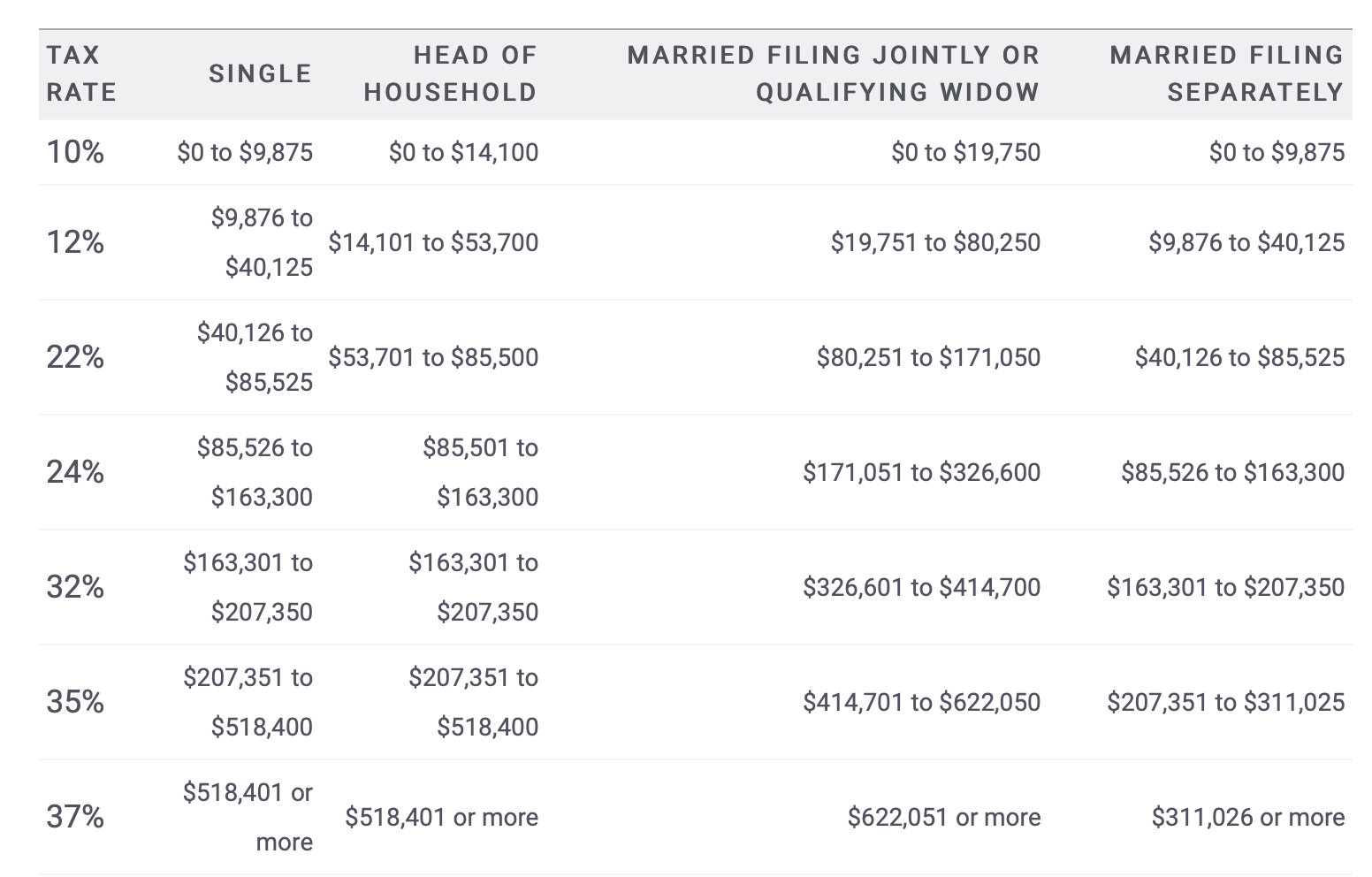
a. Using the current tax brackets and the standard deduction for federal income taxes, find John's marginal tax rate and effective tax rate for the years prior to John's purchase. Furthermore, compute the marginal tax rate and effective tax rate if no dividends or capital gains are reported as taxable income. Compared both marginal rates and effective tax rates, how much taxes would John have saved each year?
B. Using the current tax brackets and the itemized deduction for federal income taxes, find your marginal tax rate and your effective tax rate for the upcoming year, now that you have mortgage and property taxes to deduct. What is the tax amount difference compared to part a?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


