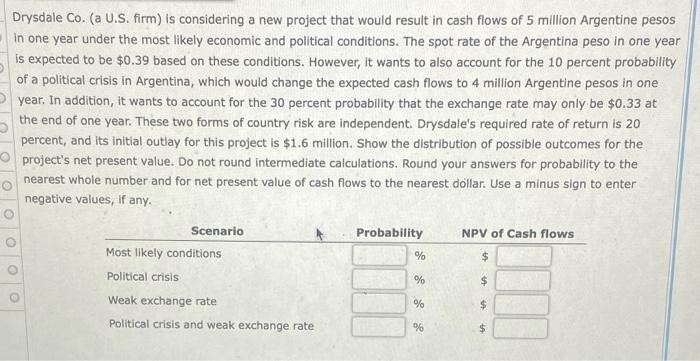
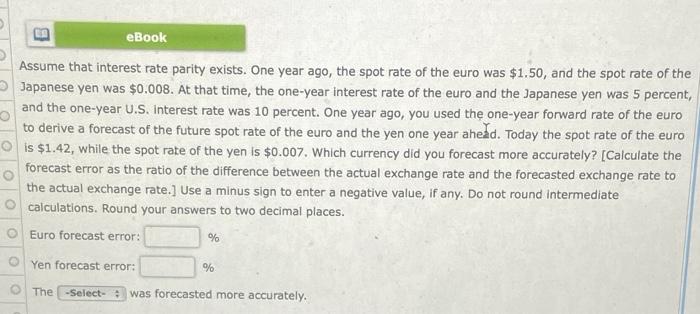
Assume that the one-year interest rate in Canada is 6 percent. The one-year U.S. interest rate is 6 percent. The spot rate of the Canadian dollar (C$) is $0.91. The forward rate of the Canadian dollar is $0.93. a. Is covered interest arbitrage feasible for U.S. Investors? Show the results if a U.S. firm engages in covered interest arbitrage to support your answer. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. U.S. Investors -Select- benefit from covered interest arbitrage because U.S. Investors would generate a yield of %, which -Select- the U.S. interest rate of 6 percent. b. Assume that the spot rate and interest rates remain unchanged as coverage interest arbitrage is attempted by U.S. Investors. Do you think the forward rate of the Canadian dollar will be affected? If so, state whether it will increase or decrease, and explain why. The forward rate of the Canadian dollar should -Select- due to the heavy forward -Select- of the Canadian dollar that will occur as a result of covered interest arbitrage. Drysdale Co. (a U.S. firm) is considering a new project that would result in cash flows of 5 million Argentine pesos in one year under the most likely economic and political conditions. The spot rate of the Argentina peso in one year is expected to be $0.39 based on these conditions. However, it wants to also account for the 10 percent probability of a political crisis in Argentina, which would change the expected cash flows to 4 million Argentine pesos in one year. In addition, it wants to account for the 30 percent probability that the exchange rate may only be $0.33 at the end of one year. These two forms of country risk are independent. Drysdale's required rate of return is 20 percent, and its initial outlay for this project is $1.6 million. Show the distribution of possible outcomes for the project's net present value. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers for probability to the nearest whole number and for net present value of cash flows to the nearest dollar. Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. Probability NPV of Cash flows % $ Sce rio Most likely conditions Political crisis Weak exchange rate Political crisis and weak exchange rate % $ % $ % $ eBook Assume that interest rate parity exists. One year ago, the spot rate of the euro was $1.50, and the spot rate of the Japanese yen was $0.008. At that time, the one-year interest rate of the euro and the Japanese yen was 5 percent and the one-year U.S. Interest rate was 10 percent. One year ago, you used the one-year forward rate of the euro to derive a forecast of the future spot rate of the euro and the yen one year ahead. Today the spot rate of the euro is $1.42, while the spot rate of the yen is $0.007. Which currency did you forecast more accurately? [Calculate the forecast error as the ratio of the difference between the actual exchange rate and the forecasted exchange rate to the actual exchange rate.] Use a minus sign to enter a negative value, if any. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Euro forecast error: % Yen forecast error: % The -Select- was forecasted more accurately. Assume that the one-year interest rate in Canada is 6 percent. The one-year U.S. interest rate is 6 percent. The spot rate of the Canadian dollar (C$) is $0.91. The forward rate of the Canadian dollar is $0.93. a. Is covered interest arbitrage feasible for U.S. Investors? Show the results if a U.S. firm engages in covered interest arbitrage to support your answer. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. U.S. Investors -Select- benefit from covered interest arbitrage because U.S. Investors would generate a yield of %, which -Select- the U.S. interest rate of 6 percent. b. Assume that the spot rate and interest rates remain unchanged as coverage interest arbitrage is attempted by U.S. Investors. Do you think the forward rate of the Canadian dollar will be affected? If so, state whether it will increase or decrease, and explain why. The forward rate of the Canadian dollar should -Select- due to the heavy forward -Select- of the Canadian dollar that will occur as a result of covered interest arbitrage. Drysdale Co. (a U.S. firm) is considering a new project that would result in cash flows of 5 million Argentine pesos in one year under the most likely economic and political conditions. The spot rate of the Argentina peso in one year is expected to be $0.39 based on these conditions. However, it wants to also account for the 10 percent probability of a political crisis in Argentina, which would change the expected cash flows to 4 million Argentine pesos in one year. In addition, it wants to account for the 30 percent probability that the exchange rate may only be $0.33 at the end of one year. These two forms of country risk are independent. Drysdale's required rate of return is 20 percent, and its initial outlay for this project is $1.6 million. Show the distribution of possible outcomes for the project's net present value. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers for probability to the nearest whole number and for net present value of cash flows to the nearest dollar. Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. Probability NPV of Cash flows % $ Sce rio Most likely conditions Political crisis Weak exchange rate Political crisis and weak exchange rate % $ % $ % $ eBook Assume that interest rate parity exists. One year ago, the spot rate of the euro was $1.50, and the spot rate of the Japanese yen was $0.008. At that time, the one-year interest rate of the euro and the Japanese yen was 5 percent and the one-year U.S. Interest rate was 10 percent. One year ago, you used the one-year forward rate of the euro to derive a forecast of the future spot rate of the euro and the yen one year ahead. Today the spot rate of the euro is $1.42, while the spot rate of the yen is $0.007. Which currency did you forecast more accurately? [Calculate the forecast error as the ratio of the difference between the actual exchange rate and the forecasted exchange rate to the actual exchange rate.] Use a minus sign to enter a negative value, if any. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Euro forecast error: % Yen forecast error: % The -Select- was forecasted more accurately