Question: Assumption CPU clock = 1 GHz 1 OP requires 5 clock cycles (arithmetic instruction, conditional, etc.) 1 memory access requires 100 clock cycles (Read or
Assumption
- CPU clock = 1 GHz
- 1 OP requires 5 clock cycles (arithmetic instruction, conditional, etc.)
- 1 memory access requires 100 clock cycles (Read or Write)
- Problem size: N = 1,000,000 (1 million)
There is no cost memory access cost associated with the loop index variable: do not count any arithmetic instructions for initializing or incrementing the loop index value, do not count any memory accesses for accessing and using the loop index variable in your computation of a sum. Assume that accessing and incrementing the loop index variable is "free of charge".
There is no memory access cost for accessing and updating your accumulator variable (e.g., sum += ...) but there is an arithmetic operation involved in updating the accumulator variable.
For algorithm #2, vector sum:
- How many arithmetic instructions are required by this algorithm?
- How many memory accesses are required by this algorithm?
- How many clocks are required by this algorithm?
- What is the CPI (cycles per instruction) required by this algorithm?
- What is the estimated execution time for this algorithm in seconds or fractions of seconds, not counting the print and any problem setup?
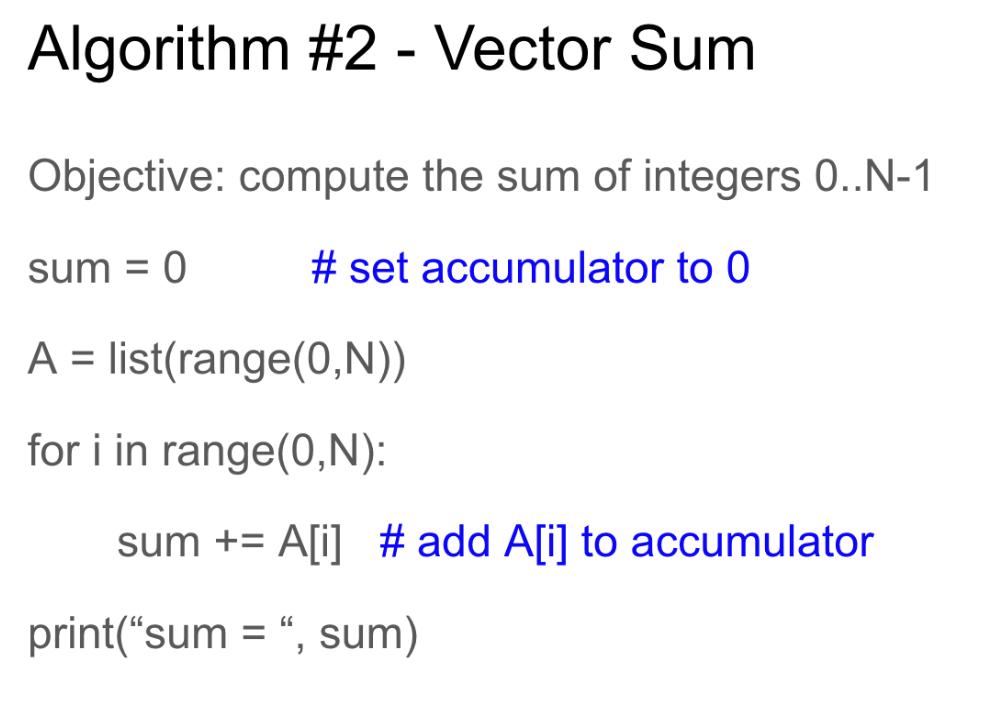
Algorithm #2 - Vector Sum Objective: compute the sum of integers 0..N-1 sum = 0 # set accumulator to 0 A = list(range(0,N)) for i in range(0,N): sum += A[i] # add A[i] to accumulator print("sum = ", sum)
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
In Algorithm 2 Vector Sum you are summing the integers from 0 to N1 where N 1000000 Lets analyze the algorithm as per the given assumptions 1 How many ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


